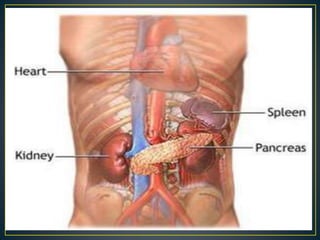
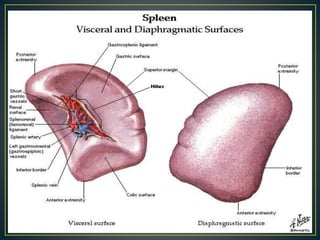
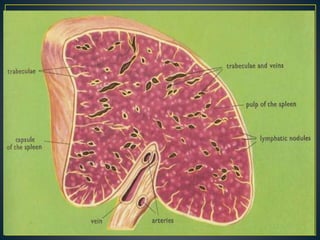
The spleen is a lymphatic organ located in the left upper abdomen under the diaphragm and ribs. It is oval shaped, 7-14cm long and weighs 150-200g. The spleen has several surfaces - a diaphragmatic surface facing upward, a visceral surface divided into gastric and renal regions, and borders. It filters blood and recycles iron, and contains red and white pulp. The spleen receives blood from the splenic artery and drains into the splenic vein. Diseases can cause an enlarged or absent spleen.