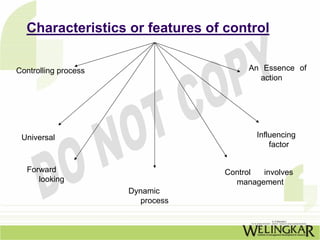
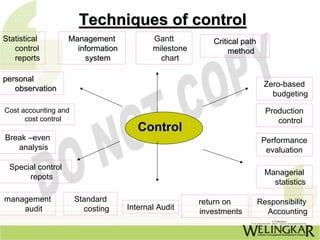
Chapter 17 discusses the controlling function of management, highlighting its importance in ensuring that planning leads to desired outcomes. It outlines the areas of control, steps in the control process, advantages and limitations of control systems, and the role of budgeting in effective management. Budgetary control is defined, along with its characteristics, advantages, and potential problems, emphasizing the need for efficient budgeting systems within organizations.