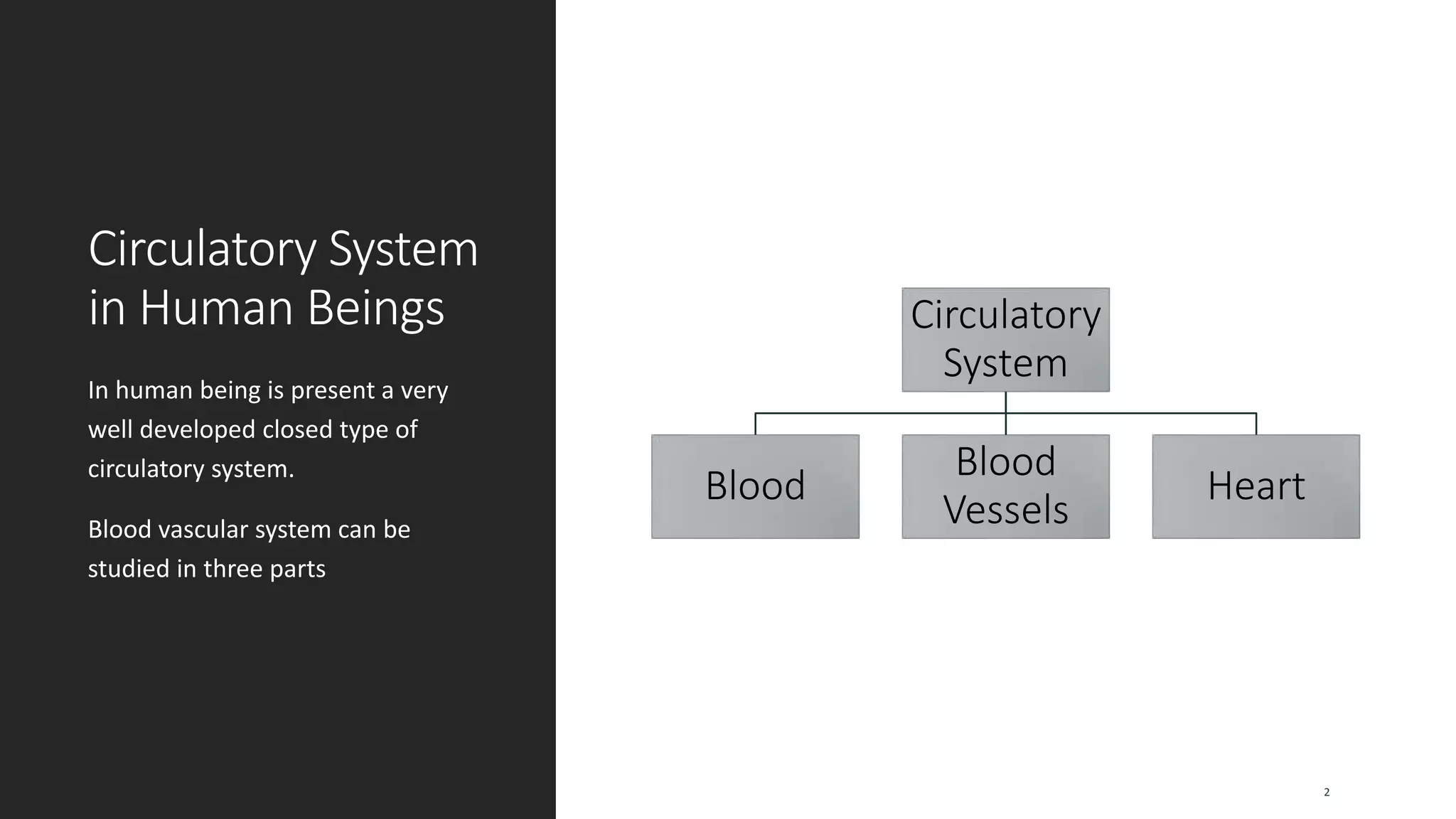
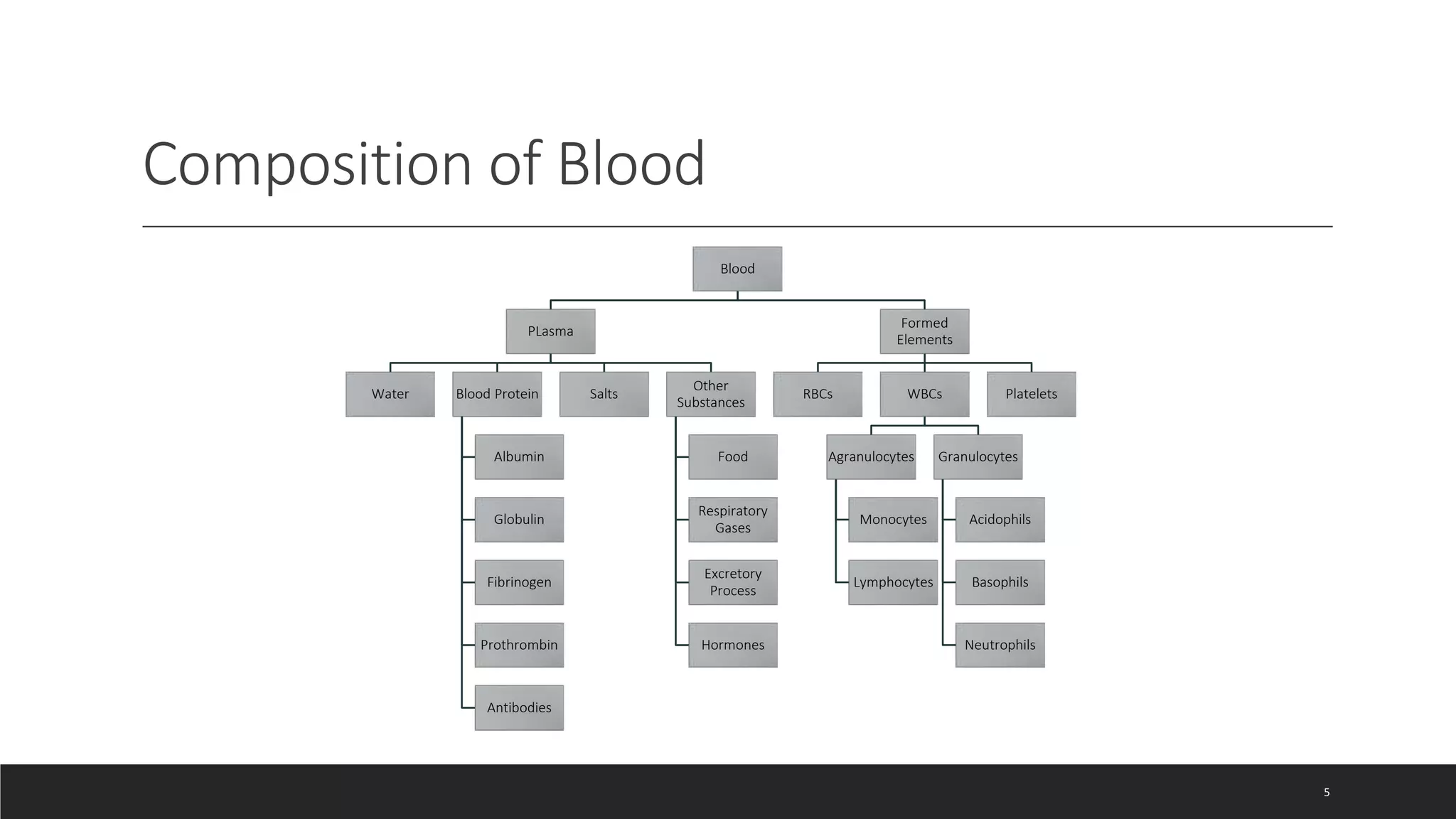
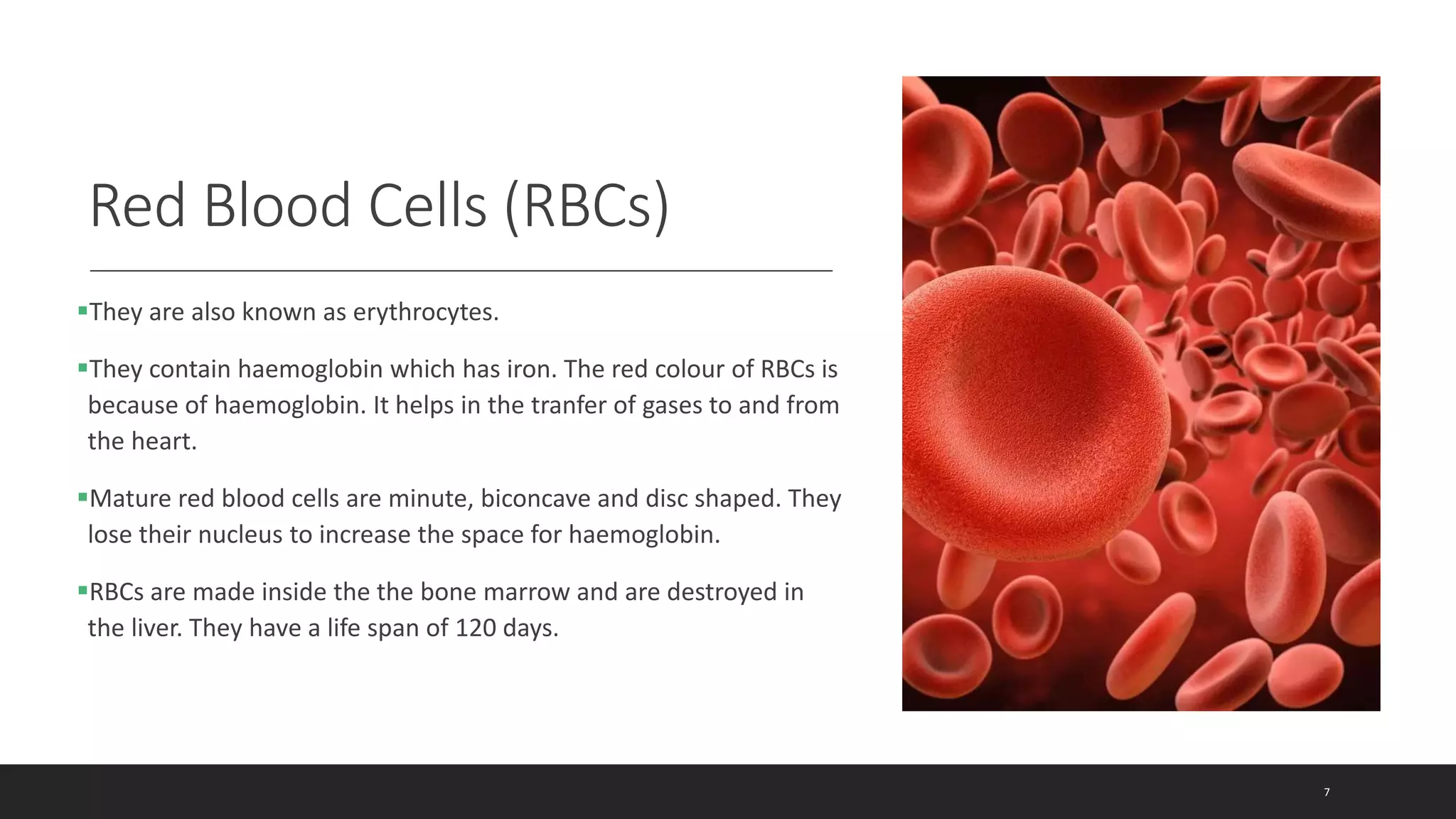
