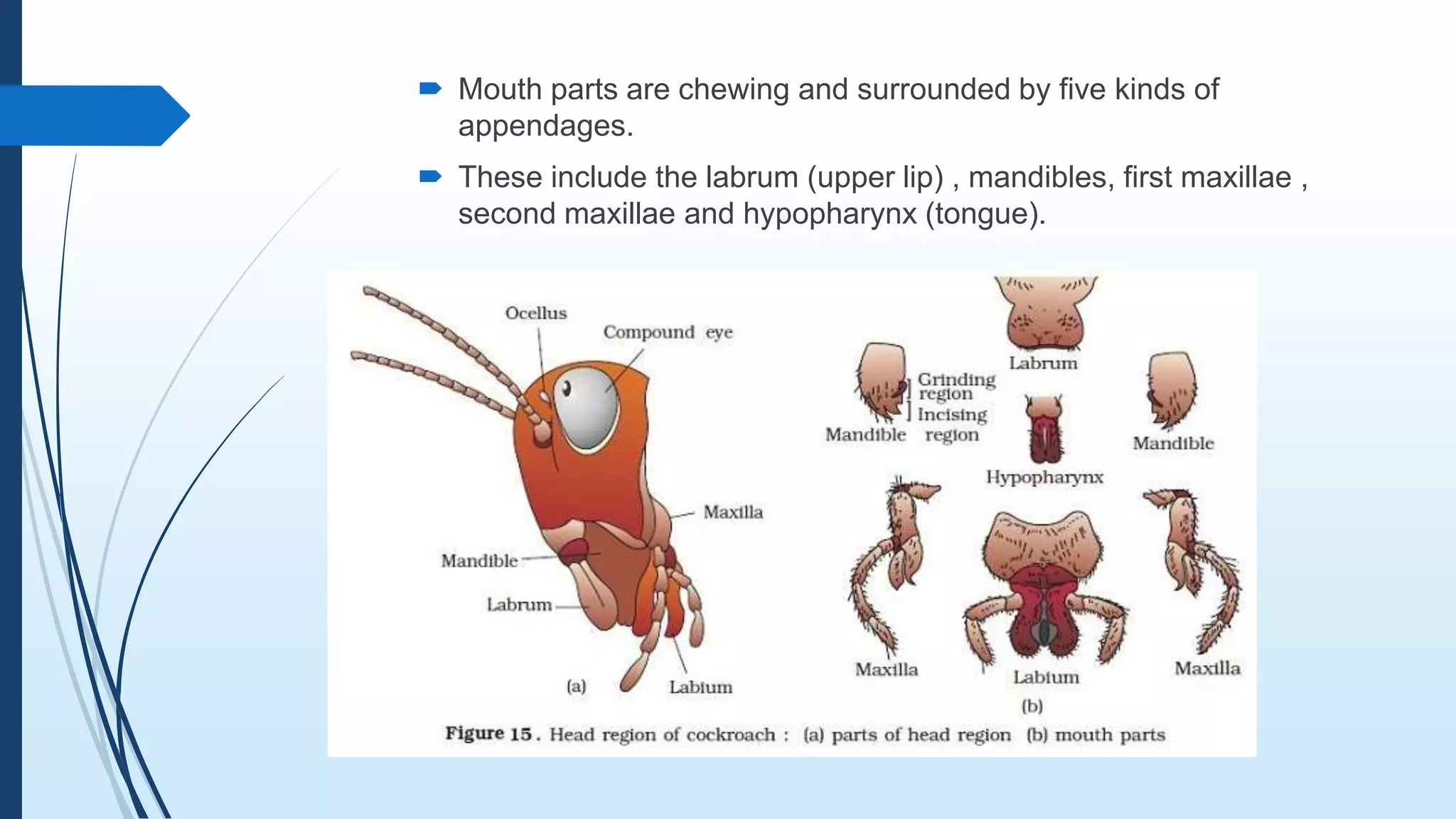
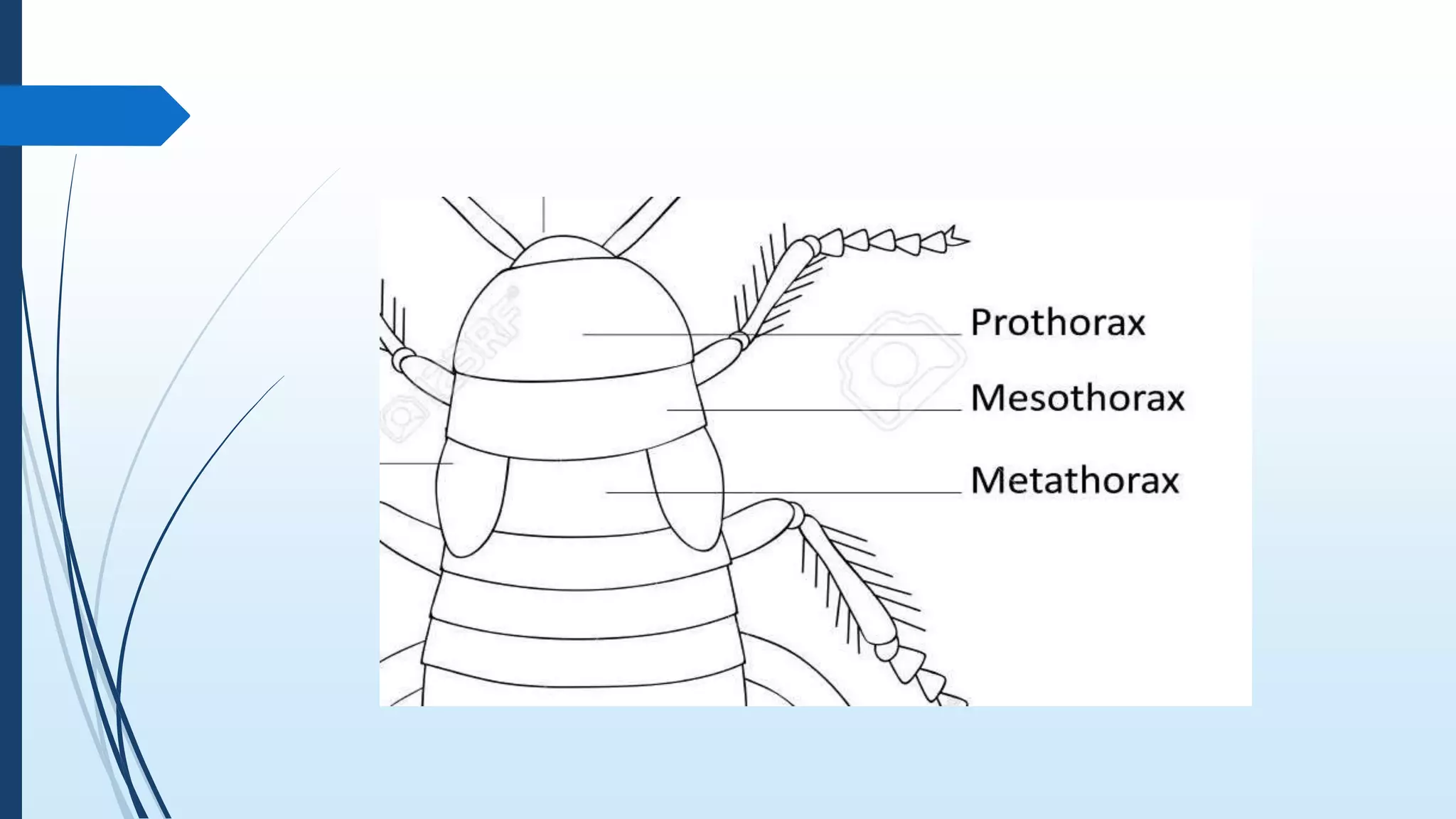
