This document discusses sampling methods for research. It defines key terms like population, sample, and sampling. It covers the main types of sampling:
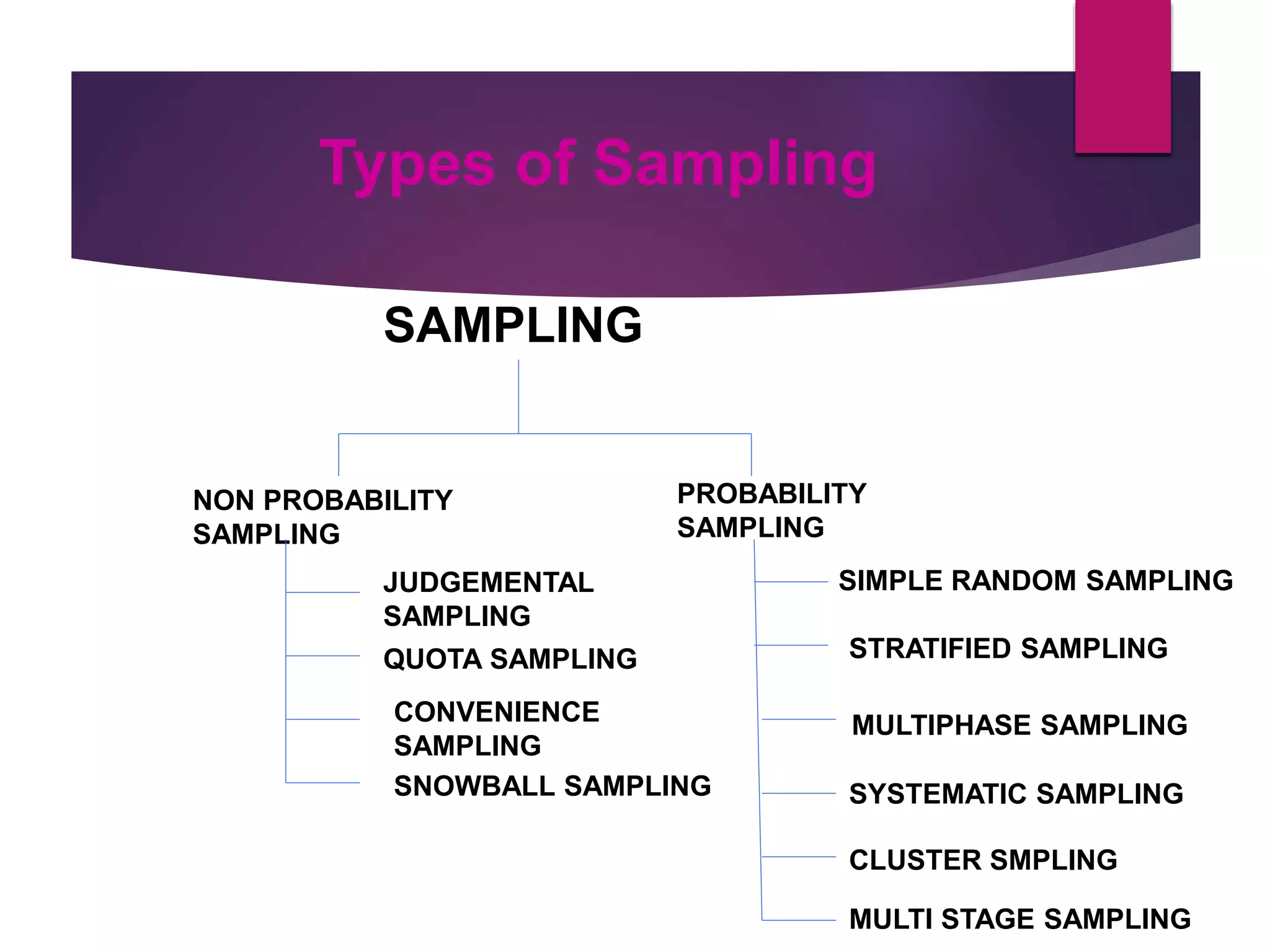
