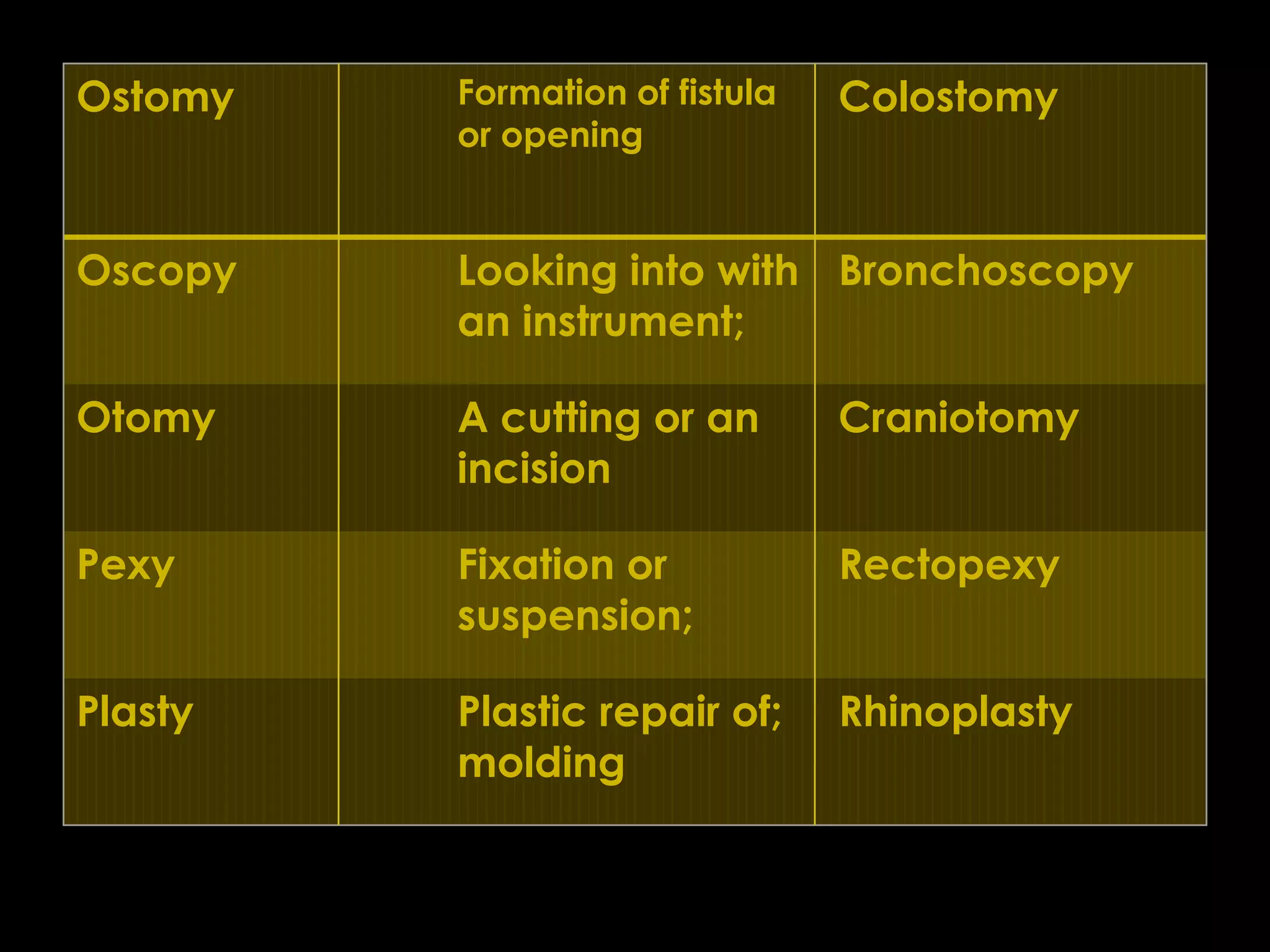
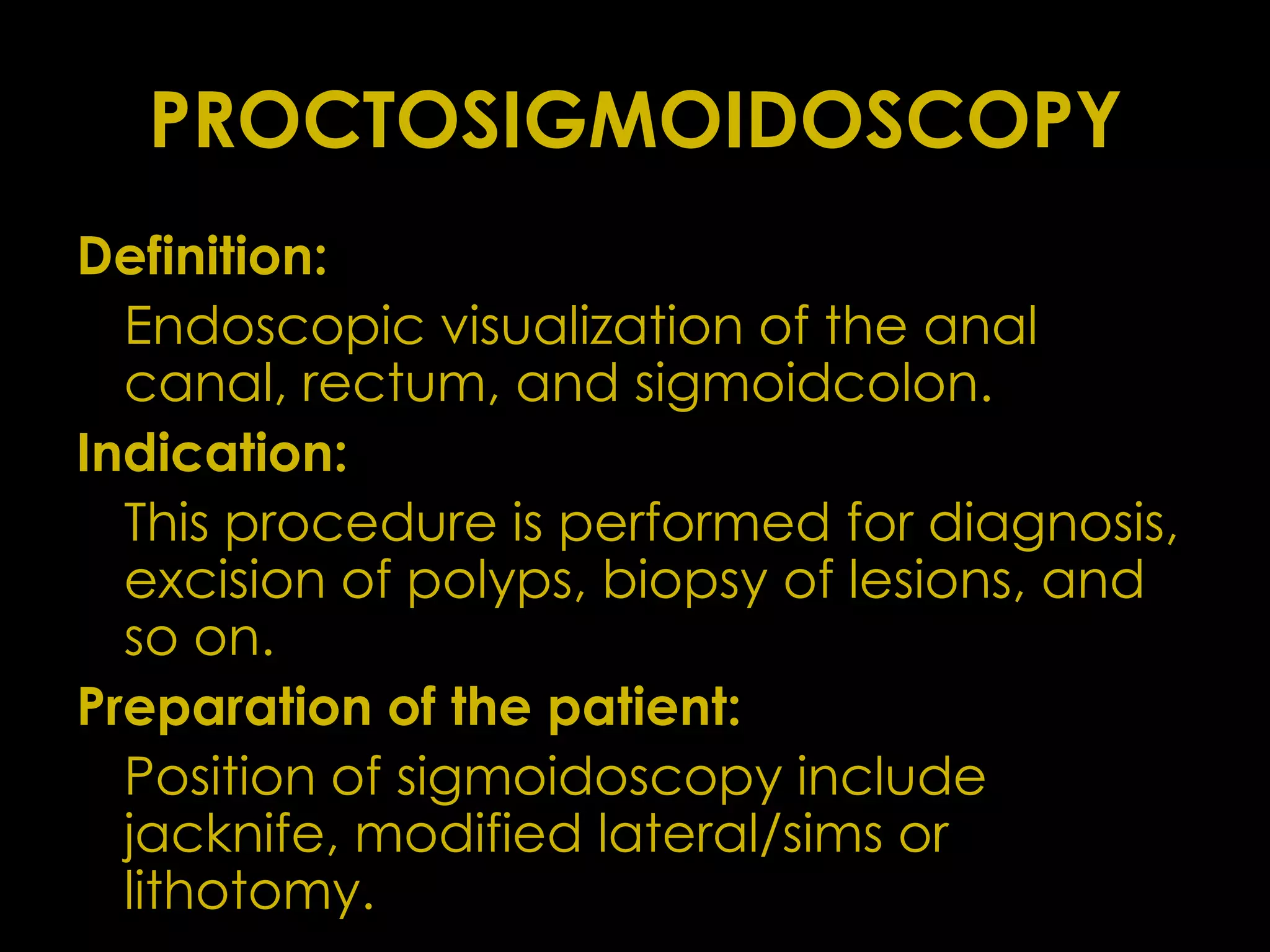
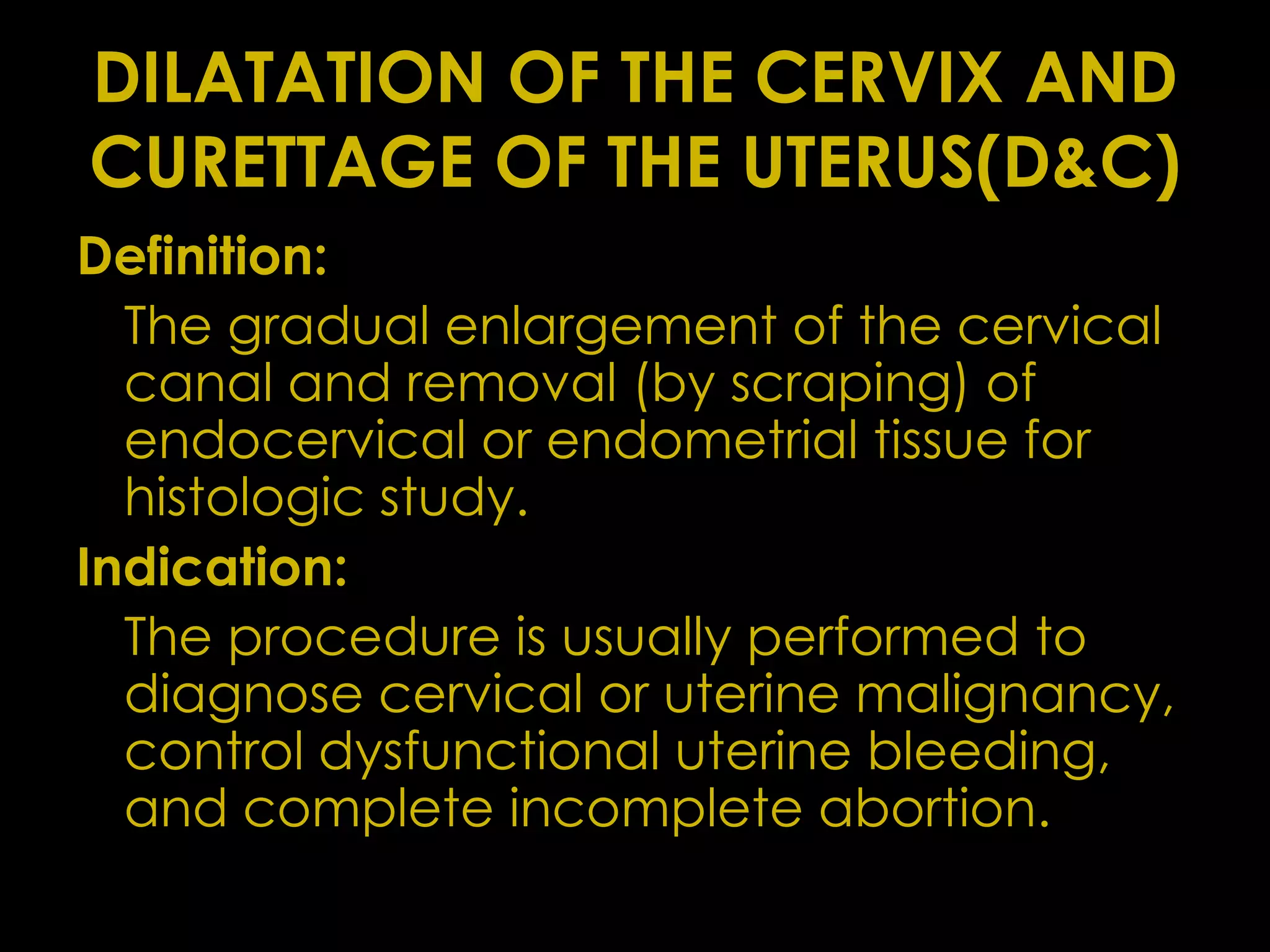
This document defines and describes common surgical procedures including herniorrhaphy to correct hernias, amputation to remove limbs, turp to resect the prostate, gastrectomy to remove part of the stomach, thoracostomy to access the thoracic cavity, tonsillectomy to remove the tonsils, colostomy to create a stoma in the colon, hemorrhoidectomy to remove hemorrhoids, dilatation and curettage of the uterus, hysterectomy to remove the uterus and ovaries, pulmonary lobectomy to remove a lung lobe, pneumonectomy to remove an entire lung, and more. It provides indications for each procedure and relevant definitions.