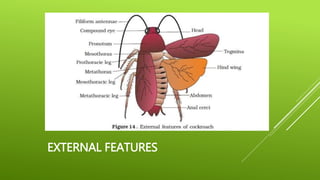
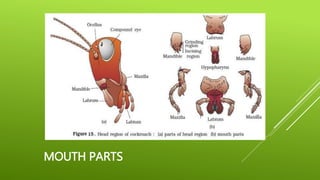
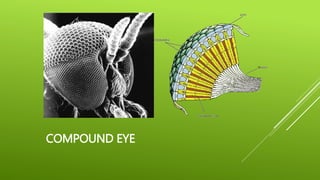
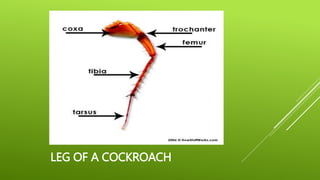
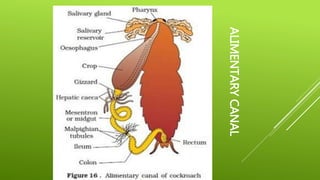
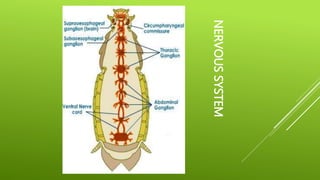
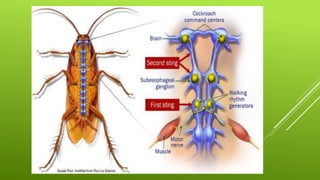
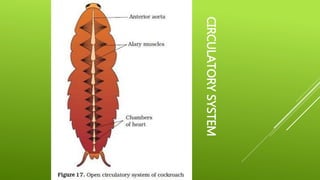
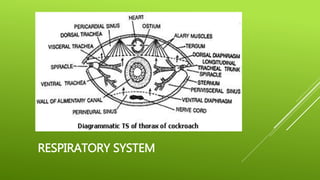
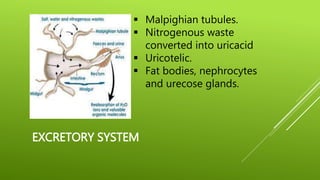
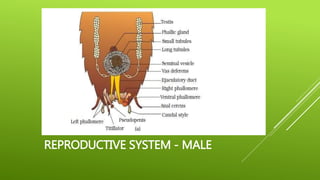
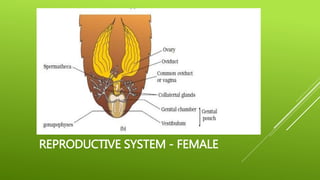
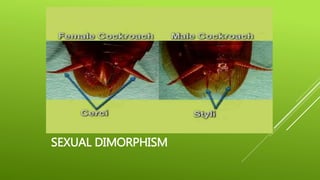
This document summarizes the morphology of cockroaches. It describes the classification of cockroaches in the phylum Arthropoda and order Dictyoptera. The external features, internal systems and life cycle stages of cockroaches are outlined including the digestive, circulatory, respiratory, excretory, reproductive, nervous and sensory systems. The economic importance of cockroaches as pests that can spread disease is also mentioned.