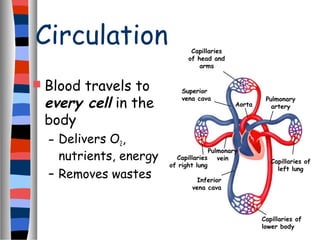
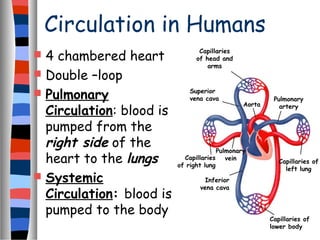
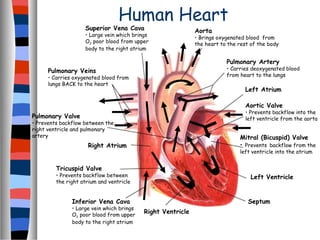
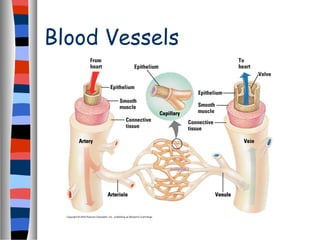
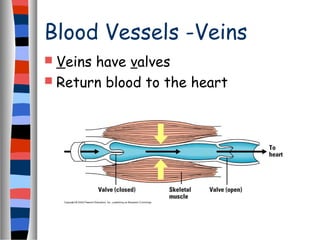
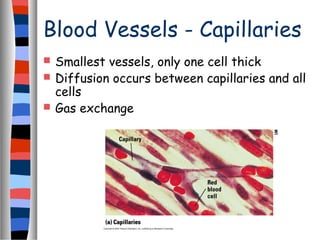
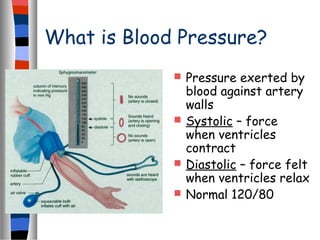
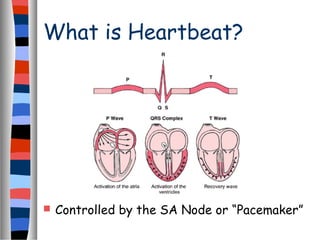
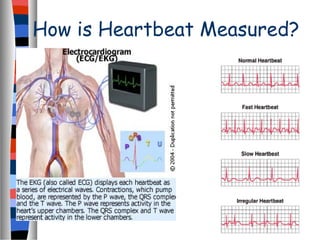
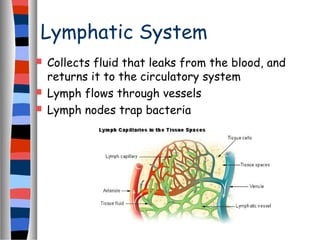
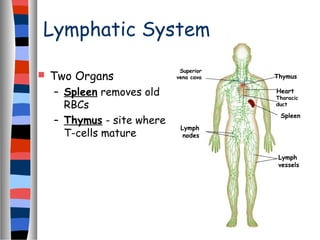
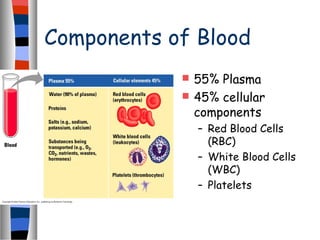
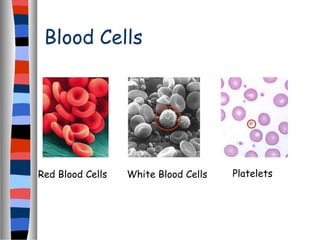
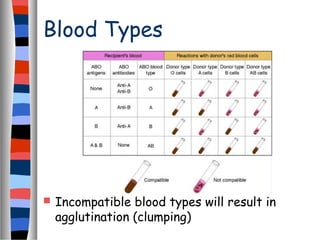
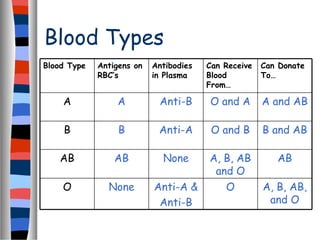
The circulatory system delivers oxygen, nutrients, and energy to cells throughout the body and removes wastes. Blood is pumped from the heart through arteries, capillaries, and veins in two circuits - pulmonary circulation to the lungs and systemic circulation to the body. The heart has four chambers and valves that ensure blood flows in one direction. Blood vessels include arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood pressure, heartbeat, and blood components like red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma are also discussed.