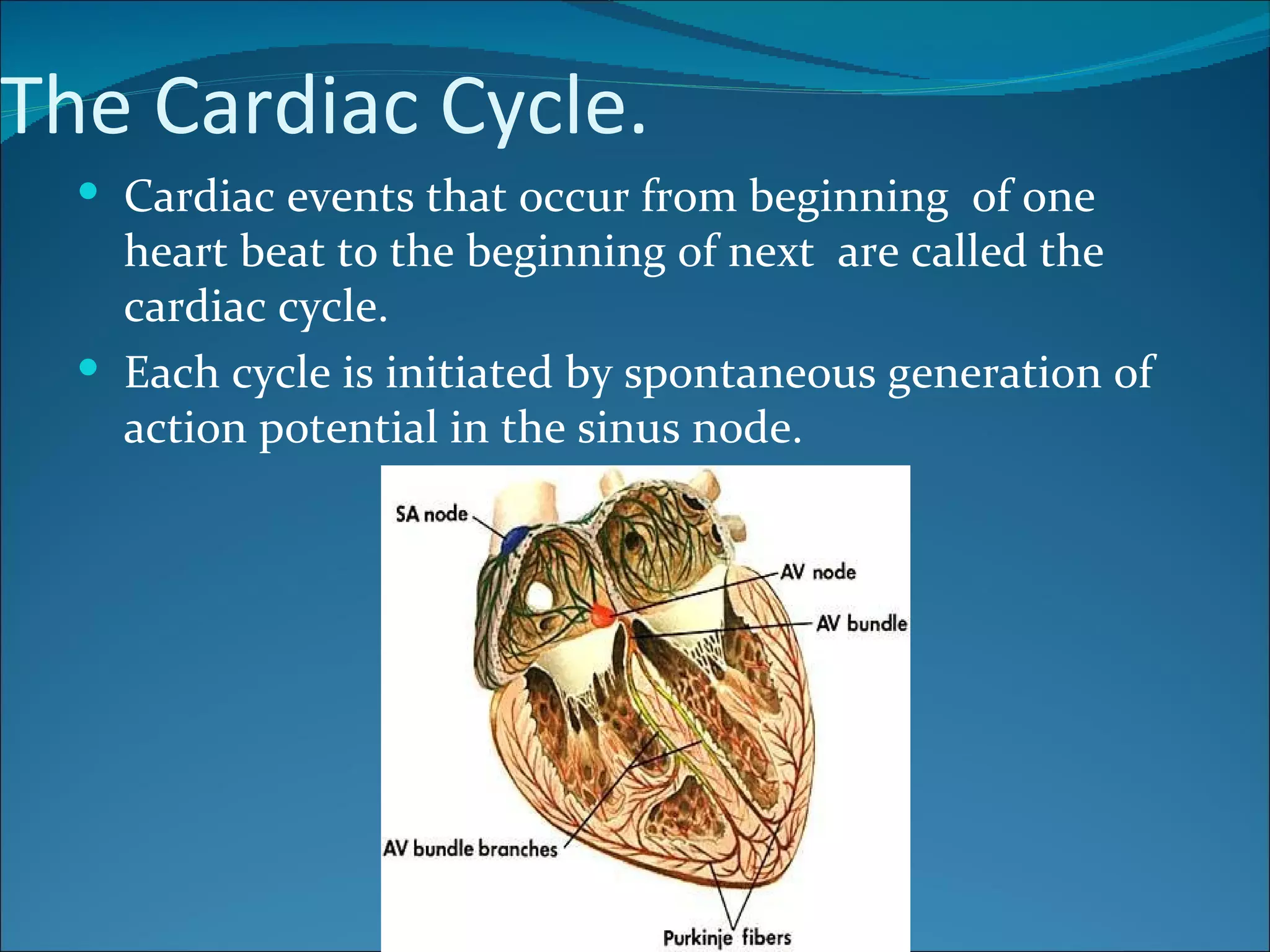
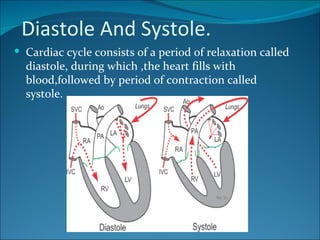
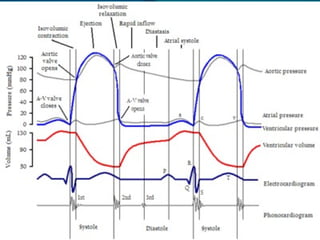
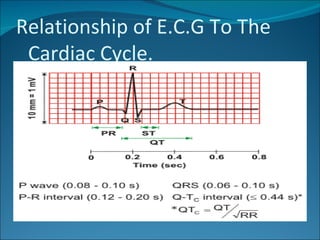
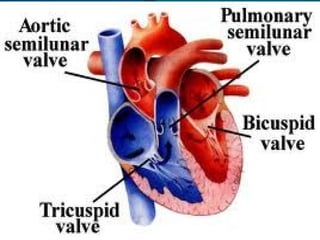
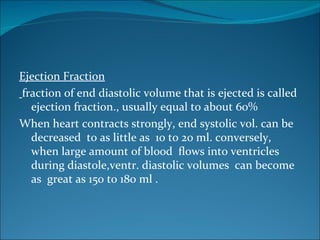
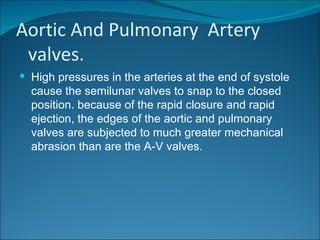
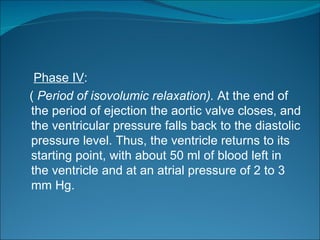
The cardiac cycle consists of relaxation (diastole) and contraction (systole) of the heart. Each cycle begins with an electrical impulse from the sinus node which causes atrial contraction and is recorded as the P wave on an ECG. Contraction of the ventricles follows, recorded as the QRS complex, pumping blood into the arteries. Ventricular relaxation is recorded as the T wave. The heart's pumping is regulated intrinsically via the Frank-Starling mechanism and extrinsically by the autonomic nervous system.