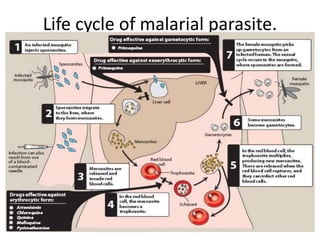
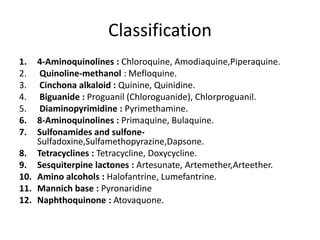
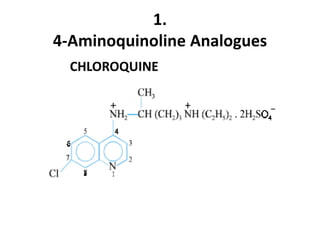
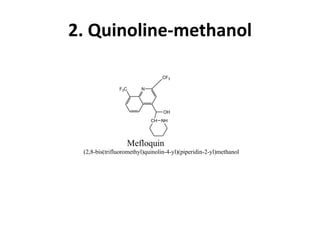
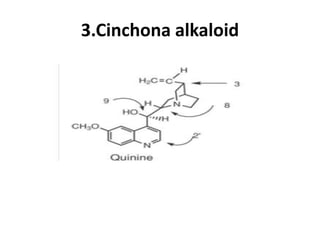
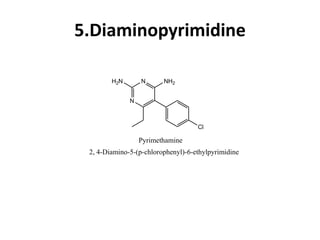
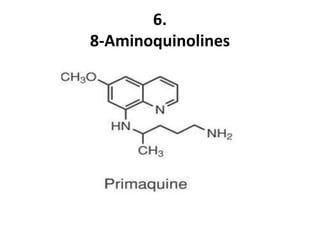
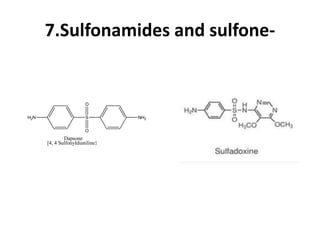
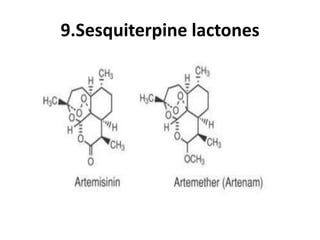
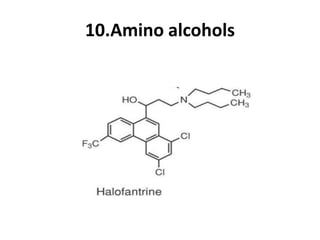
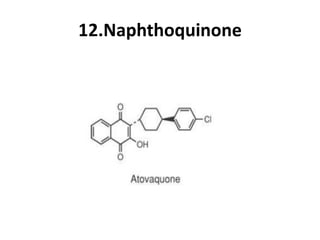
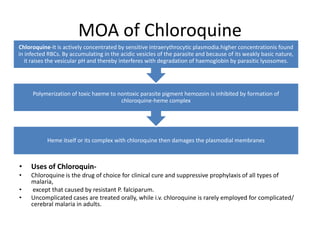
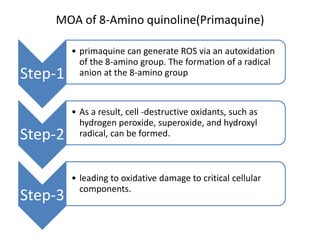
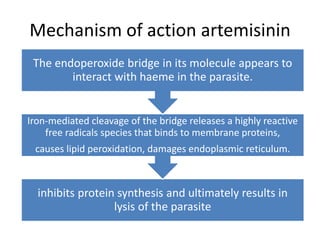
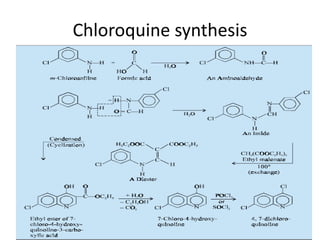
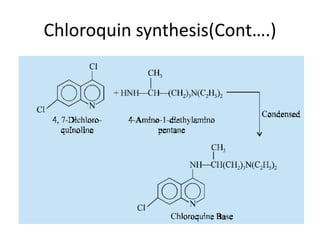
Antimalarial agents are chemotherapeutic agents used to prevent and treat malaria caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium. There are four main species that cause human malaria: P. malariae, P. vivax, P. falciparum, and P. ovale. Common antimalarial classes include 4-aminoquinolines like chloroquine, quinoline-methanols like mefloquine, cinchona alkaloids like quinine, and diaminopyrimidines like pyrimethamine. These work by accumulating in the parasite and raising vesicular pH to interfere with hemoglobin degradation or through other mechanisms like oxidative damage. Artemisinins