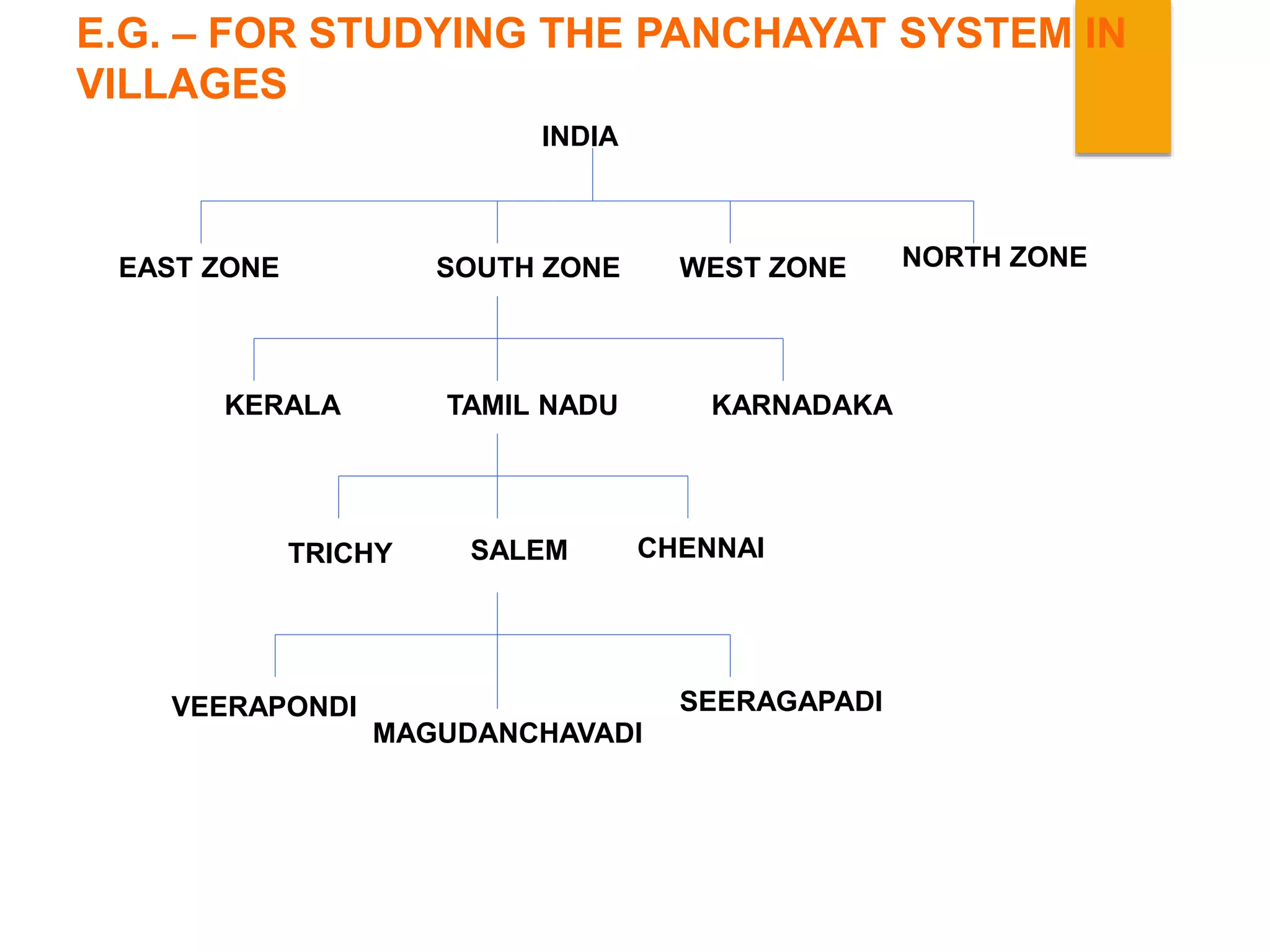
1. Probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, stratified sampling, and systematic sampling which give all units an equal chance of selection.
