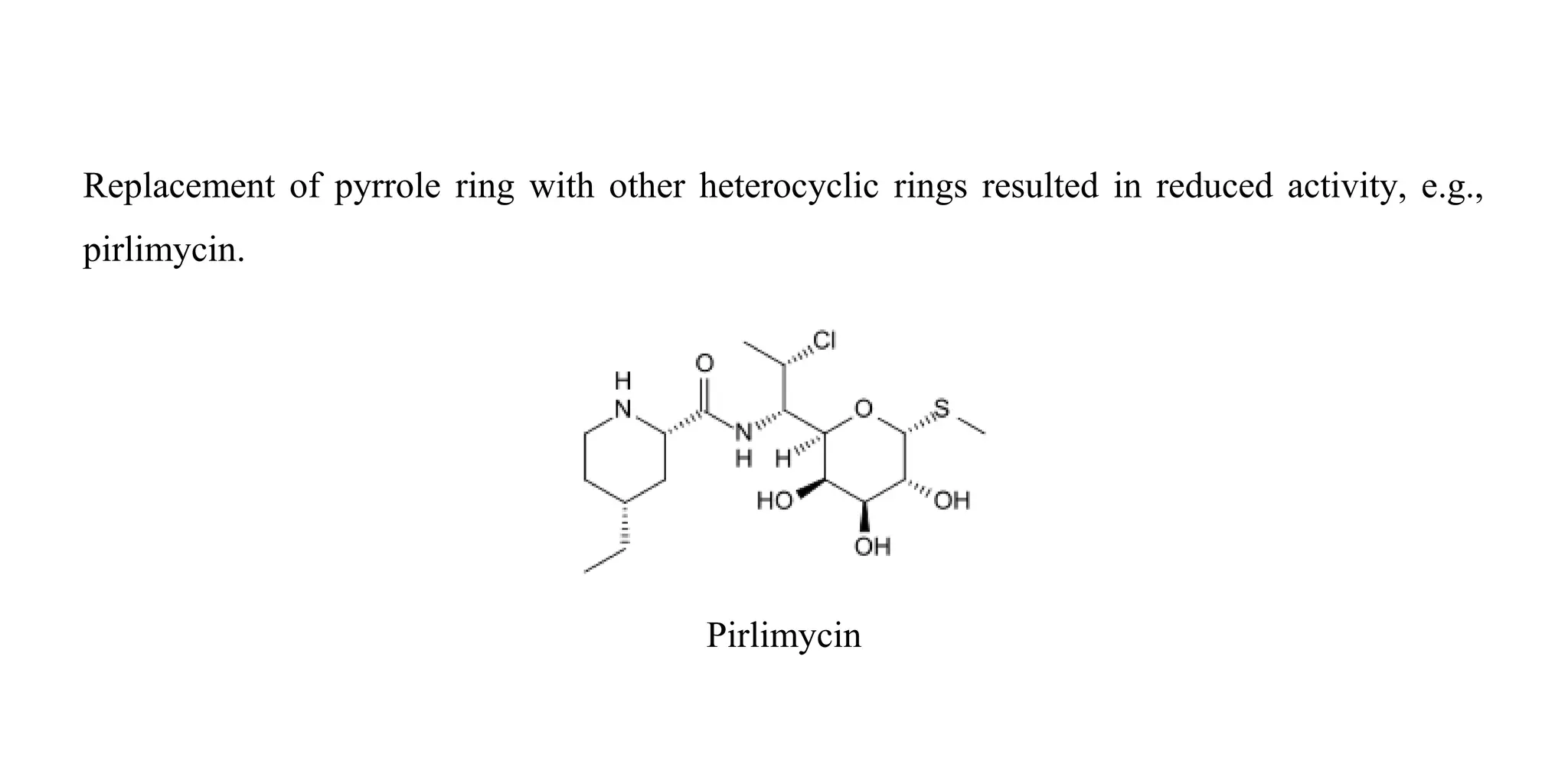
Clindamycin is a semi-synthetic antibiotic derived from lincomycin, a natural antibiotic produced by Streptomyces lincolnensis bacteria. It works by blocking bacterial protein synthesis. Clindamycin is used to treat various bacterial infections, including those affecting the skin, soft tissue, bones, respiratory tract, and more. It can be administered orally or applied topically. Clindamycin is degraded through hydrolysis at low pH and loses its chlorine group at higher pH to become less active lincomycin. It remains an important antibiotic for treating both gram-positive and gram-negative infections.