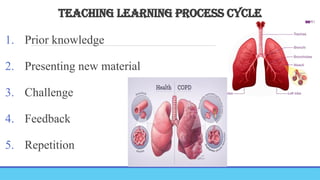
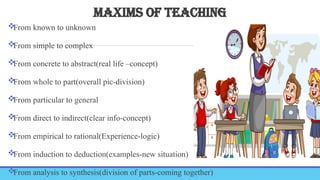
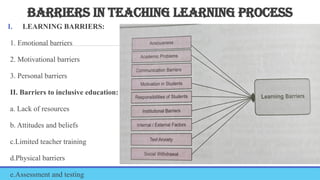
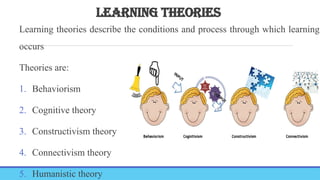
TEACHING LEARNING PROCESS-MEANING, OBJECTIVE, PRINCIPLES, TEACHING LEARNING CYCLE,PHASES OF TEACHING, TEACHING LEARNING STRATEGIES, TEACHING-PRINCIPLES, STRATEGIES, PRINCIPLES, GENERAL & PSYCHOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES, MAXIMS OF TEACHING, FACTORS AFFECTING T-L PROCESS, BARRIERS. LEARNING-CONCEPT, PRINCIPLES, DOMAINS, THEORIES OF LEARNING-BEHAVIOURISM, COGNITIVE THEORY, CONSTRUCTIVISM, CONNECTIVISM THEORY, HUMANISTIC THEORY