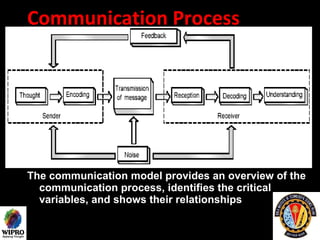
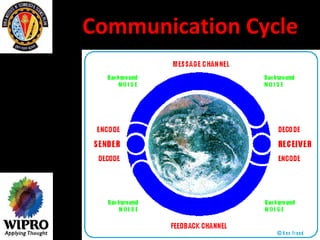
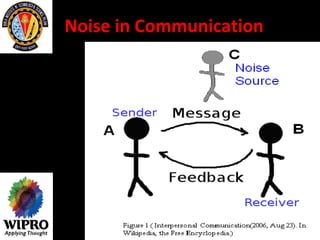
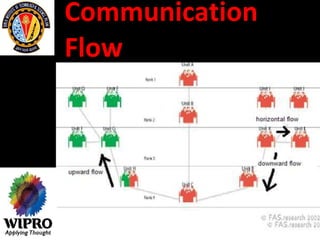
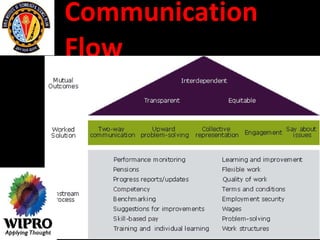
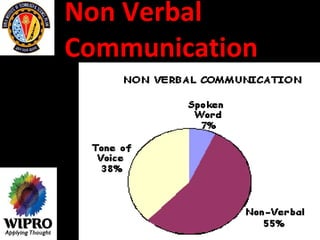
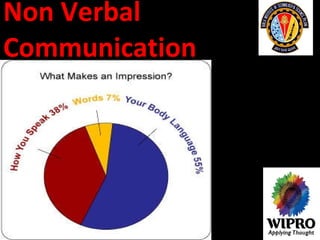
This document summarizes key points about principles of management communication. It discusses the basic communication process, communication flow within an organization, and characteristics of different communication methods. Barriers to effective communication are also outlined, including noise during transmission, ambiguous symbols, inattention, unclarified assumptions, and selective perception. The purpose is to understand how to improve communication and overcome barriers within an organizational context.