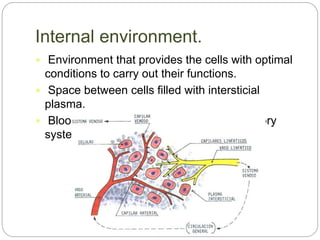
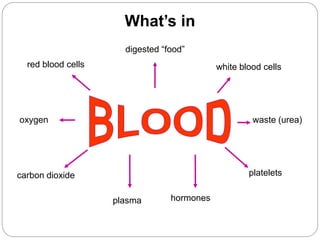
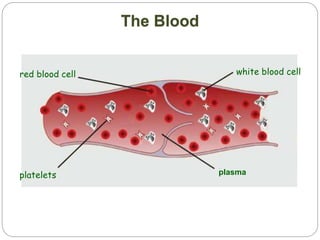
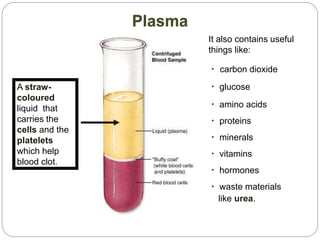
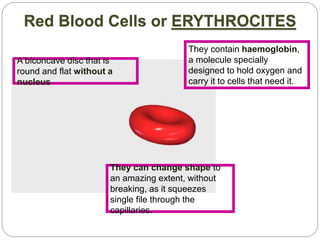
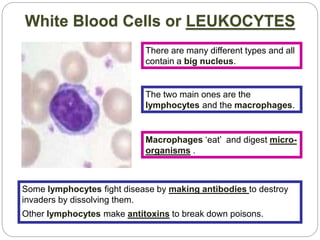
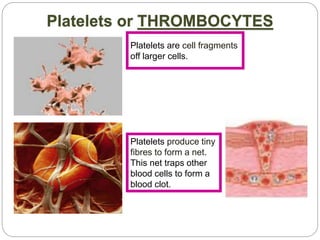
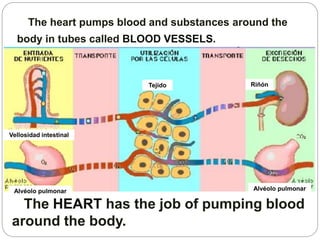
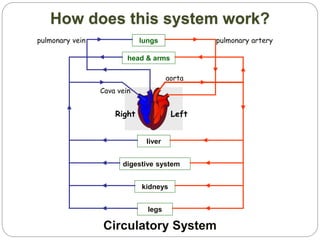
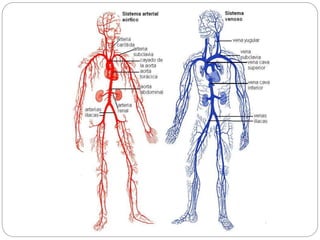
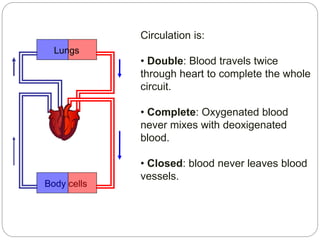
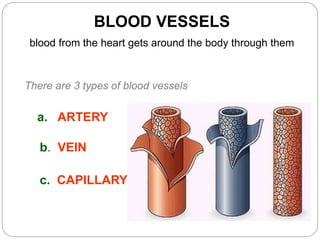
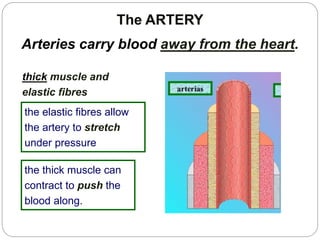
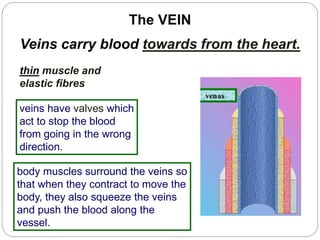
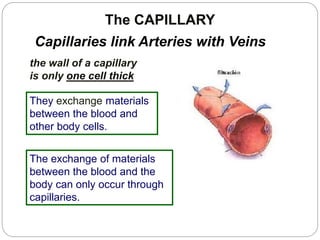
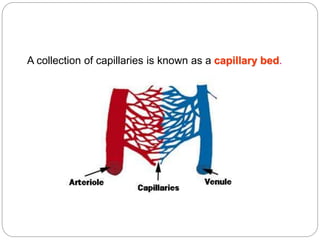
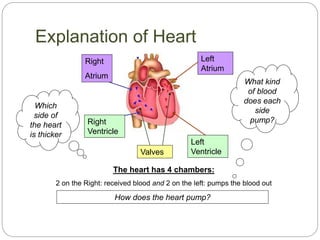
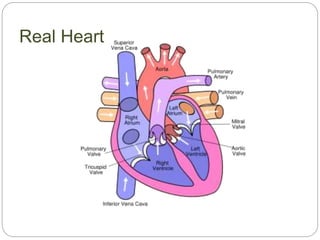
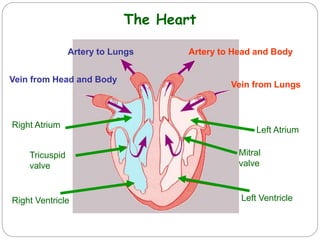
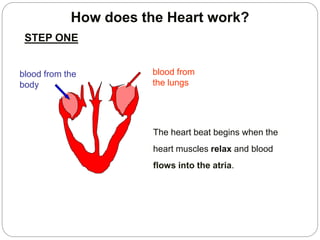
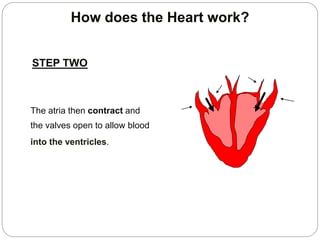
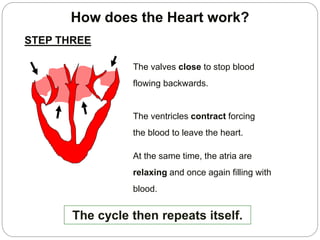
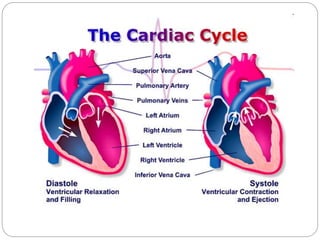
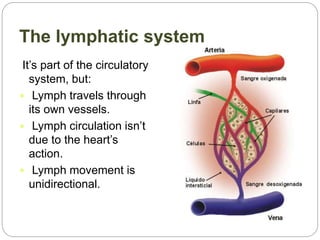
