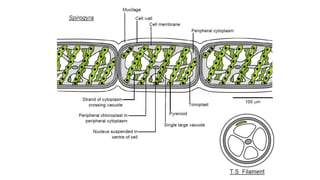
Spirogyra is a genus of filamentous green algae that is commonly found in freshwater habitats around the world. It has a fiber-like structure called a thallus that is made of individual tubular cells arranged end to end. Each cell contains chloroplasts and performs photosynthesis. Spirogyra reproduces both asexually through fragmentation of filaments and sexually through the conjugation of filaments to form zygospores. During conjugation, specialized structures called papillae form on adjacent cells and allow the transfer of cytoplasm between them, resulting in fertilization and the formation of a zygote. The zygote then develops a thick protective coating and can remain dormant for