Embed presentation
Download to read offline


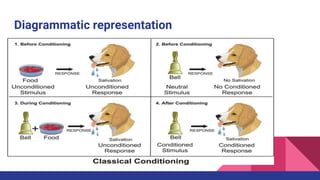



Classical conditioning theory proposes that learning is a process of forming associations between stimuli and responses. It involves modifying natural responses by pairing a conditioned stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a desired response. Pavlov's classical conditioning experiments showed that a dog could learn to associate a bell with food and eventually salivate upon hearing the bell alone. The theory has educational implications for developing good habits in children, motivating learning, and using audiovisual aids to reinforce conditioning.




