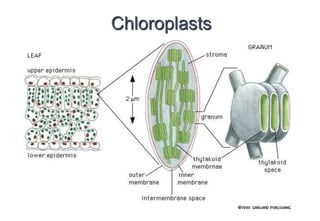
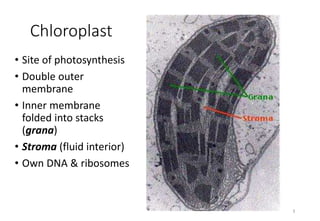
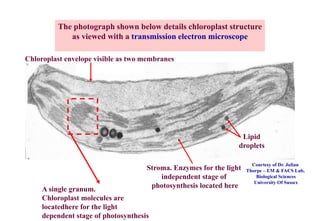
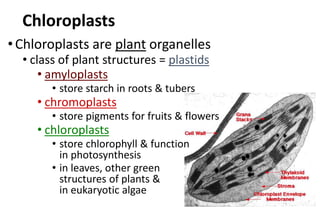
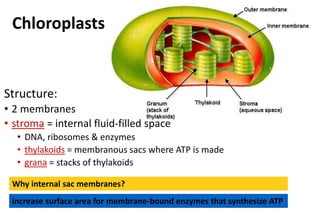
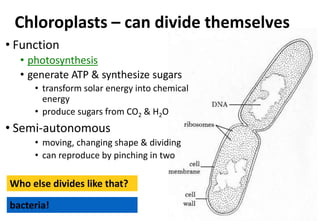
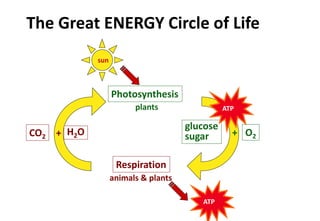
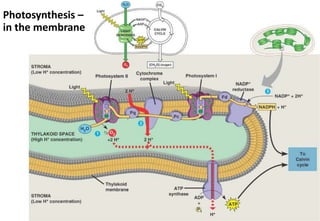
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that contain chlorophyll, which allows them to carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts have an inner and outer membrane, as well as internal structures called thylakoids that are stacked to form grana. Within the chloroplast is the stroma, which contains enzymes and DNA, allowing the chloroplast to divide itself. Chloroplasts are able to convert sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis.