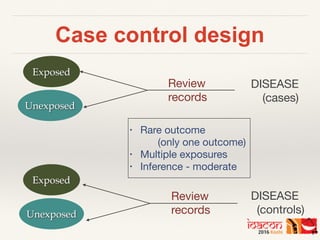
This document discusses key considerations for designing a retrospective study. It explains that retrospective studies analyze existing data collected for other purposes. The document outlines different retrospective study designs including cross-sectional, case-control, and cohort studies. It emphasizes important elements like defining a research question, conducting a literature review, determining sample size and sampling strategy, developing data collection instruments, establishing inclusion/exclusion criteria, ensuring reliability of data abstraction, and piloting the study methodology. Overall, the document provides guidance on setting up a rigorous retrospective study design.