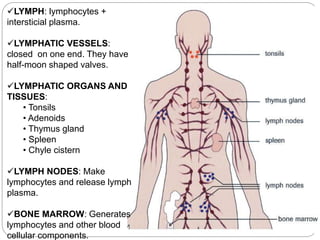
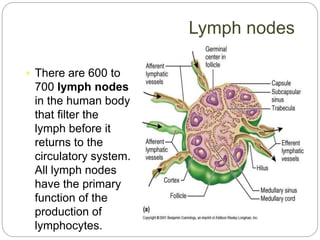
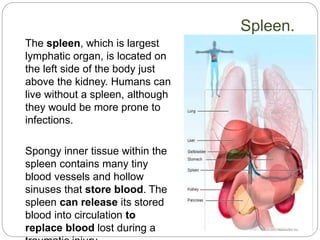
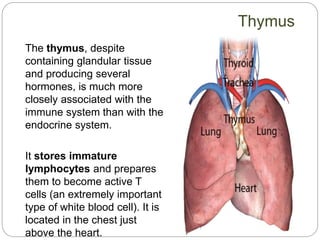
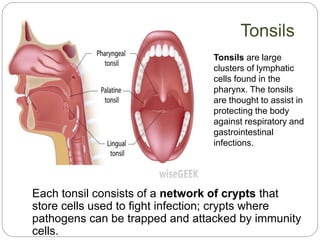
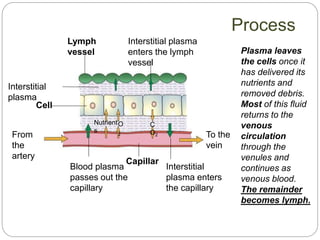
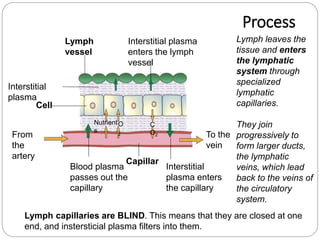
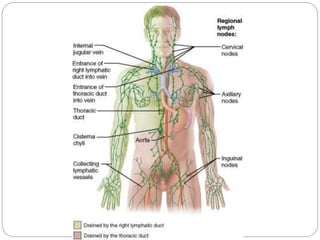
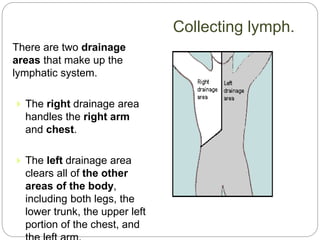
The circulatory and lymphatic systems work together to transport nutrients, oxygen, hormones, carbon dioxide, and waste throughout the body. The circulatory system is composed of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood is pumped from the heart through arteries and returns via veins, exchanging materials with tissues through capillaries. The lymphatic system drains excess fluid from tissues, transports it via lymph vessels, and returns it to the blood. Together these systems maintain homeostasis by circulating nutrients, gases, hormones, and waste products to and from cells, while also fighting pathogens and regulating fluid balance.