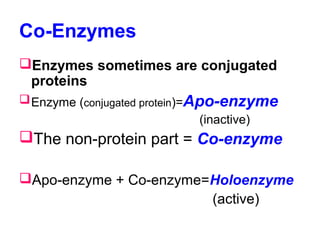
This document discusses co-enzymes, which are non-protein parts of enzymes that help enzymes be active. Co-enzymes can be classified based on their functional characteristics, such as transferring groups other than hydrogen, or transferring hydrogen. They can also be classified based on their structures, with many being derivatives of adenosine monophosphate. Co-enzymes work with enzymes and help transfer atoms or groups between substrates. They are required for many reactions in the body and are related to different B vitamins. Some enzymes are initially produced as inactive proenzymes and require activation by other enzymes or pH changes before becoming active.