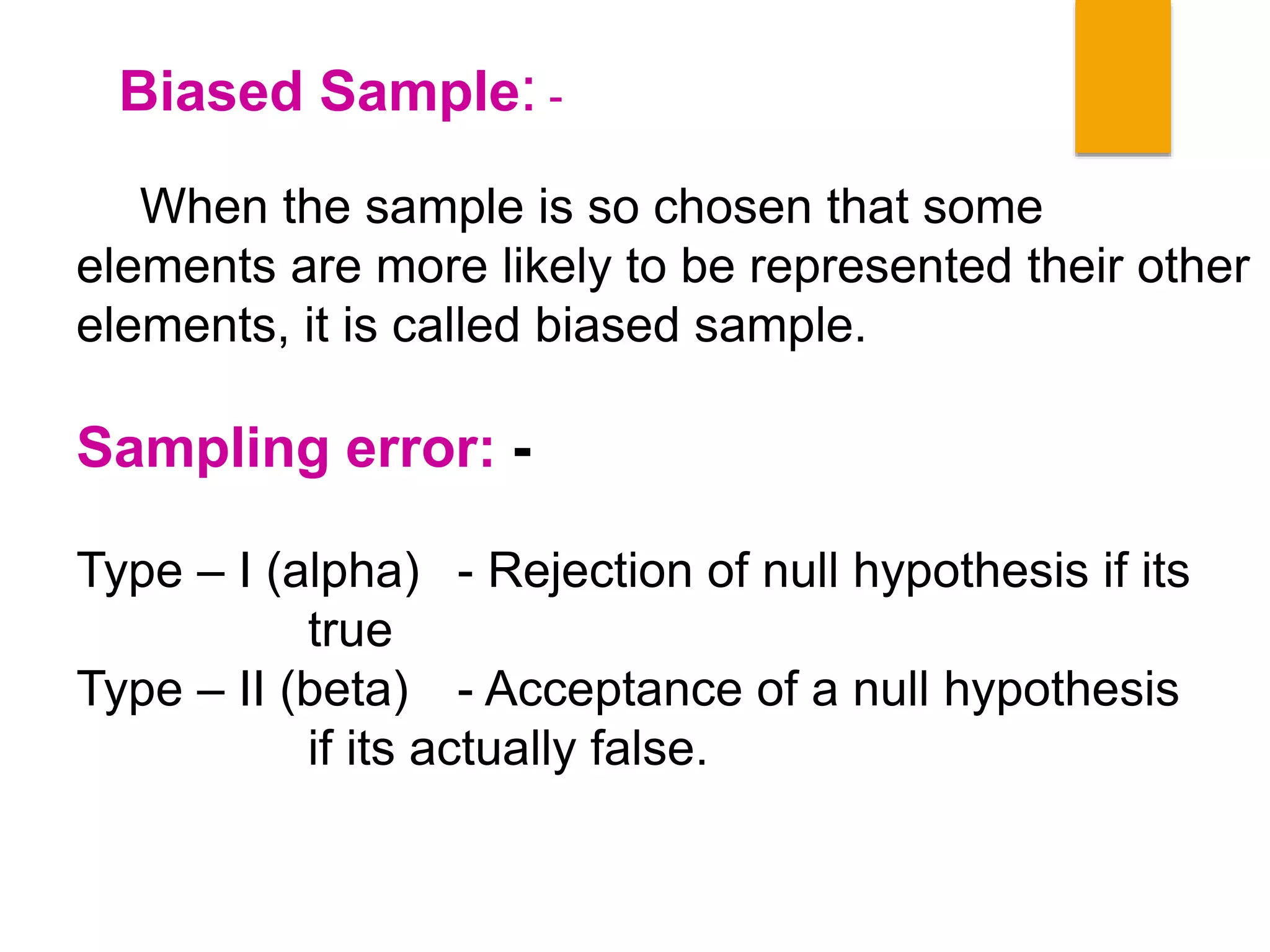
2. Non-probability sampling methods like judgement, quota, and convenience sampling which do not give all units an equal chance and can be biased.
