The post operative period begins after surgery and focuses on enabling successful recovery. It aims to reduce mortality, length of stay, and costs through quality care. Patients are monitored in the PACU or SICU by nurses. They assess vitals, consciousness, bleeding, pain/anxiety and more to detect complications and ensure stability for discharge. The goal is safe transfer from intensive recovery phases to continued recovery in step-down units or at home with instructions.




![POST OPERATIVE CARE UNIT
OR POST ANESTHETIC CARE
UNIT[PACU]
Patients still under anesthesia or
recovering from anesthesia are
placed in the unit for observation by
highly skilled nurses,anesthetist and
surgeon.
PACU should be sound proof, painted
in soft colour, isolated and these
features will help the patient to
reduce anxiety and promote comfort.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postoperativecarepleasedontdeleteplease-130129233843-phpapp02/75/Post-operative-care-5-2048.jpg)






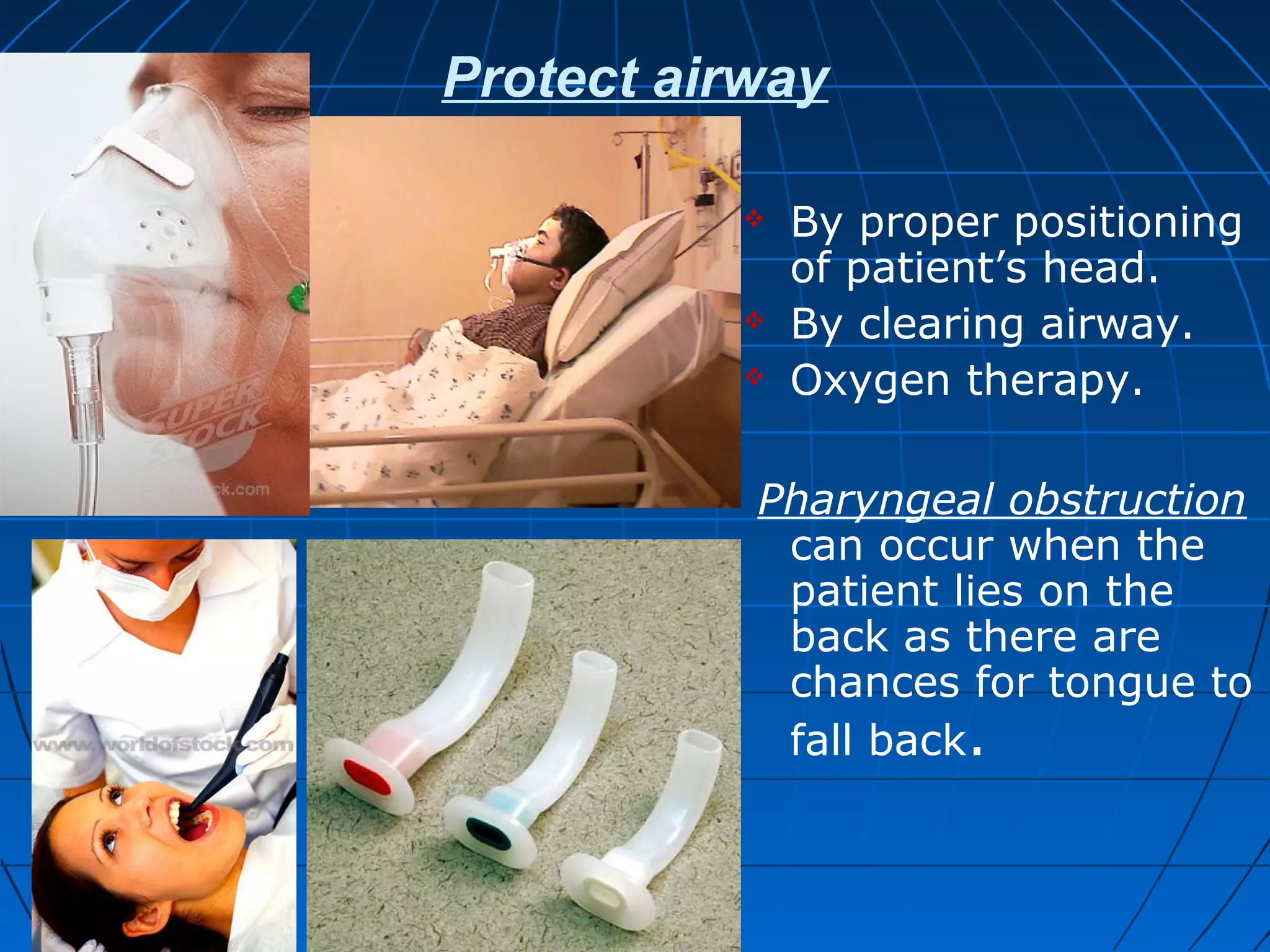
![Maintaining IV Stability
Hypovolemic shock: can be
avoided by timely
administration of IV Fluids,
blood and blood products and
medication.
Replacement of fluids.[colloids
and crystalloids]
Keep the patient warm.
Monitor intake and output
balance.
Monitor the vitals continuously
with the patient condition.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postoperativecarepleasedontdeleteplease-130129233843-phpapp02/75/Post-operative-care-14-2048.jpg)









