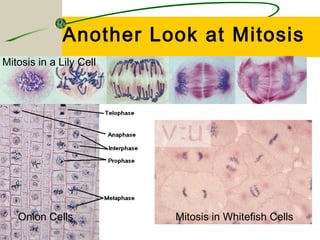
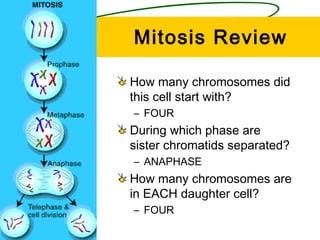
The document summarizes the cell cycle and the process of mitosis. [1] It describes the four phases of the cell cycle - G1, S, G2, and M phase. [2] It then explains the key stages of mitosis - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase - where chromosomes condense and duplicate, align, separate, and the nuclear envelope reforms. [3] It compares mitosis in plant and animal cells, noting that plant cells form a cell plate while animal cells pinch at a cleavage furrow.