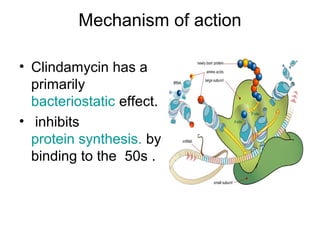
Clindamycin is an antibiotic of the lincosamide class used to treat infections caused by certain bacteria. It works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. It is absorbed well orally or parenterally and distributes widely throughout the body. Common uses include treating respiratory, skin, bone, and intra-abdominal infections caused by anaerobic bacteria and some protozoa. Adverse effects include diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis. It is commonly prescribed for dental infections when penicillin cannot be used due to allergy.