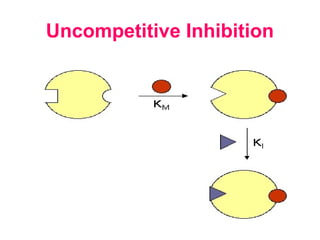
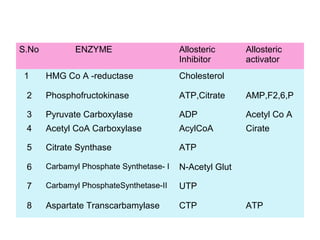
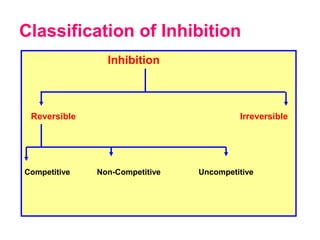
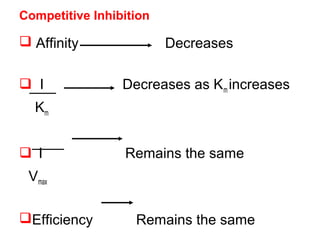
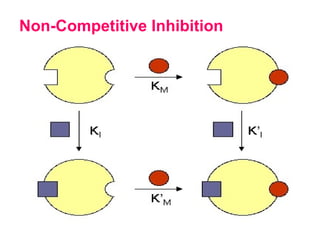
This document discusses different types of enzyme inhibition. It defines inhibitors as substances that inactivate enzymes without altering pH or ionic strength. Inhibition can be reversible or irreversible. There are three main types of reversible inhibition - competitive, non-competitive, and uncompetitive. Competitive inhibitors resemble the substrate and bind the active site. Non-competitive inhibitors bind elsewhere and reduce reaction rate. Uncompetitive inhibitors bind the enzyme-substrate complex. The document provides examples of clinically relevant competitive inhibitors and discusses suicide inhibition which uses the enzyme's reaction to irreversibly inactivate it.




















![Lineweaver Burk’s Plot for Non-
Competitive Inhibition
1/[s]1/ Km
1 / v
1 / Vmax
1 / Vmax
+ Inhibitor
No Inhibitor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzinhi-5lec-170209065851/85/Enz-inhi-5-lec-24-320.jpg)



![Uncompetitive Inhibition
+
1/V
1/V
1/V
1/ [s]
1/V
1/Km 1/Km 1/Km
More Inhibitor
+ Inhibitor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzinhi-5lec-170209065851/85/Enz-inhi-5-lec-28-320.jpg)