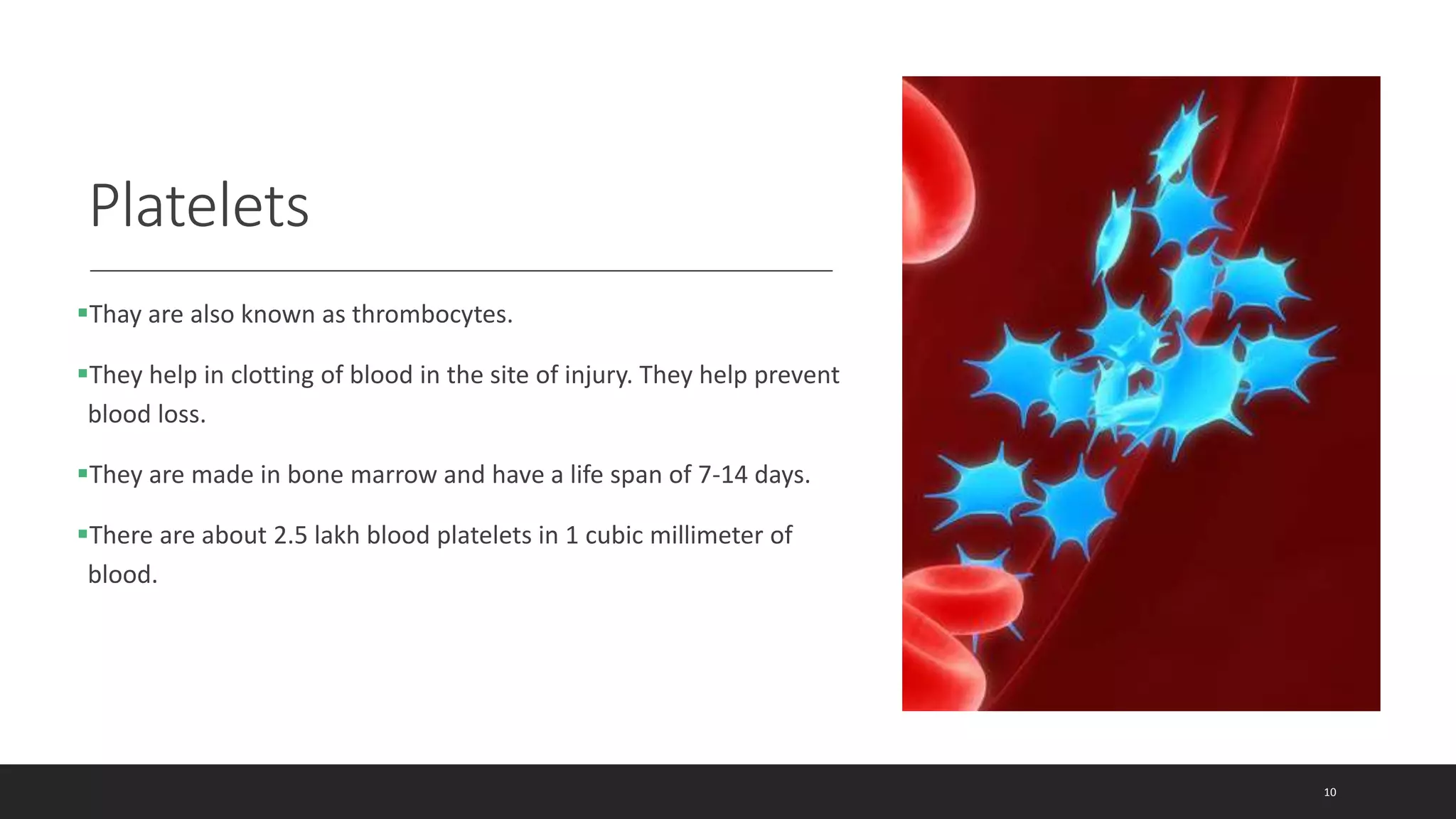
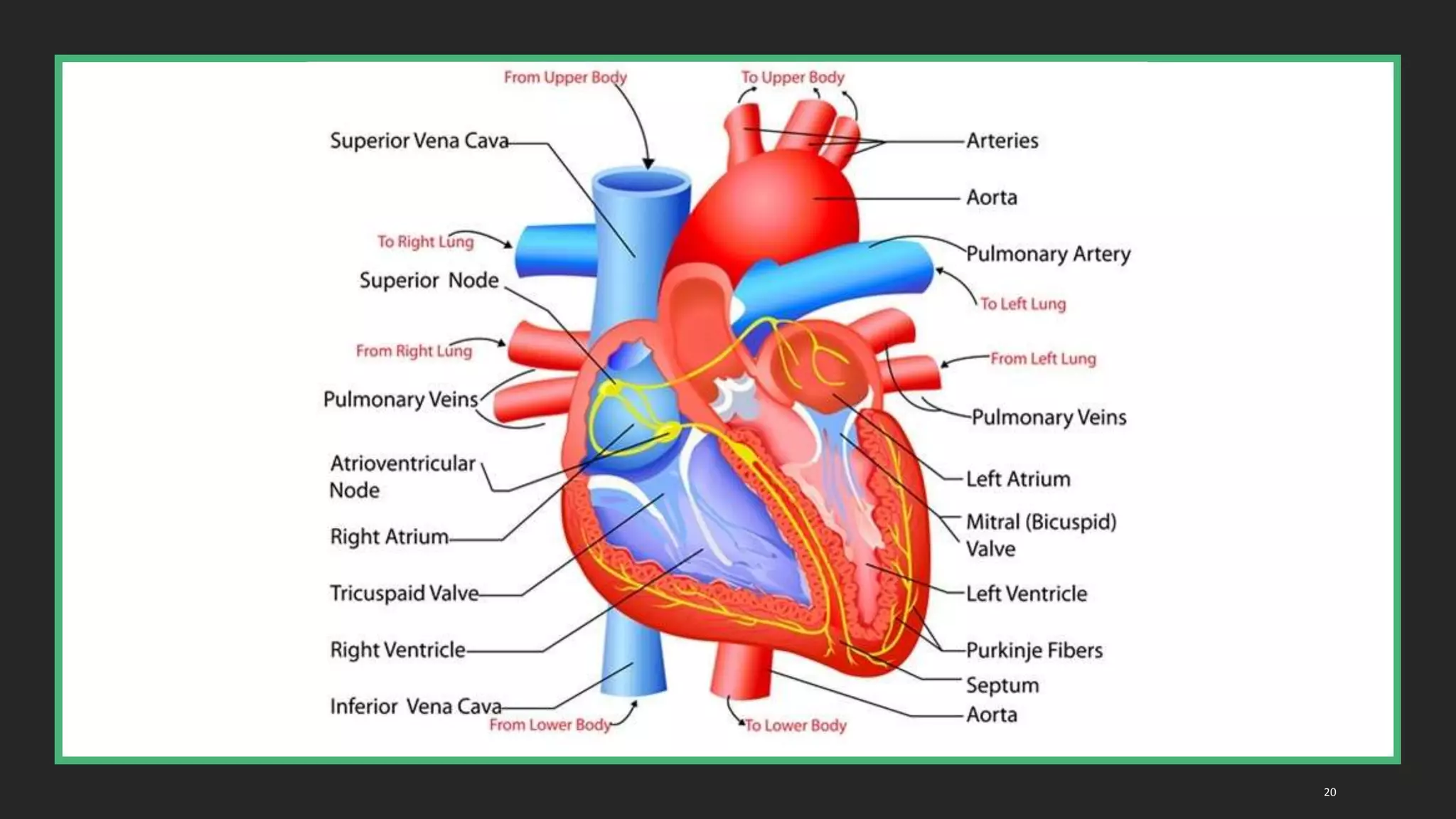
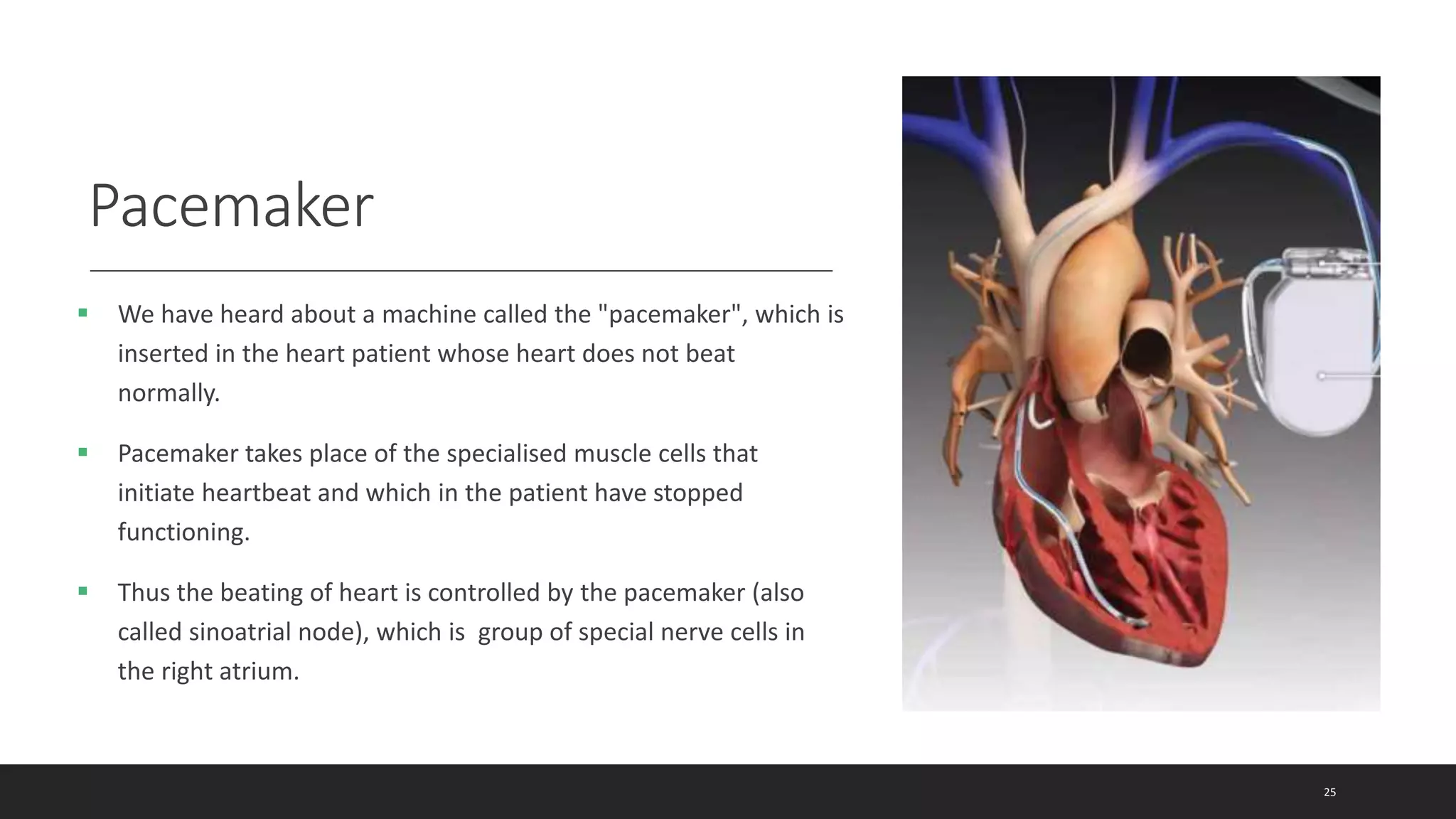
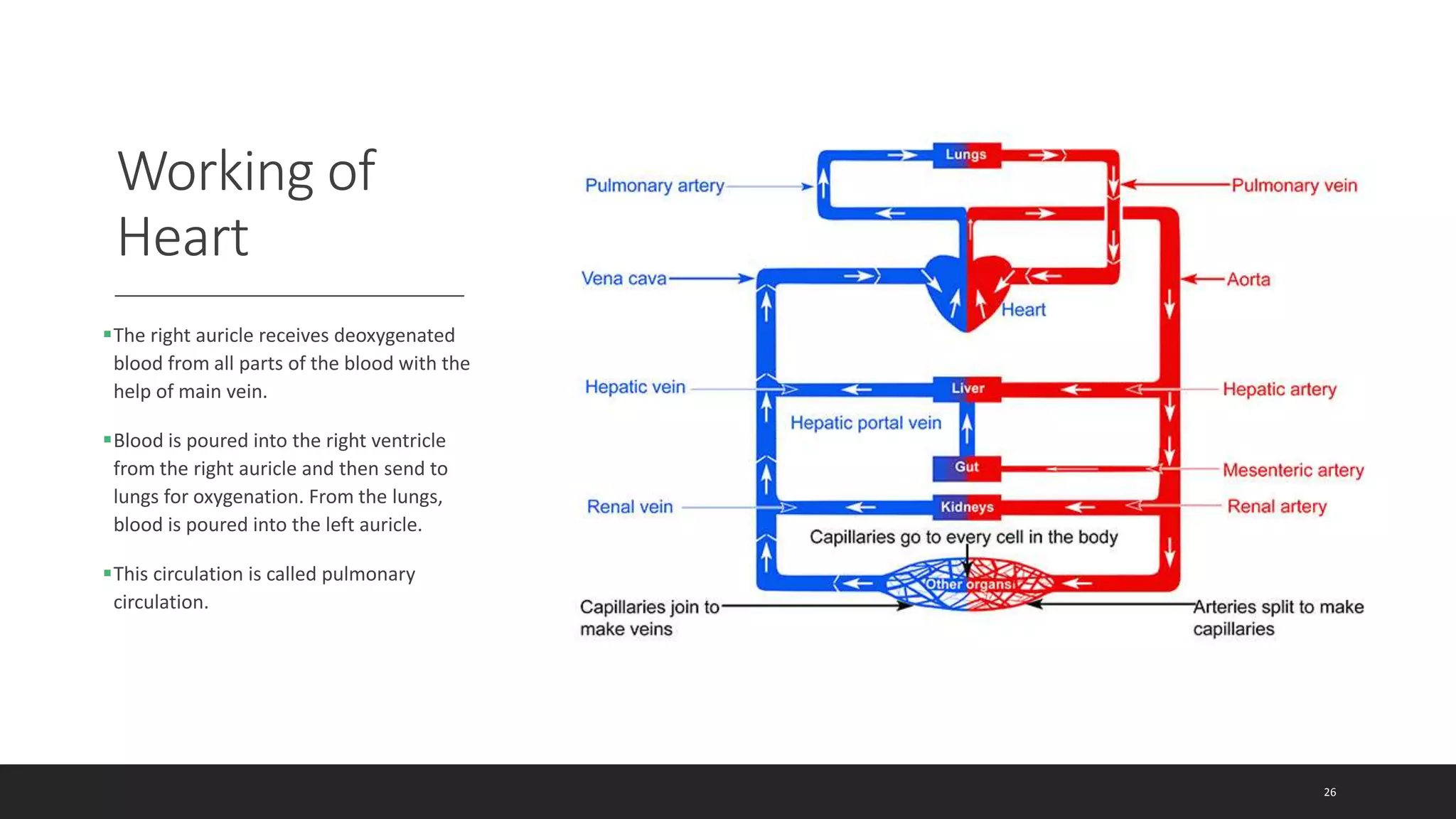
The circulatory system document summarizes the key components of the human circulatory system in 3 parts: blood, blood vessels, and heart. It describes how blood consists of plasma and formed elements like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It outlines the types of blood vessels - arteries, veins, and capillaries. Finally, it provides details on the structure and function of the heart, including the 4 chambers, valves, heartbeat, and how blood is pumped through pulmonary and systemic circulation.