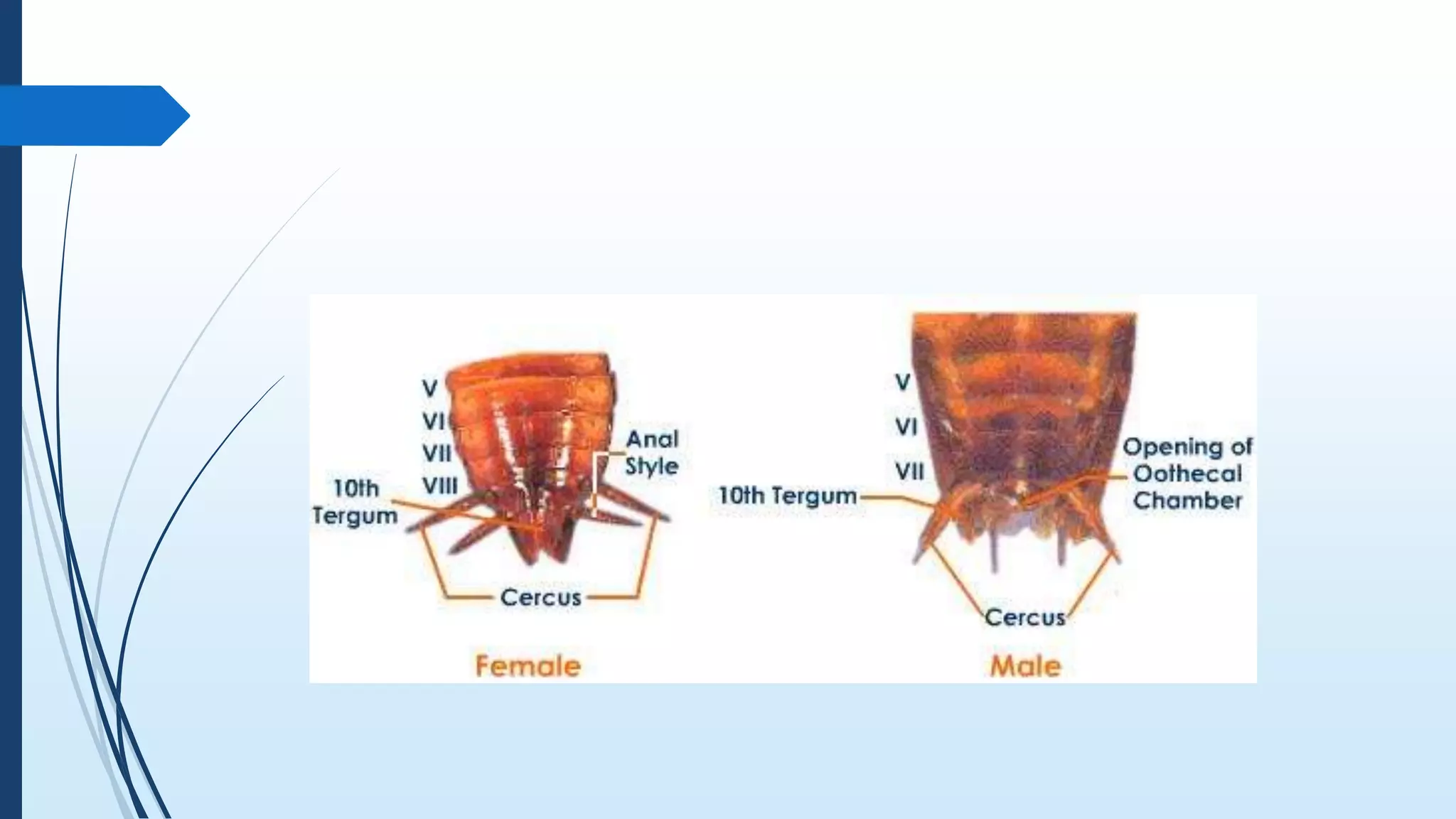
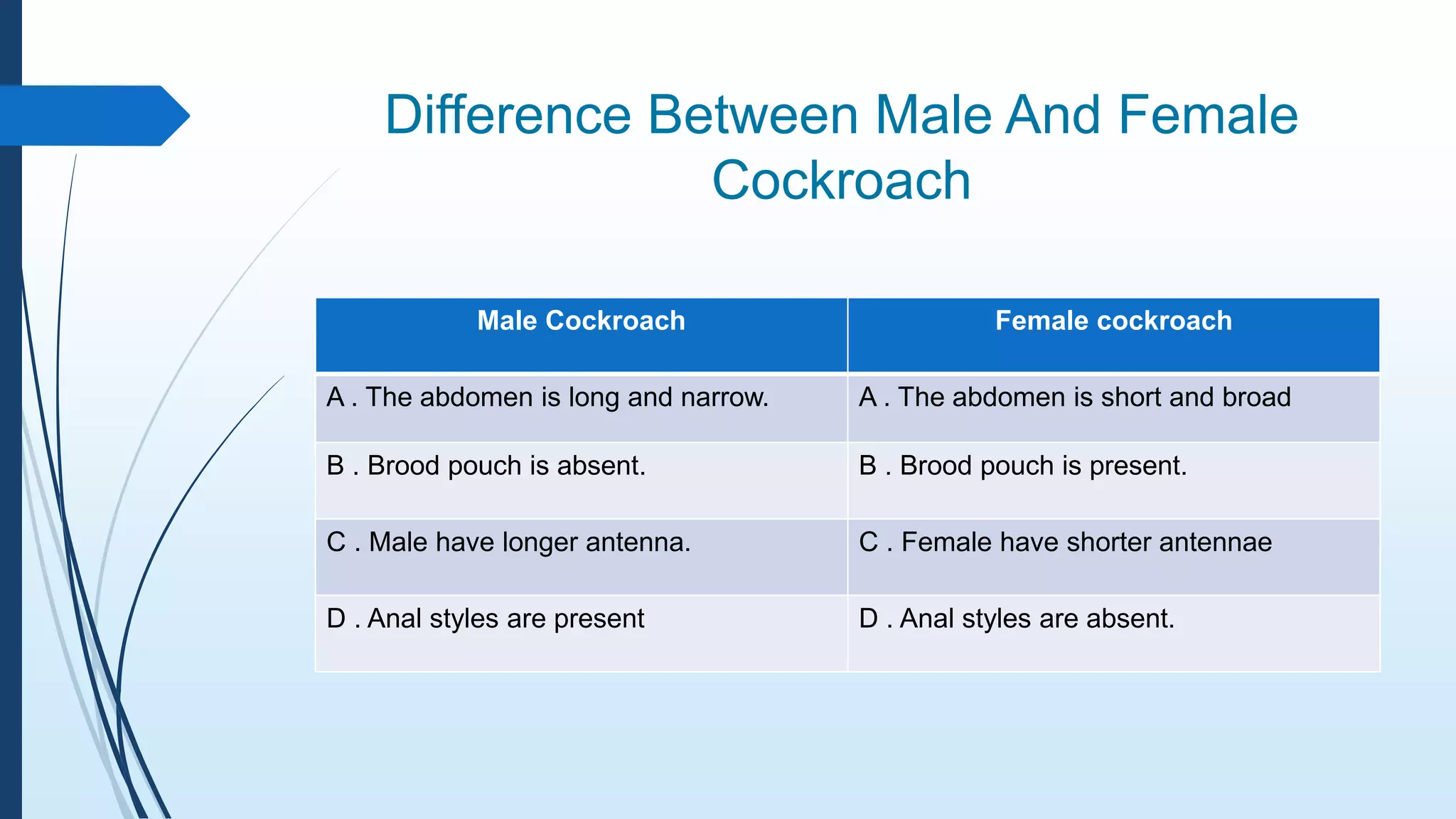
