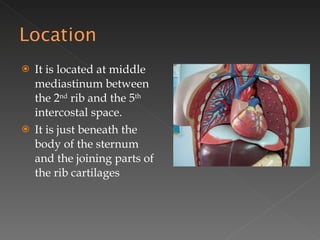
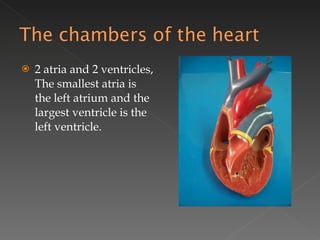
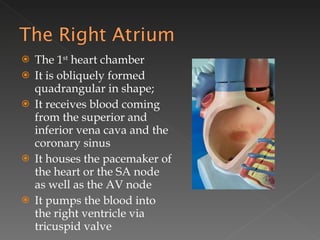
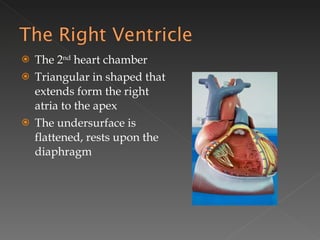
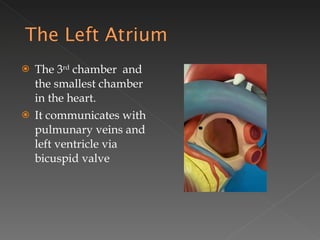
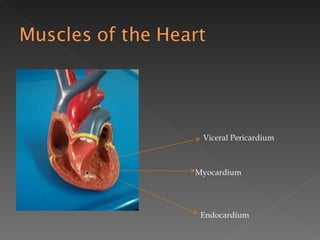
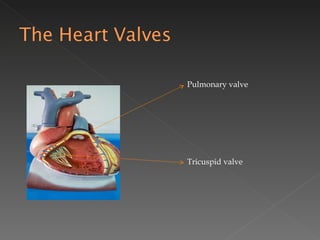
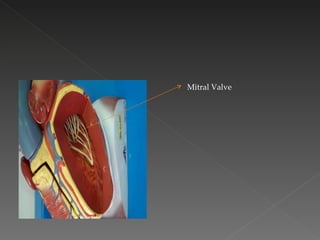
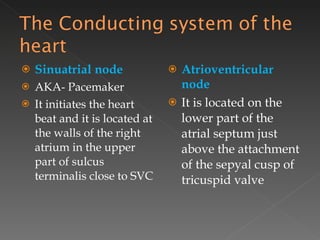
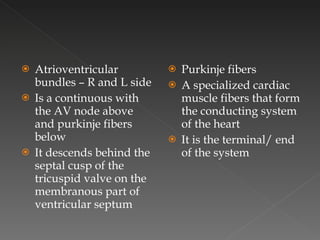
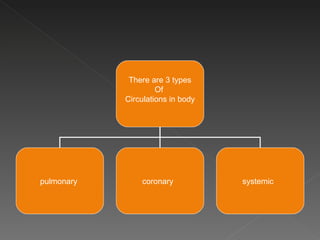
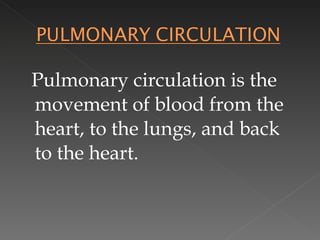
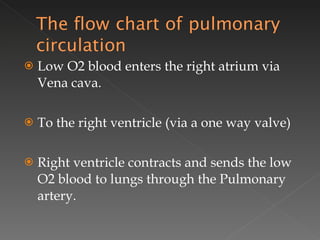
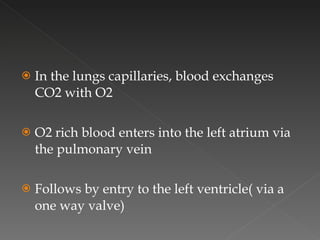
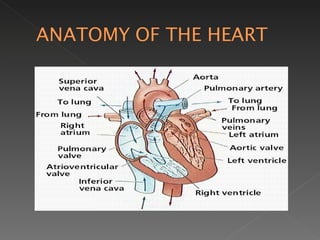
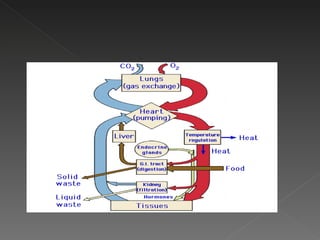
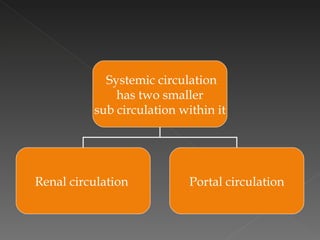
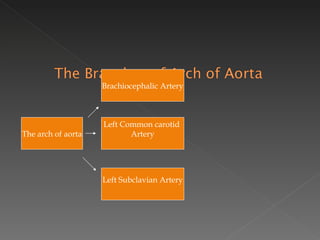
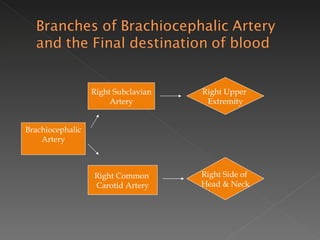
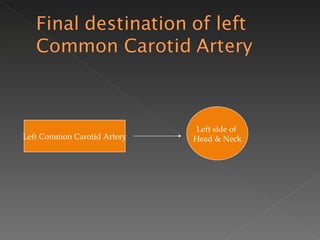
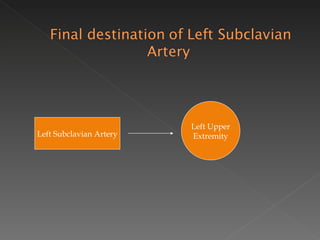
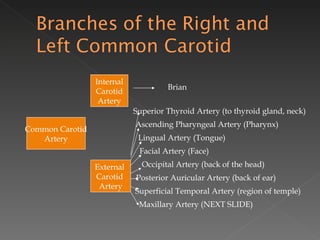
