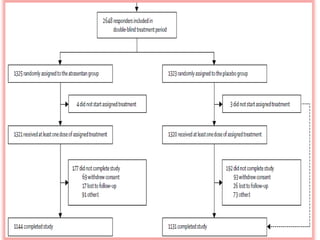
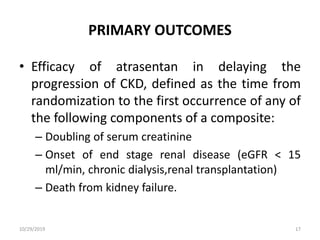
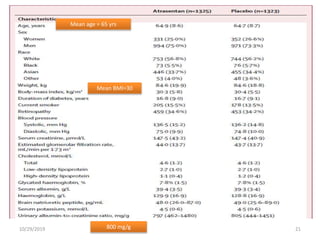
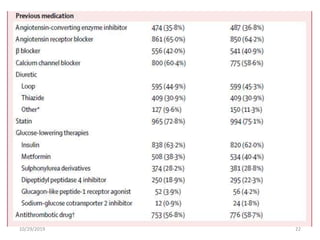
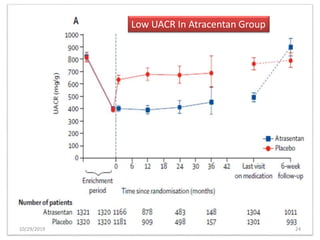
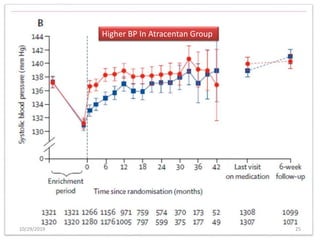
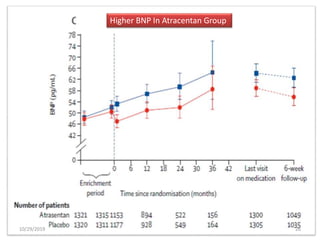
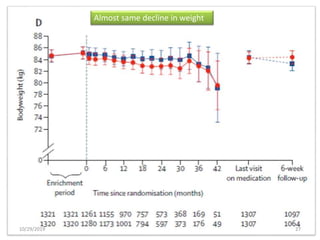
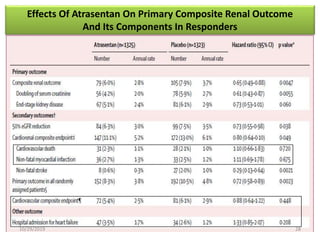
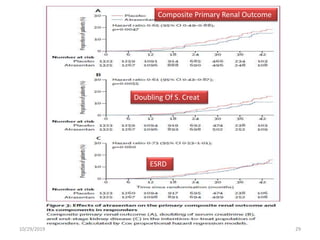
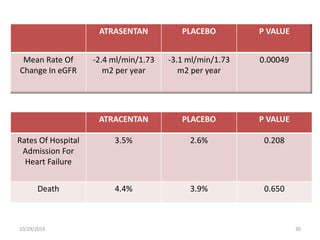
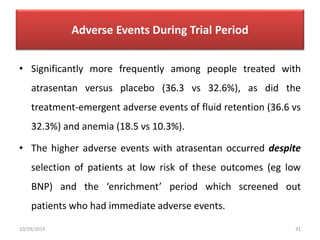
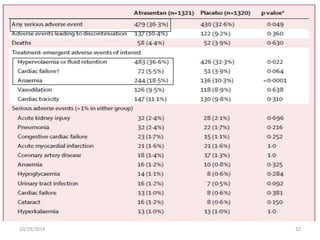
This document summarizes the Study Of Diabetic Nephropathy With AtraSentan (SONAR) trial. The trial aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of the selective endothelin receptor antagonist Atrasentan in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Over 5,000 patients were screened and 2,648 responders were randomly assigned to Atrasentan or placebo. The primary outcome was a composite of doubling of serum creatinine, end stage renal disease, or death from kidney failure. The trial found that Atrasentan reduced the risk of the primary composite renal outcome compared to placebo but was associated with more adverse events like fluid retention and anemia.