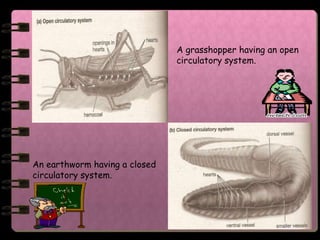
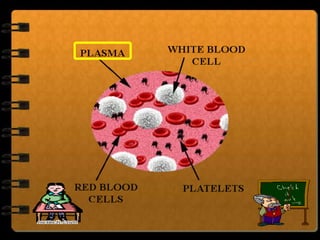
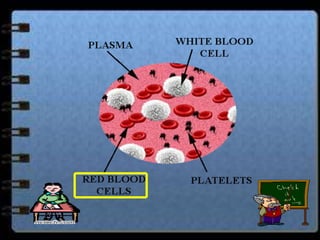
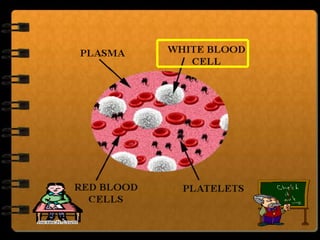
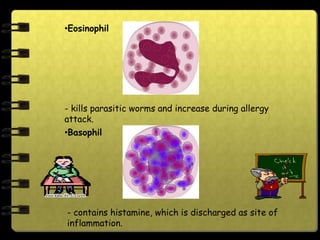
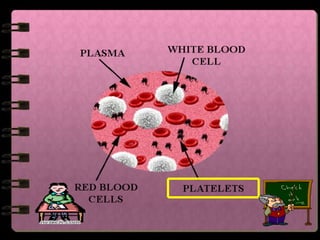
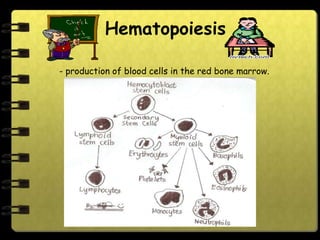
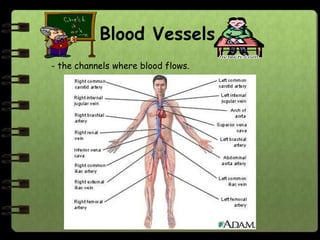
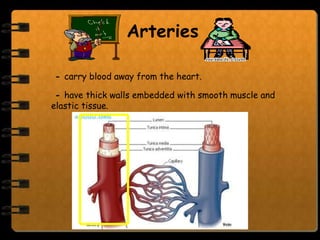
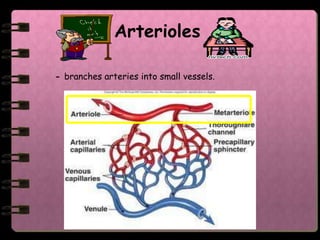
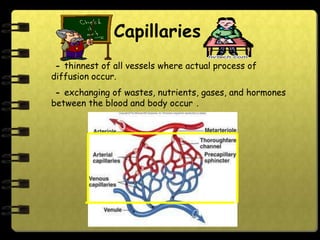
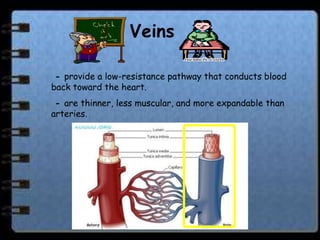
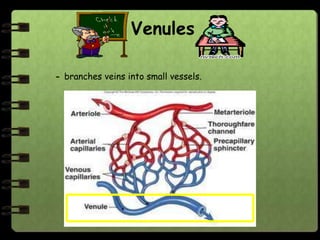
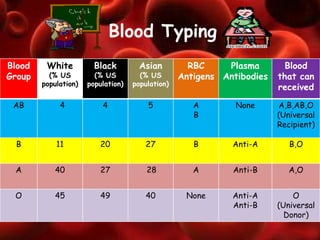
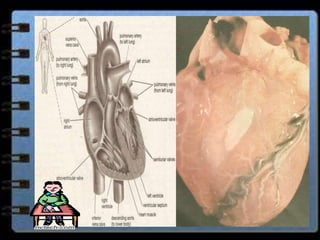
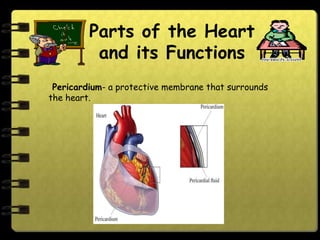
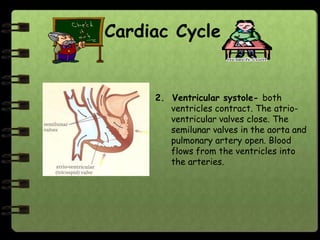
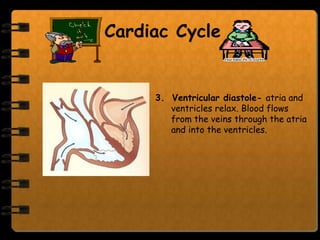
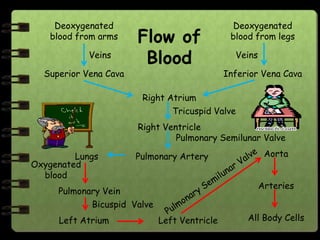
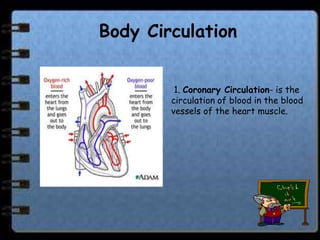
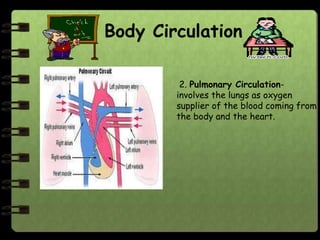
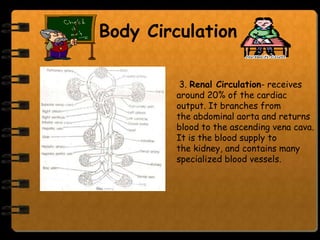
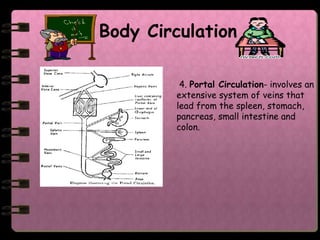