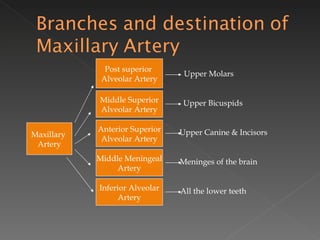
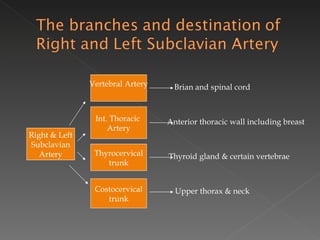
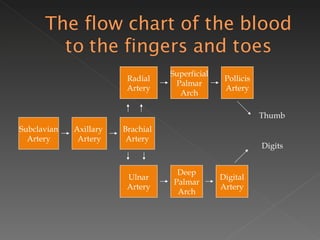
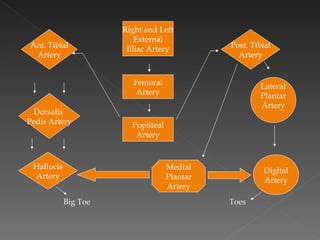
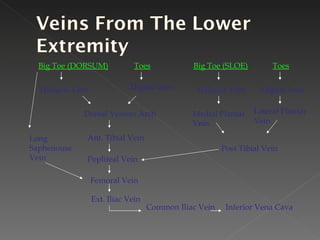
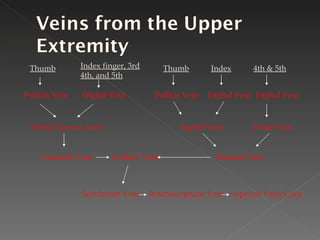
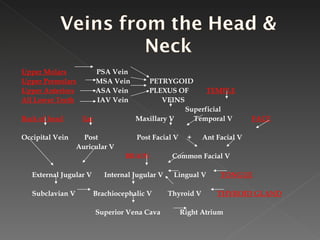
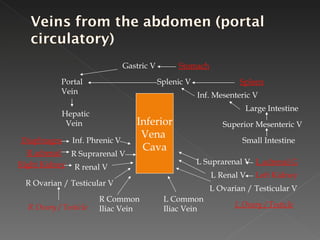
The circulatory system is responsible for transporting materials like blood, oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and water throughout the entire body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart has four chambers - two upper atria and two lower ventricles. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the body and is pumped to the lungs where it receives oxygen before reentering the left atrium and being pumped by the left ventricle out to the body through arteries. There are three main types of circulation - pulmonary, coronary, and systemic.