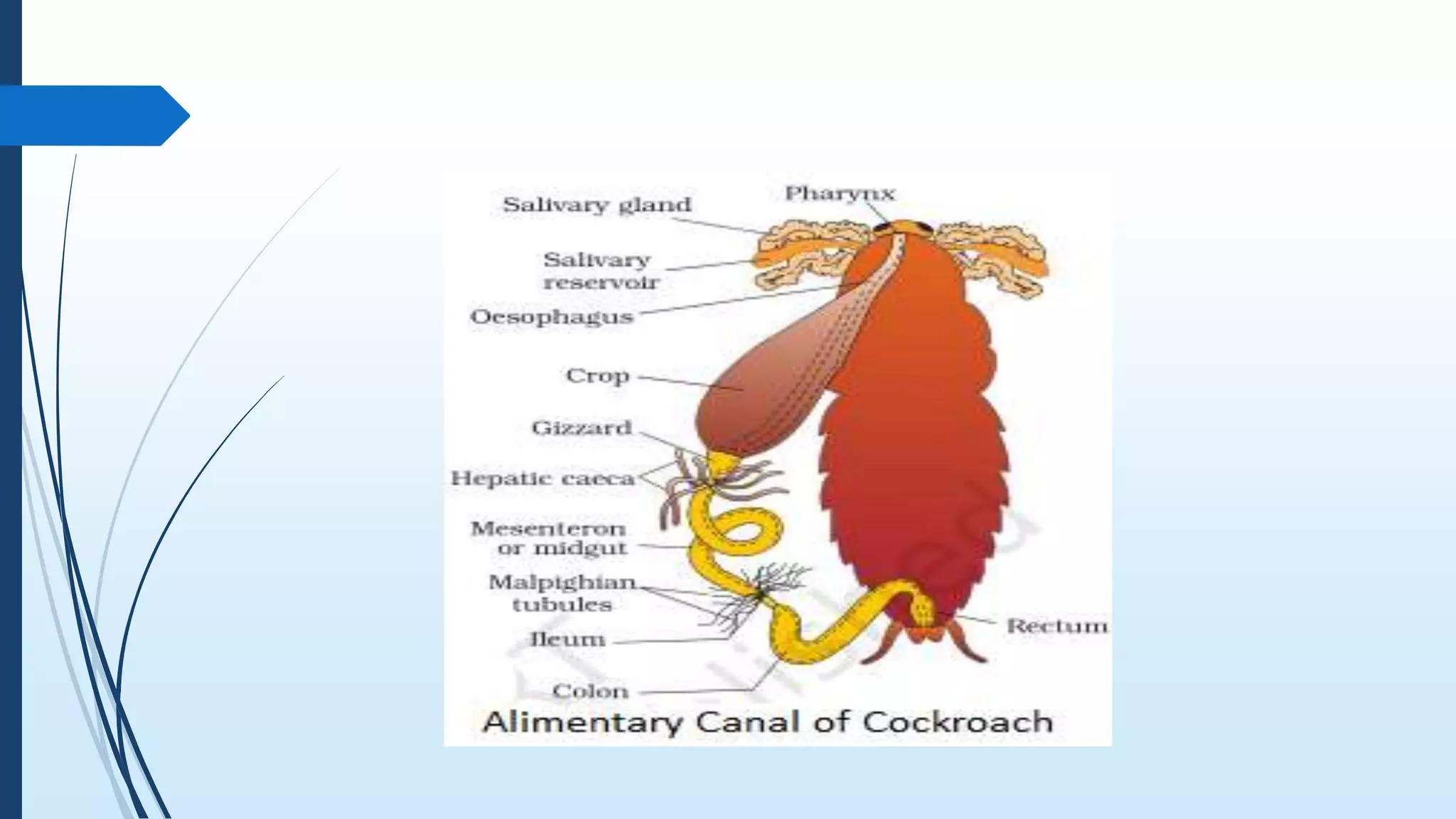
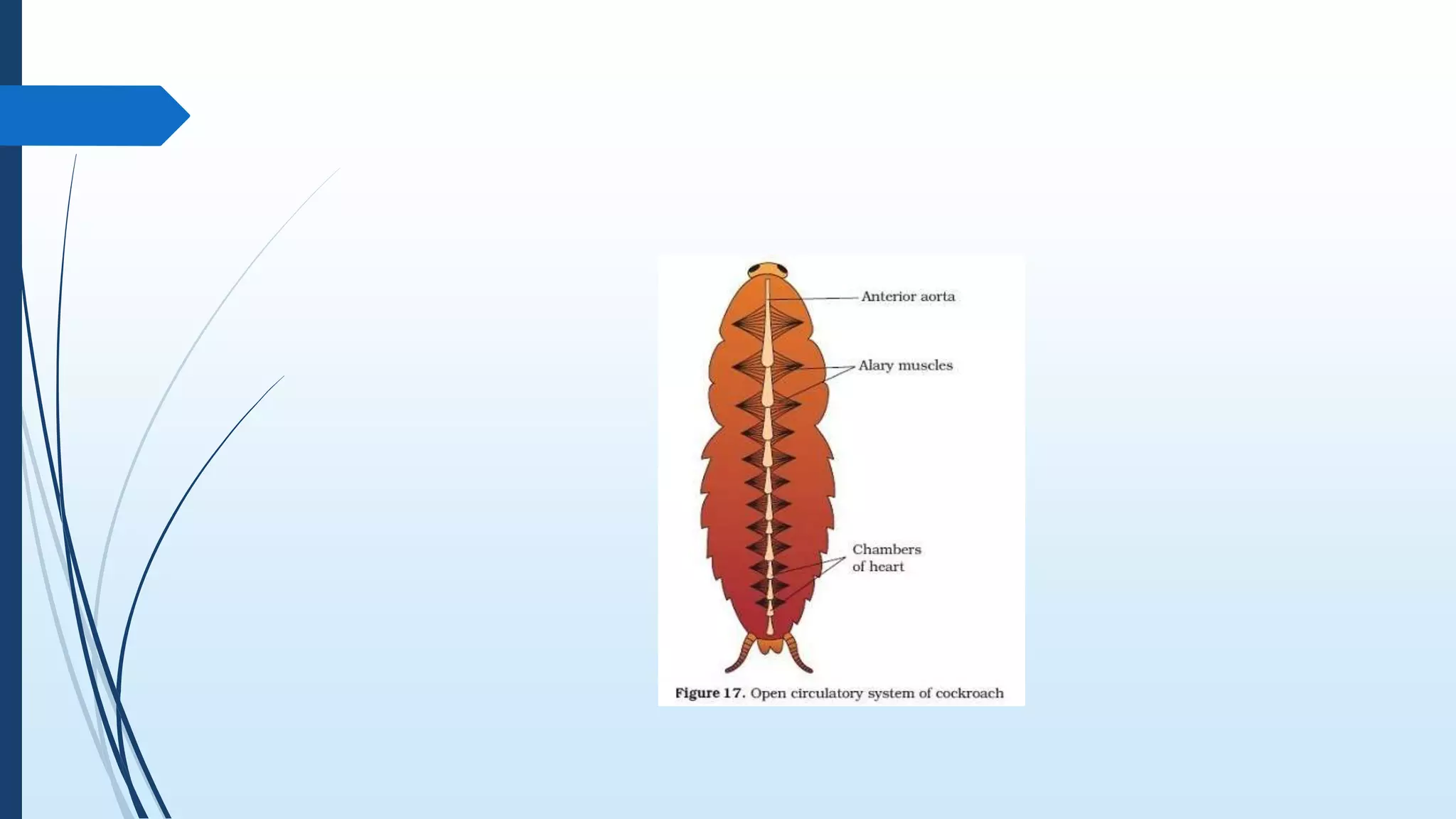
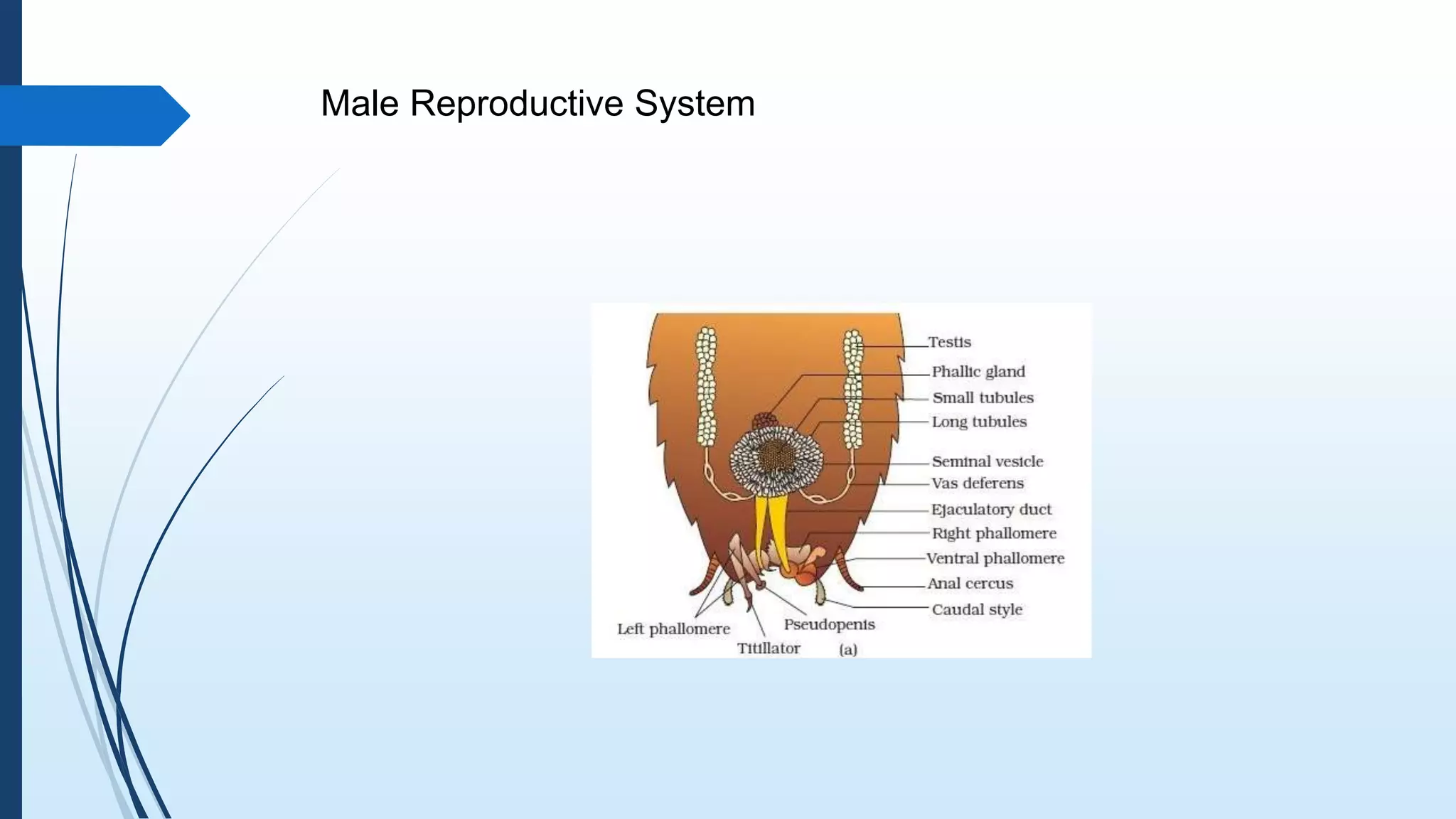
