Embed presentation
Download to read offline

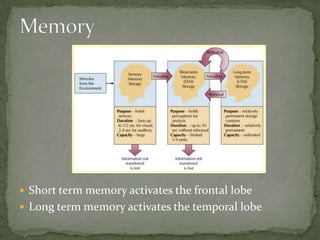
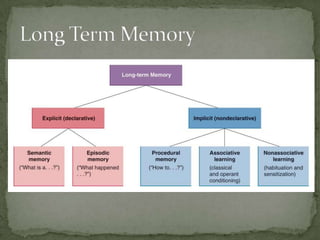
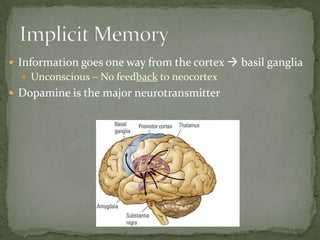
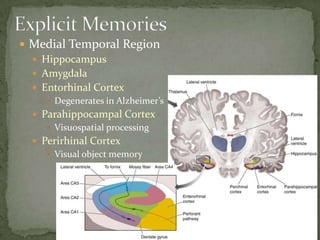

Short term memory activates the frontal lobe while long term memory activates the temporal lobe. Information flows one way from the cortex to the basal ganglia in an unconscious process without feedback to the neocortex, and dopamine is the major neurotransmitter. The medial temporal region including the hippocampus, amygdala, and entorhinal cortex are involved in memory, with the hippocampus specifically involved in spatial memory and the formation of mental maps.






