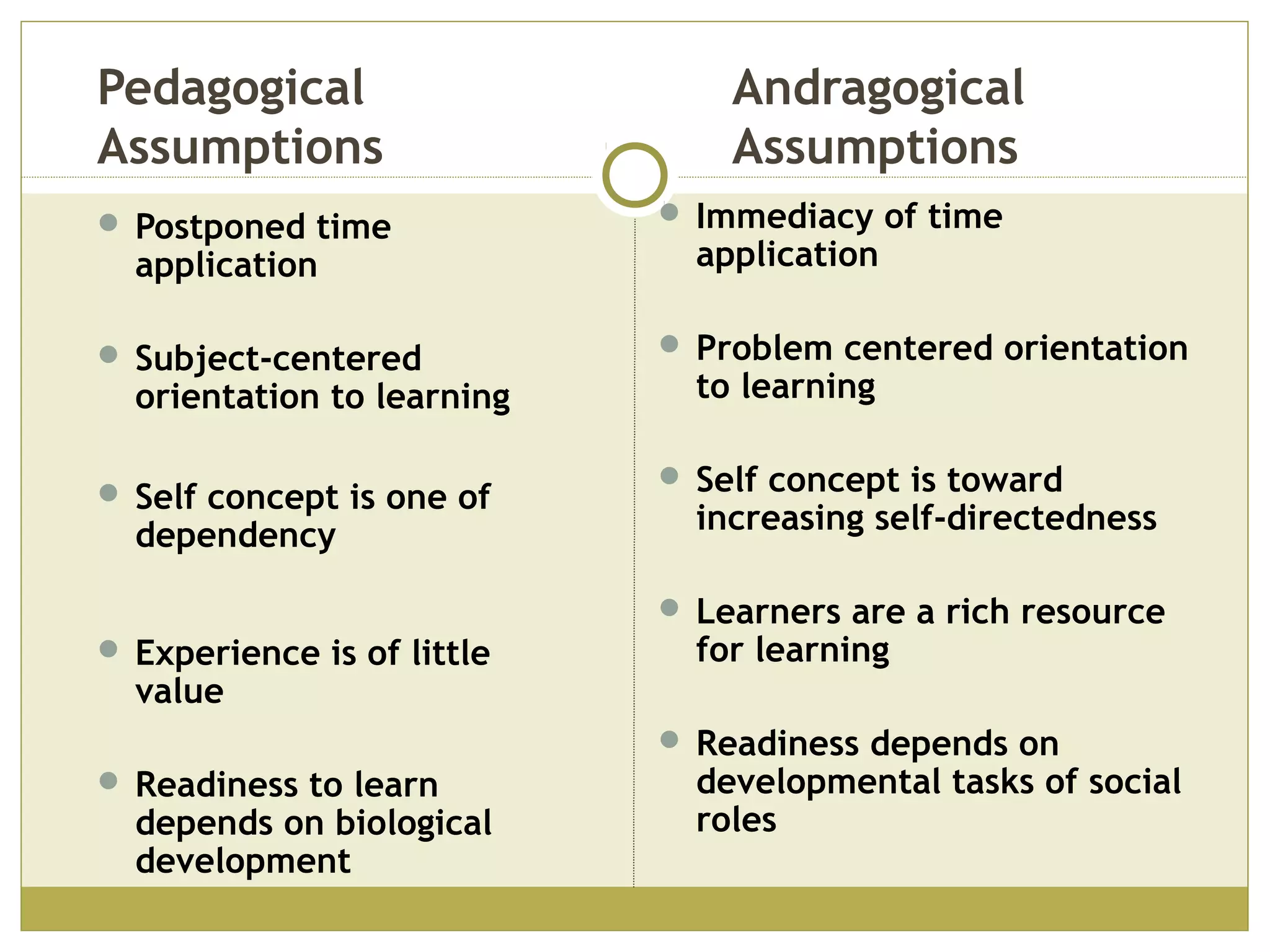
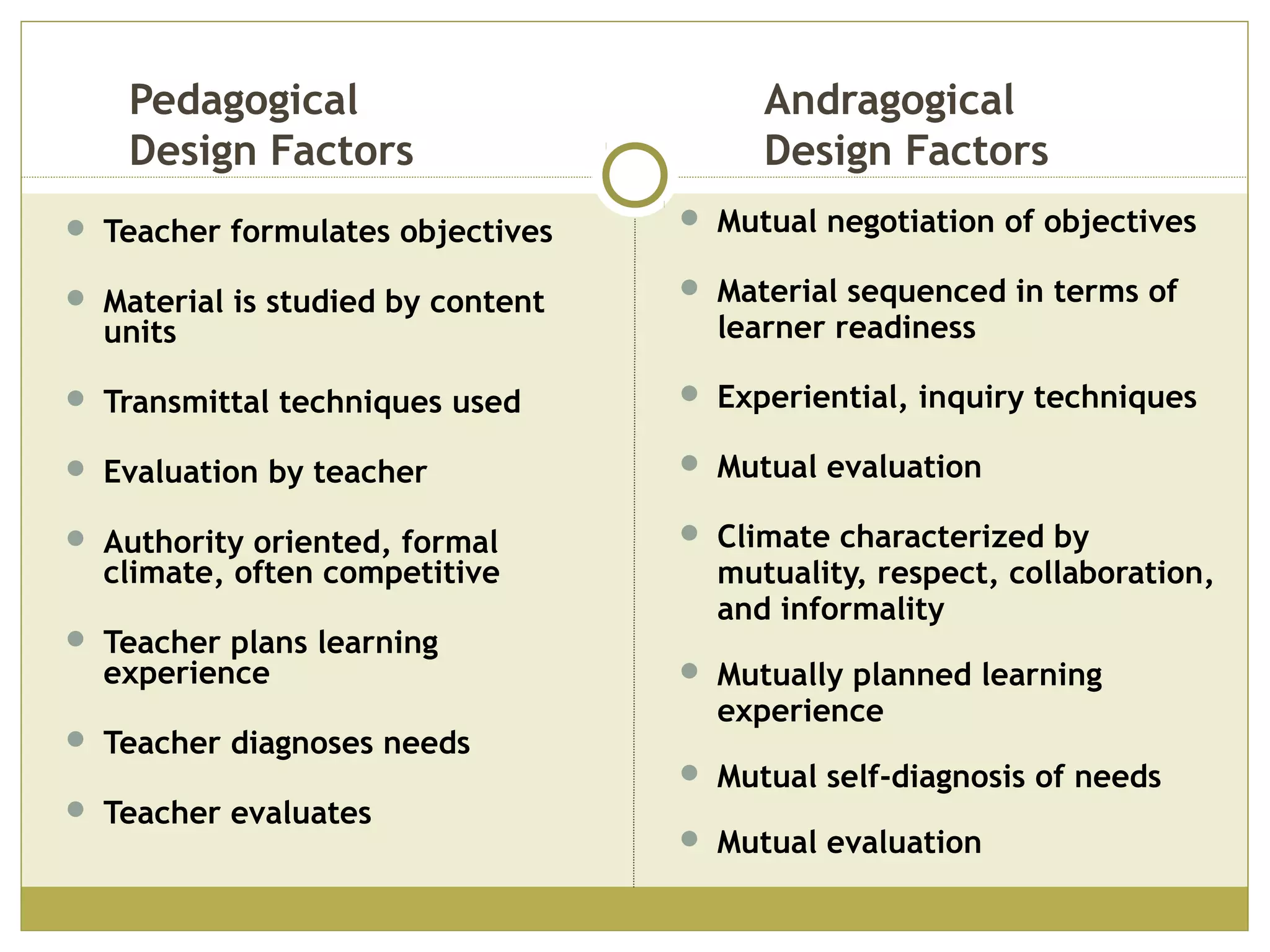
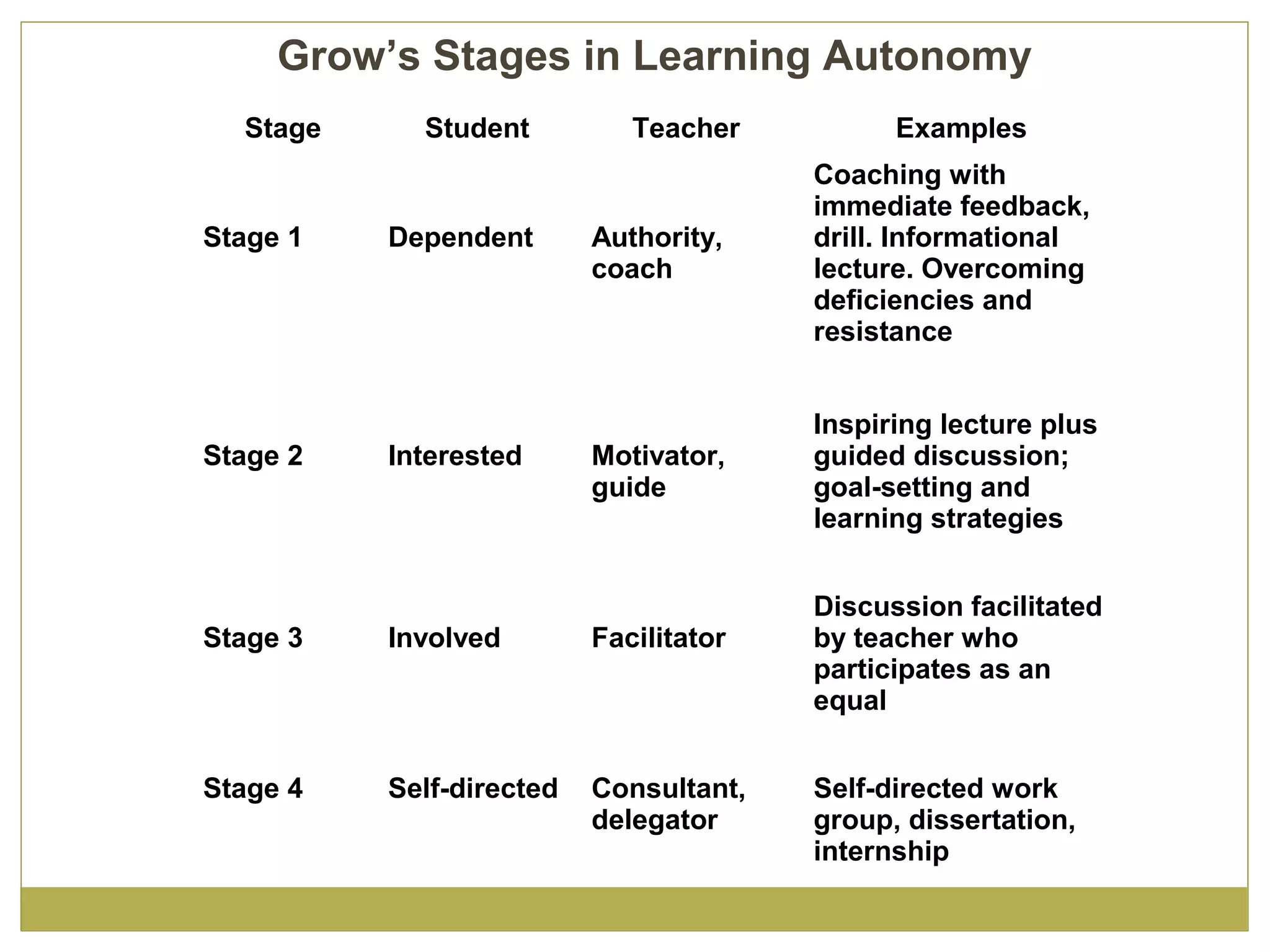
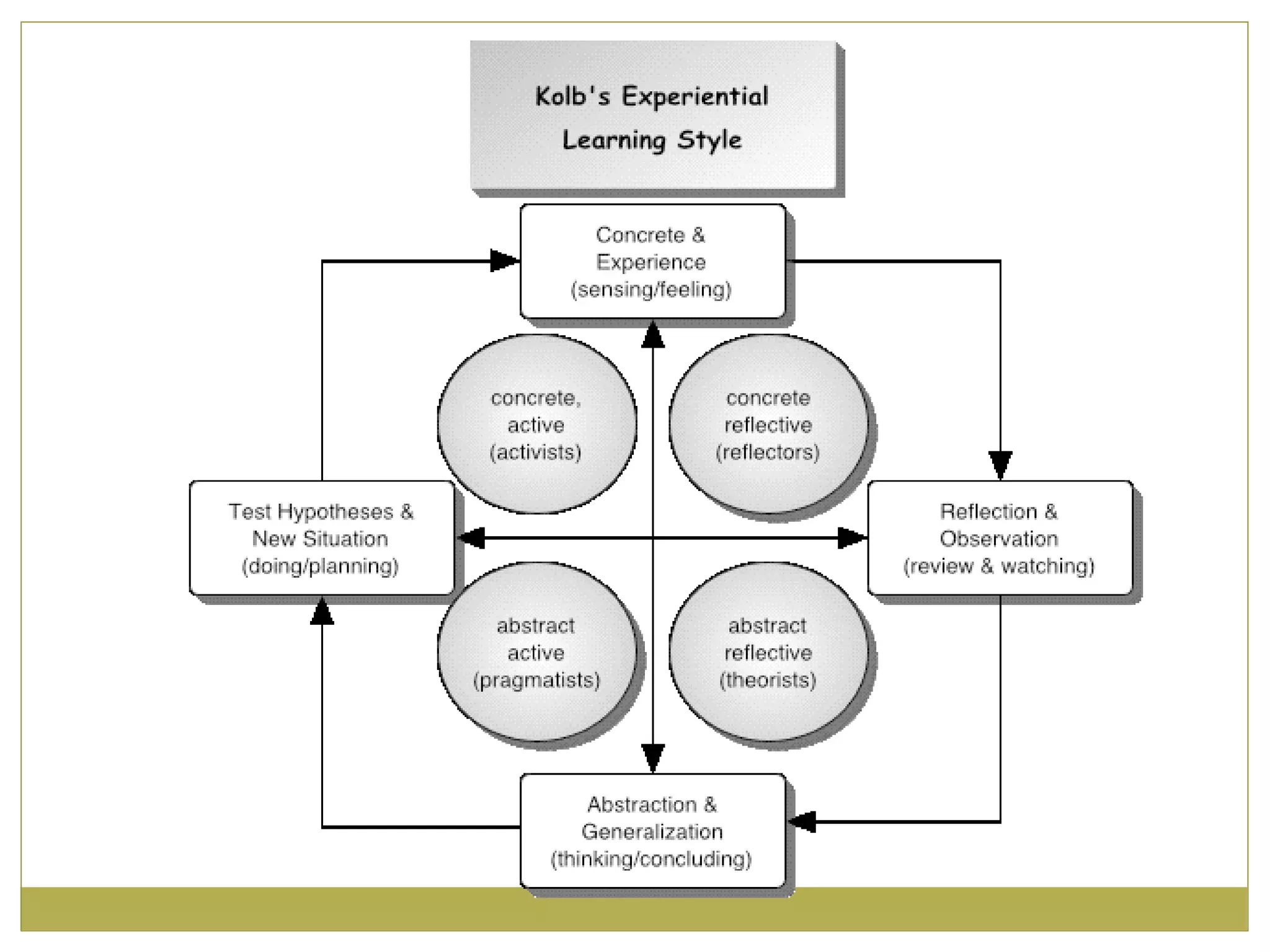
Knowles' principles of andragogy outline how adults learn best. They include that adults learn best when they feel a need to learn, are respected and trusted by others in their learning environment, help plan their learning, and can apply their experiences. Andragogical teaching focuses on self-directed learning, problem-centered orientation, and mutual planning between teacher and learner. Grow's stages of learning autonomy show how learners progress from dependent to self-directed, while Kolb's model emphasizes learning through concrete experience, observation, conceptualization, and experimentation.