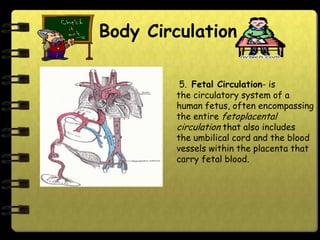
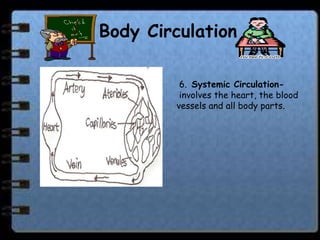
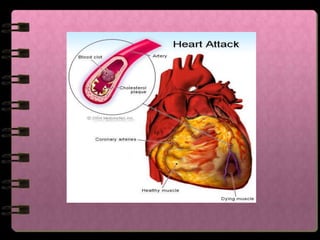
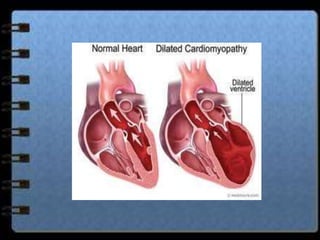
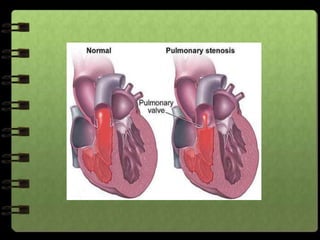
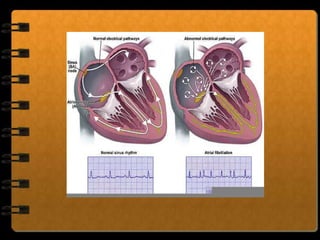
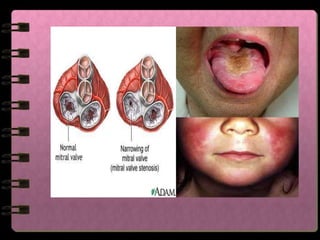
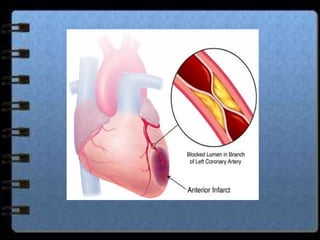
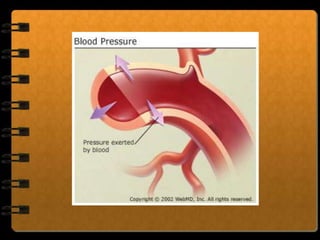
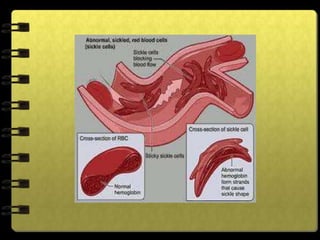
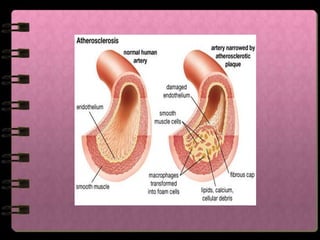
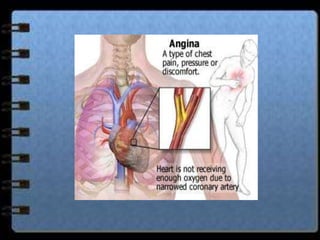
The circulatory system transports nutrients, gases, hormones, blood cells, and wastes to and from cells in the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The document discusses the components and functions of the circulatory system, types of circulatory systems, blood and its components, blood vessels, the cardiac cycle, blood circulation, common diseases, and ways to care for the circulatory system.