Embed presentation
Download to read offline




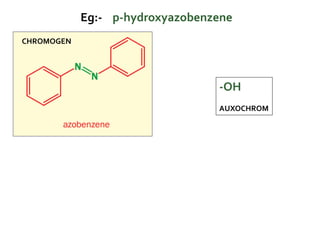







Dyes are coloured organic compounds that can impart their colour to other substances. To be an effective dye, a compound must have a suitable colour, be capable of firmly binding to fibers, and retain its colour after binding. It should also be stable during dry cleaning. Common dyes include malachite green, orange dyes, alizarin, martius yellow, indigo, congo red, quercetin, and para red. The chromophore is responsible for colour and contains an unsaturated group, while auxochromes intensify colour. Resonance contributes to dye colour by allowing pi electrons to absorb radiation. Dyes find applications in silk, wool, synthetic fibers, biological staining, indicators, and food colouring











