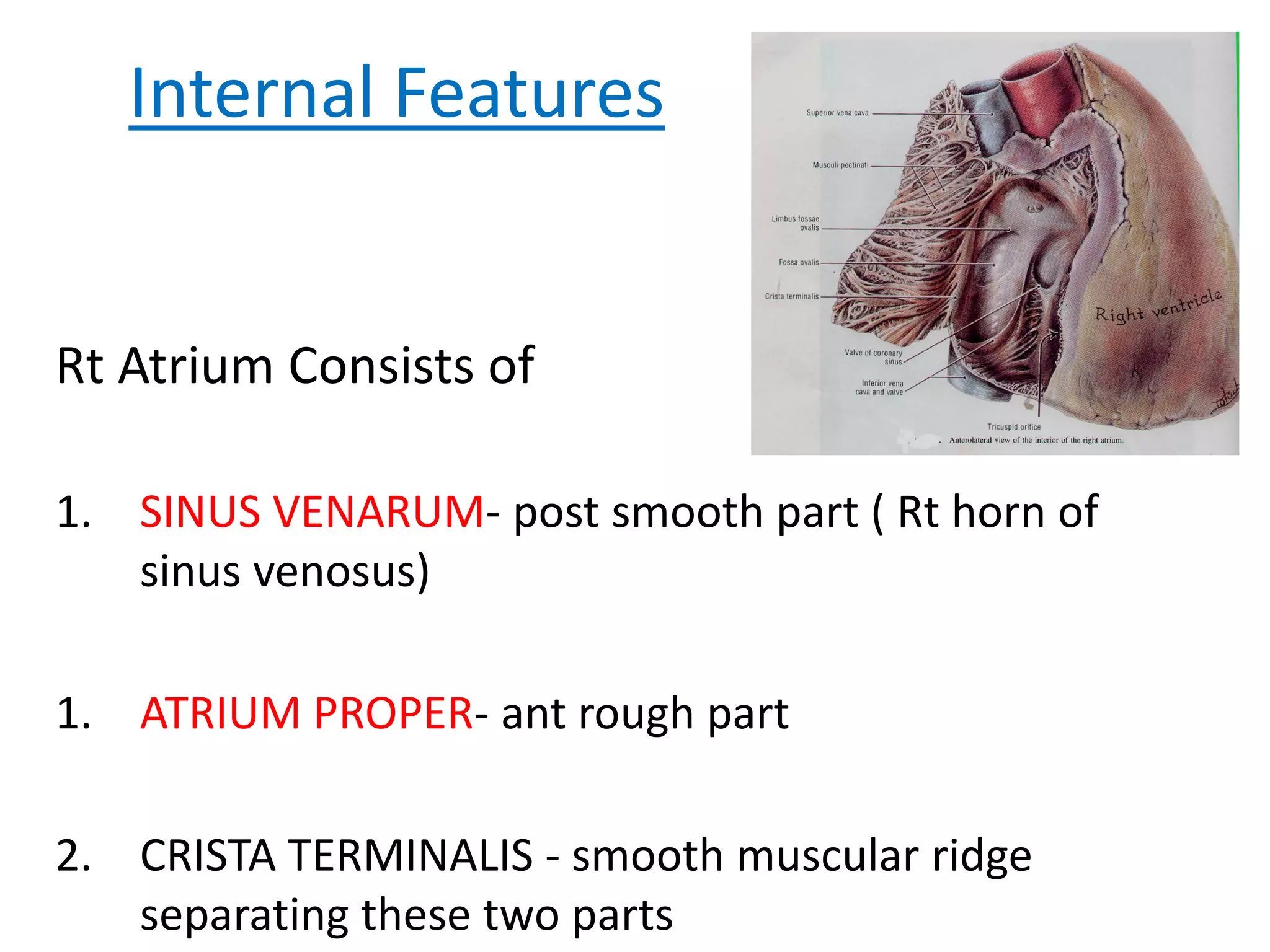
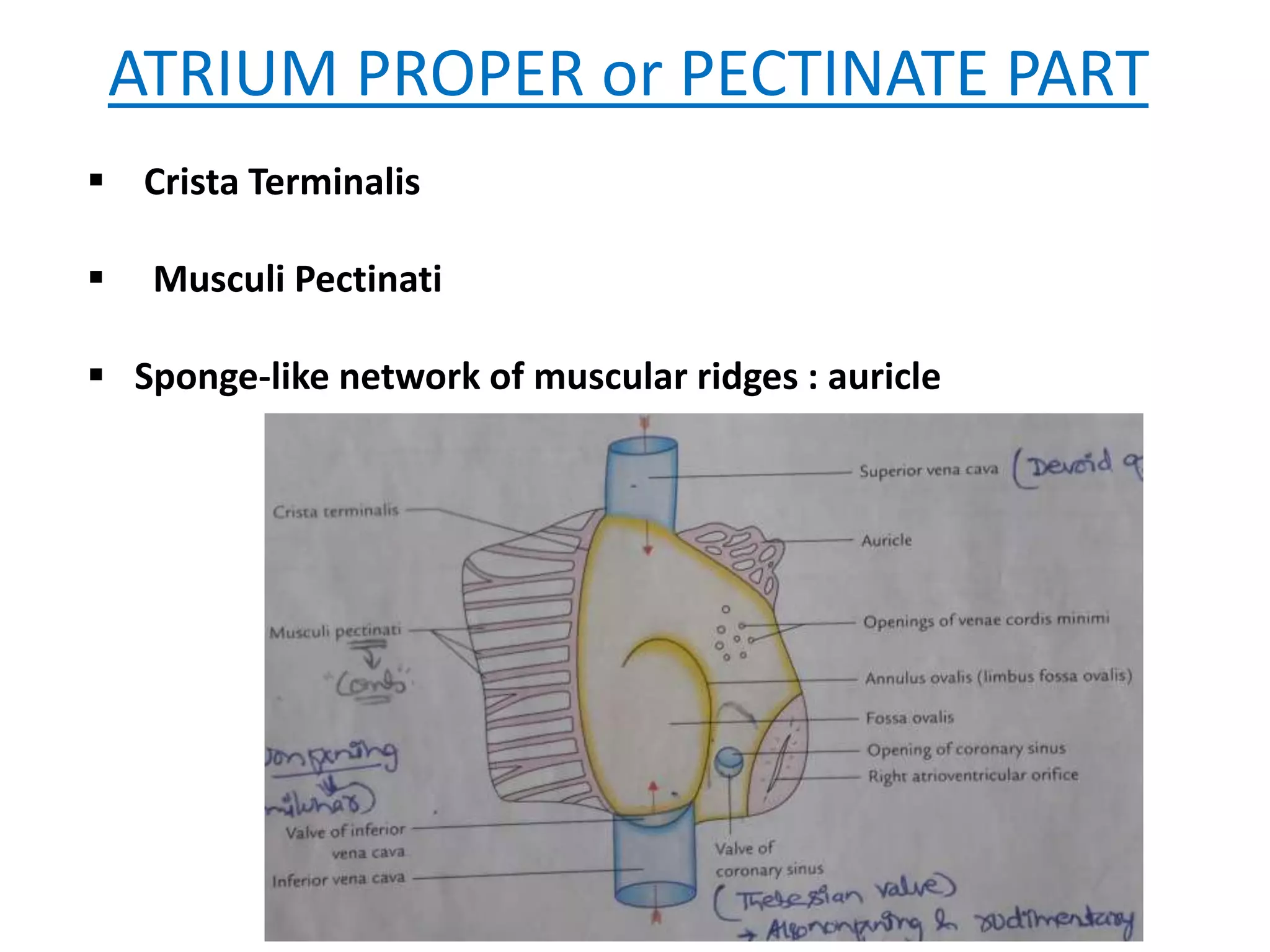
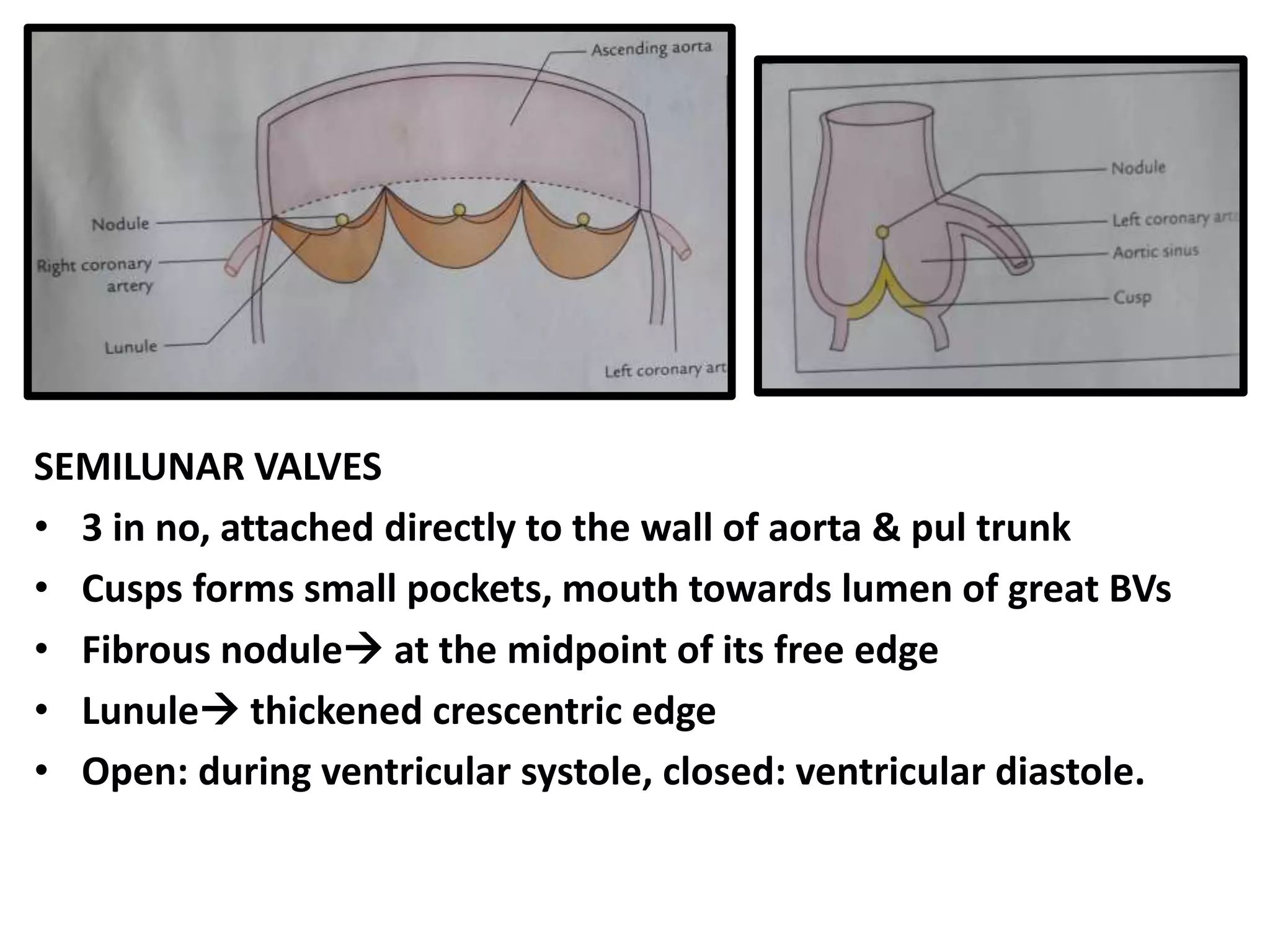
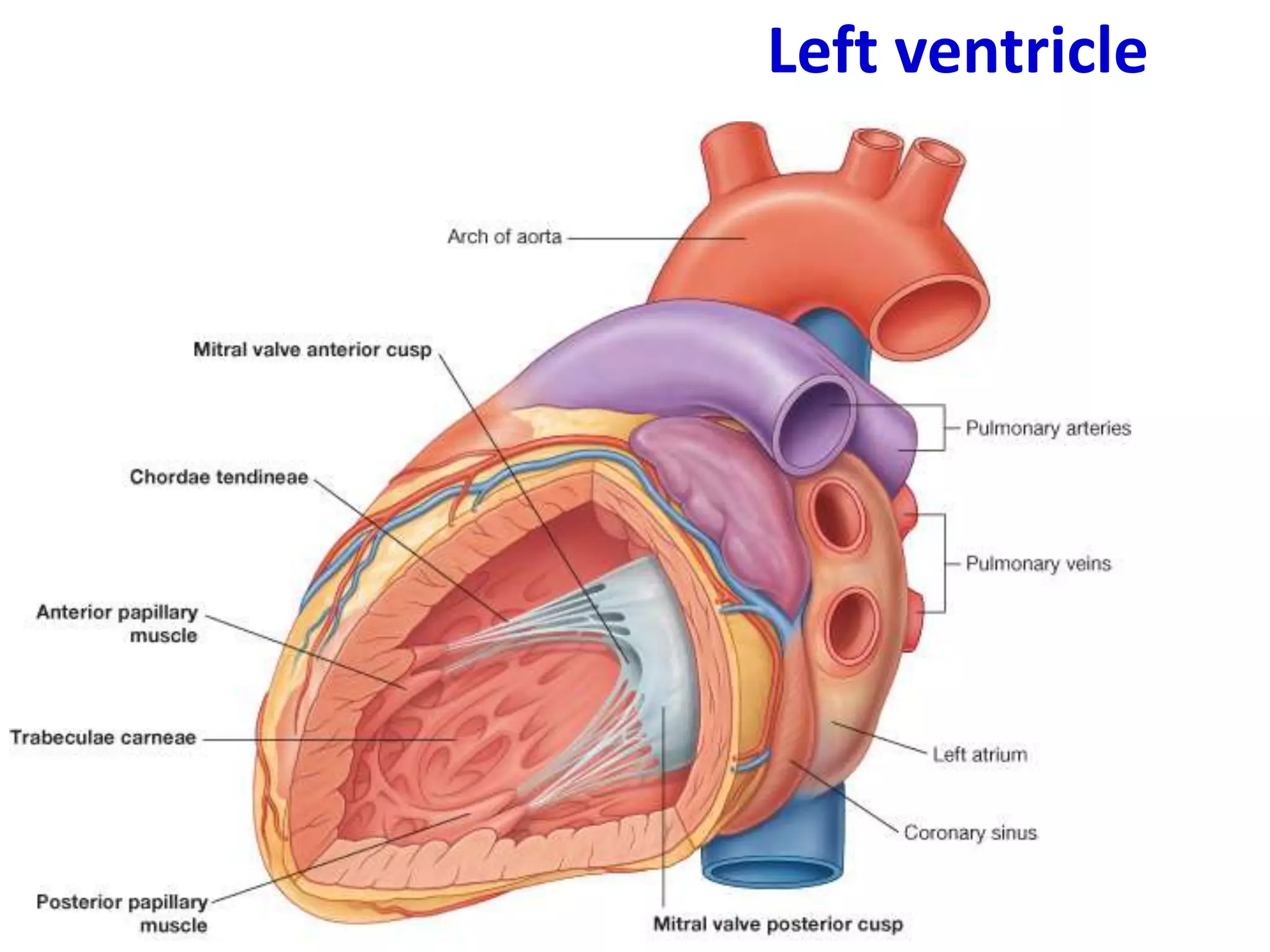
This document provides an overview of the anatomy of the heart, including descriptions of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, valves, conducting system, and blood supply. Key points include that the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the superior and inferior vena cava and pumps to the right ventricle. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the four pulmonary veins and pumps to the left ventricle. The right ventricle pumps to the pulmonary trunk while the left ventricle pumps to the aorta. Semilunar valves are located at the pulmonary trunk and aorta while atrioventricular valves are located between the atria and