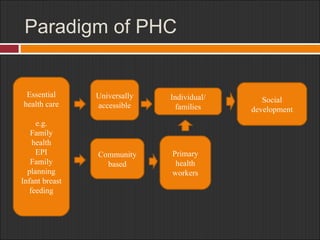
The document discusses the Philippine primary health care system and family health programs. It outlines the goals of maternal health, family planning, child health, immunization, and nutrition programs to improve health outcomes. The key objectives are to reduce morbidity and mortality rates and improve survival, health, and well-being of family members.