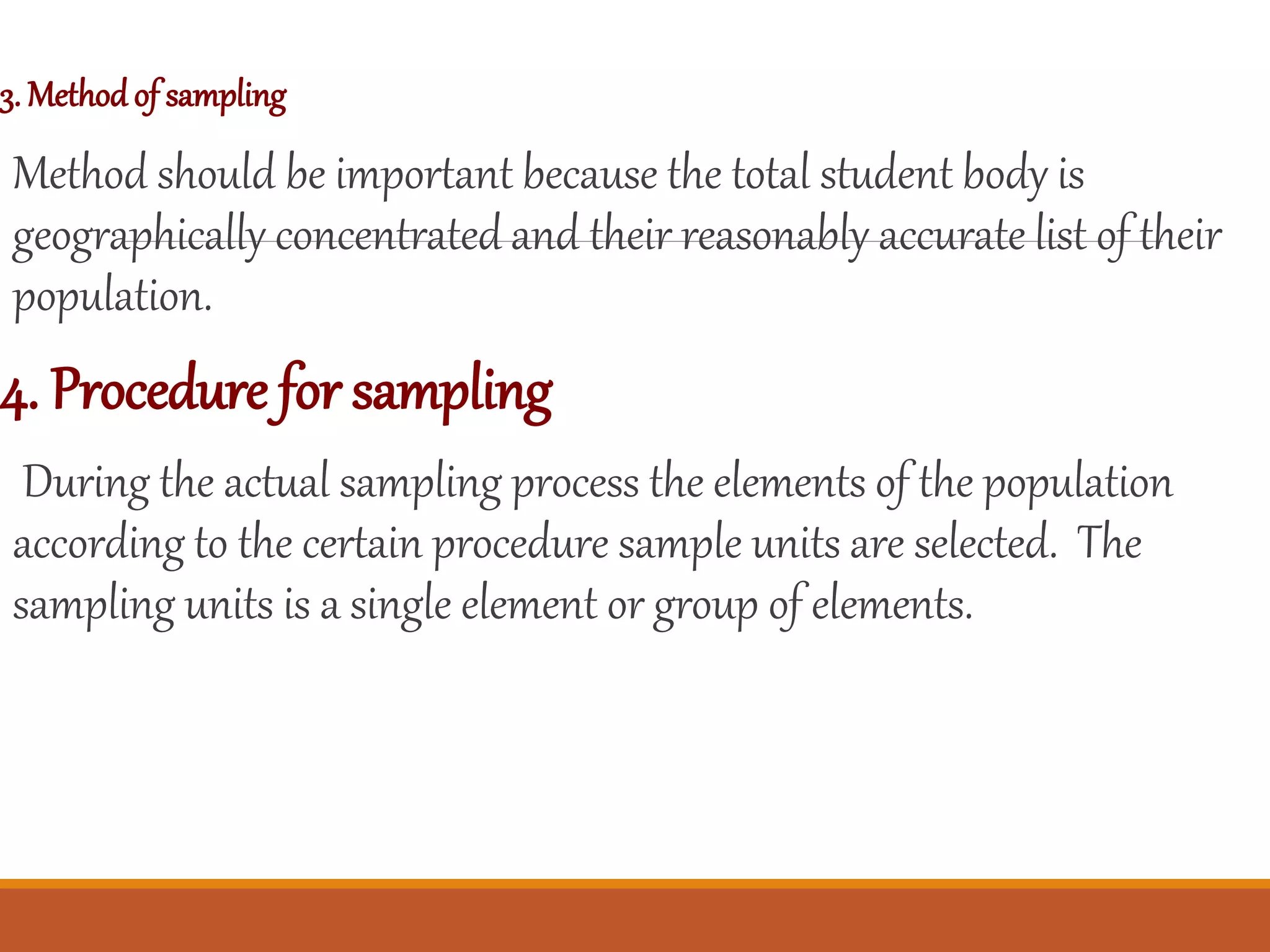
3. Factors to consider for good sampling include accuracy, precision, defining the target population, determining the sampling method and size. The document provides details on each sampling technique and their advantages and disadvantages.