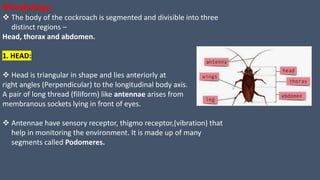
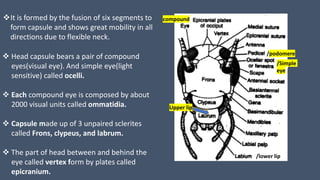
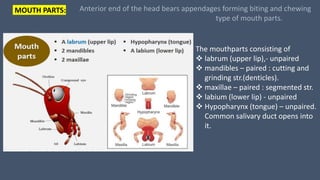
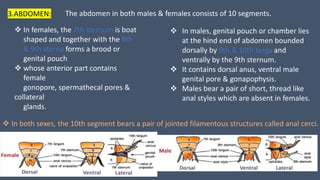
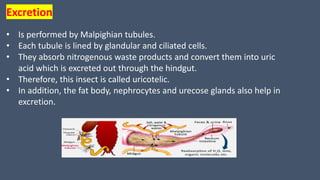
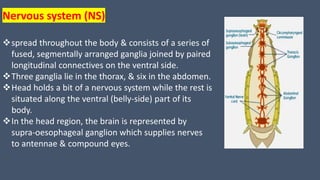
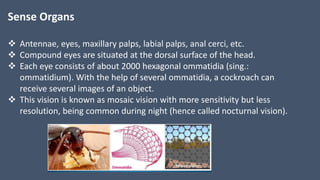
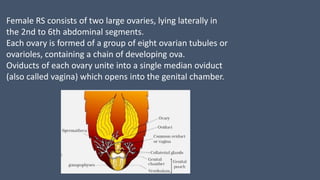
The document provides a detailed description of the cockroach (Periplaneta americana), covering its classification, anatomy, habitat, and physiology. Key points include its segmented body structure, nocturnal omnivorous behavior, various morphological features, and the intricacies of its digestive, respiratory, excretory, nervous, and reproductive systems. The cockroach is described as a pest and a vector for diseases, with various specialized adaptations for survival.