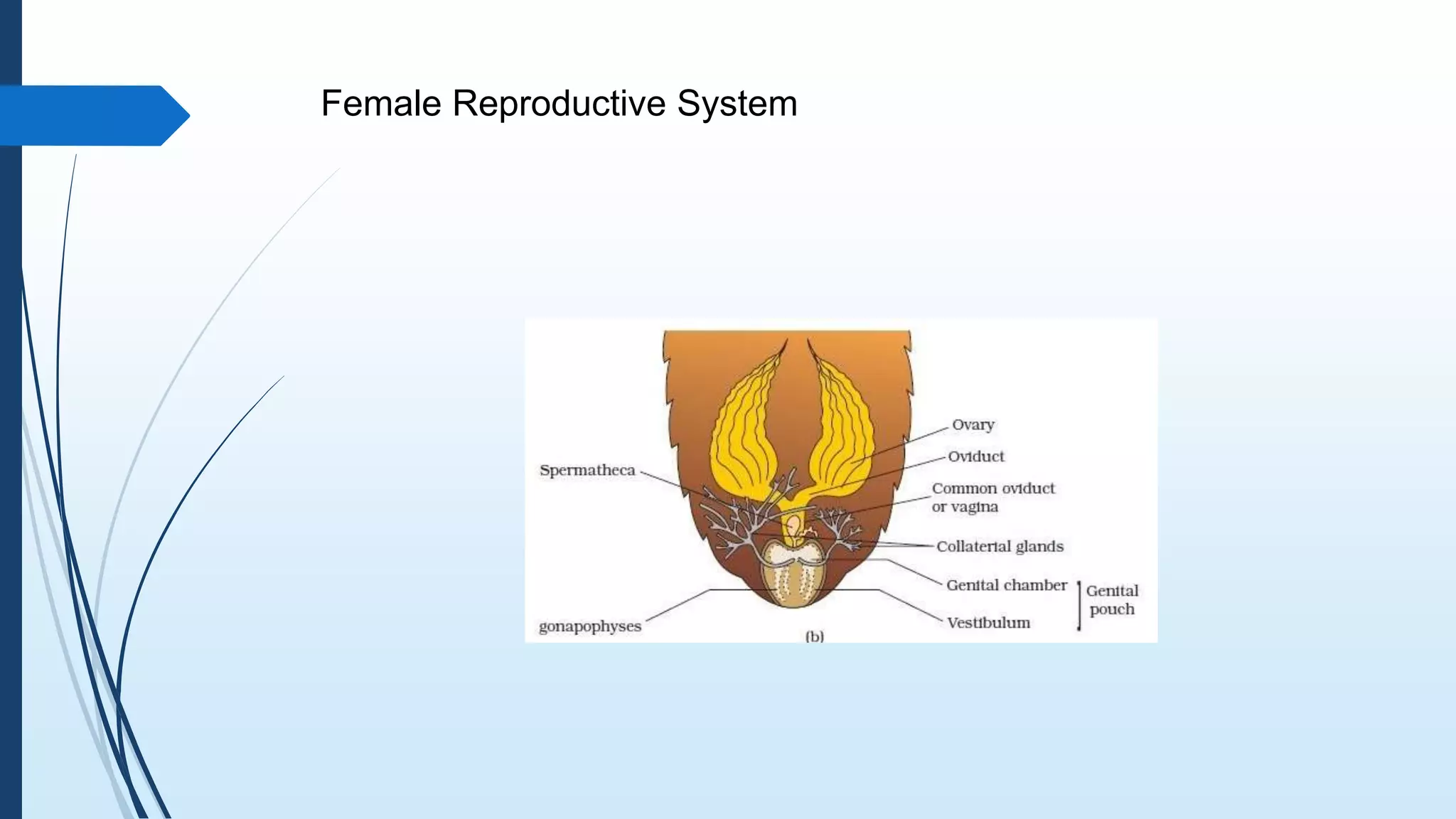
The document provides a detailed overview of cockroach classification, morphology, anatomy, and reproductive systems. It describes their physical characteristics, as well as their digestive, circulatory, respiratory, excretory, and nervous systems. The information is structured to cover differences between male and female cockroaches, their development, and includes a quiz for review.