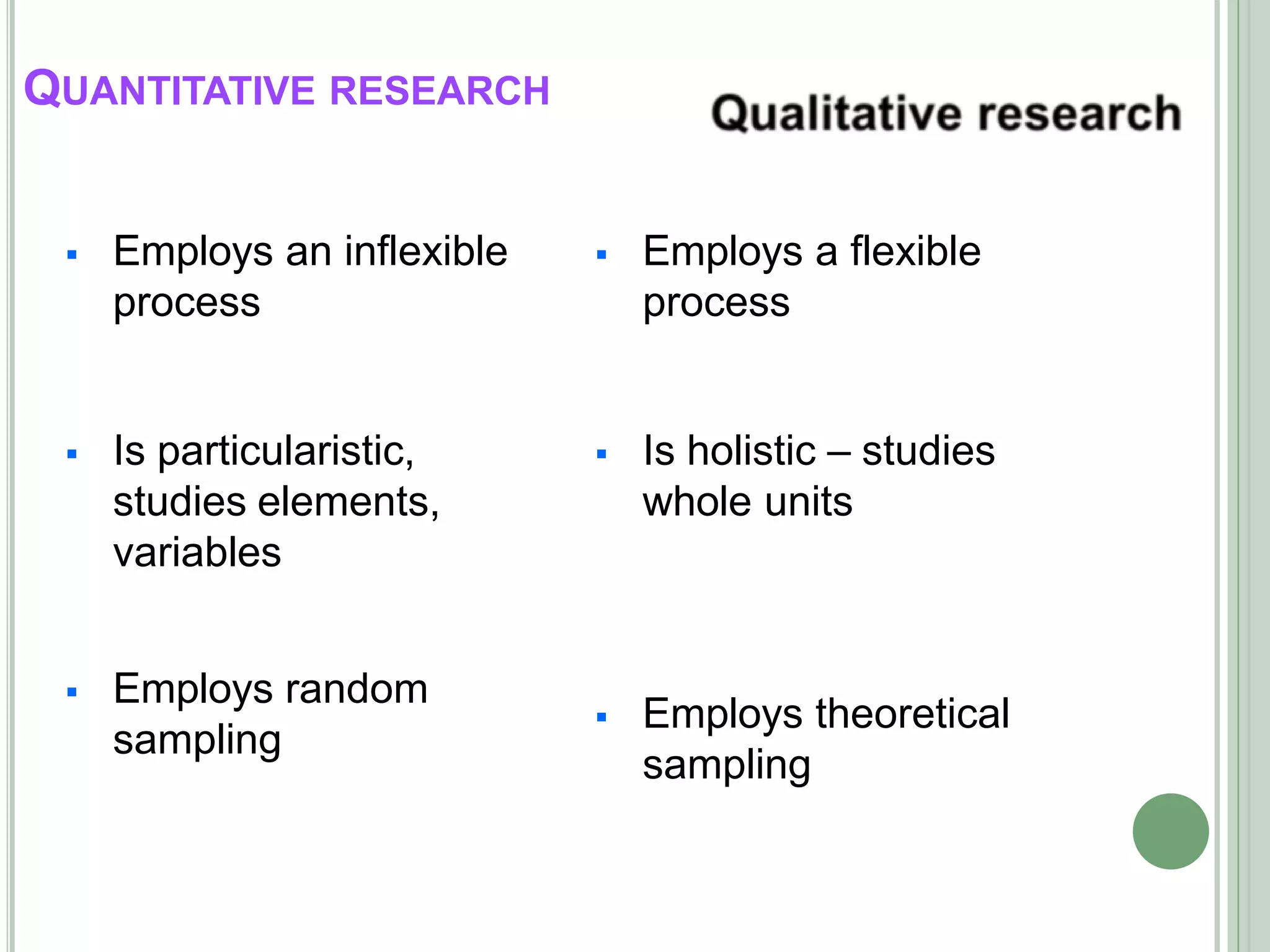
The document outlines the classification of research, emphasizing the systematic inquiry process involving data collection, documentation, and analysis. It distinguishes between quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and hypothesis testing, and qualitative research, which emphasizes meaning-making through non-numerical data and flexible methodologies. The comparison highlights their differing approaches, purposes, and data collection techniques.