Esophagectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the complete or partial removal of the esophagus, often used to treat advanced esophageal cancer, Barrett’s esophagus, or various noncancerous conditions. The surgery can be performed through several methods including transhiatal, transthoracic, thoracoabdominal, or minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, with the extent of the removal varying based on specific factors. Complications can include bleeding, infections, voice changes, and swallowing difficulties, with relative contraindications being advanced age and comorbid illnesses.




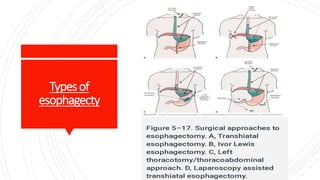

![Stepsof
transhiatal
esophagectomy
Transhiatal esophagectomy is performed in five phases,
as follows [15] :
1. Abdominal phase
2. Cervical phase
3. Mediastinal dissection
4. Creation and positioning of the gastric conduit, and
abdominal closure
5. Construction of the cervical esophagogastric
anastomosis (CEGA)
During esophagectomy, lymph nodes may also be
removed to check for possible spread of cancer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esophagectomy-211101162440/85/Esophagectomy-7-320.jpg)