This document discusses catalysis and provides an overview of the key concepts:
- A catalyst accelerates a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy without being consumed in the reaction.
- Catalysts have properties such as an optimal temperature and can be poisoned. They also exhibit selectivity.
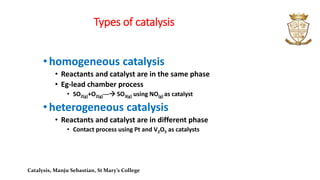
- There are two main types of catalysis: homogeneous where reactants and catalysts are in the same phase, and heterogeneous where they are in different phases.
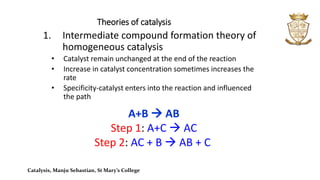
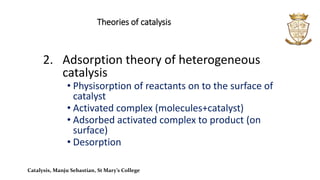
- Theories of catalysis include the intermediate compound formation theory for homogeneous catalysis and the adsorption theory for heterogeneous catalysis.
- Enzyme catalysis is a type of biocatalysis where enzymes act as biological catalysts through mechanisms like specifically binding substrates.