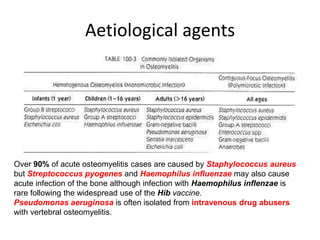
This document discusses osteomyelitis, an infection of bone tissue. It defines osteomyelitis and describes the epidemiology, sources of infection, pathogenesis, clinical features, investigations and treatment of both acute and chronic osteomyelitis. Acute osteomyelitis is usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus spreading via the bloodstream and commonly affects the long bones of children and the vertebrae, feet and pelvis of adults. Investigations include blood tests, imaging like x-rays, CT and MRI, and bone biopsy for culture and sensitivity testing. Treatment involves antibiotics, analgesia, splinting, drainage of pus if needed, and follow up to monitor for recurrence.