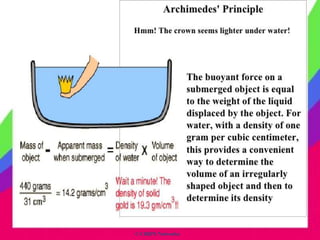
The document discusses various types of research including descriptive research, which describes characteristics without determining causes, and analytical research, which evaluates facts and information. It also discusses applied research which aims to solve immediate problems, and basic research which improves scientific understanding without specific applications. Additional types discussed are quantitative research using measurement, qualitative research investigating human behavior, conceptual research developing new ideas, empirical research using observation, and historical research studying past events.