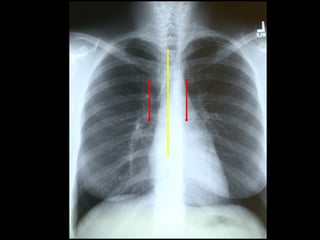
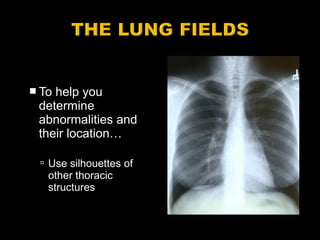
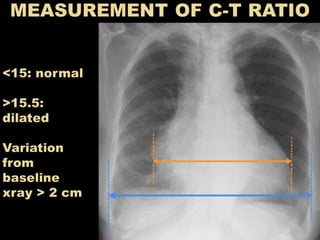
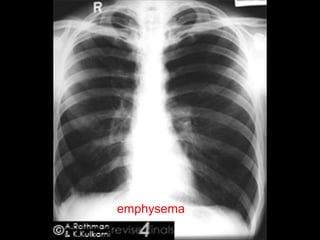
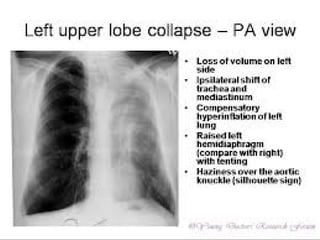
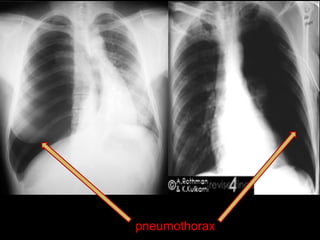
This document provides guidance on interpreting a chest x-ray. It describes how to analyze the lung fields by dividing them into upper, middle and lower zones. It also explains how to examine the heart size and position, bones, diaphragm and other structures. The document emphasizes looking for asymmetries and following a systematic approach to identify any abnormalities and determine their location. It lists common radiographic findings and conditions that may present on a chest x-ray.