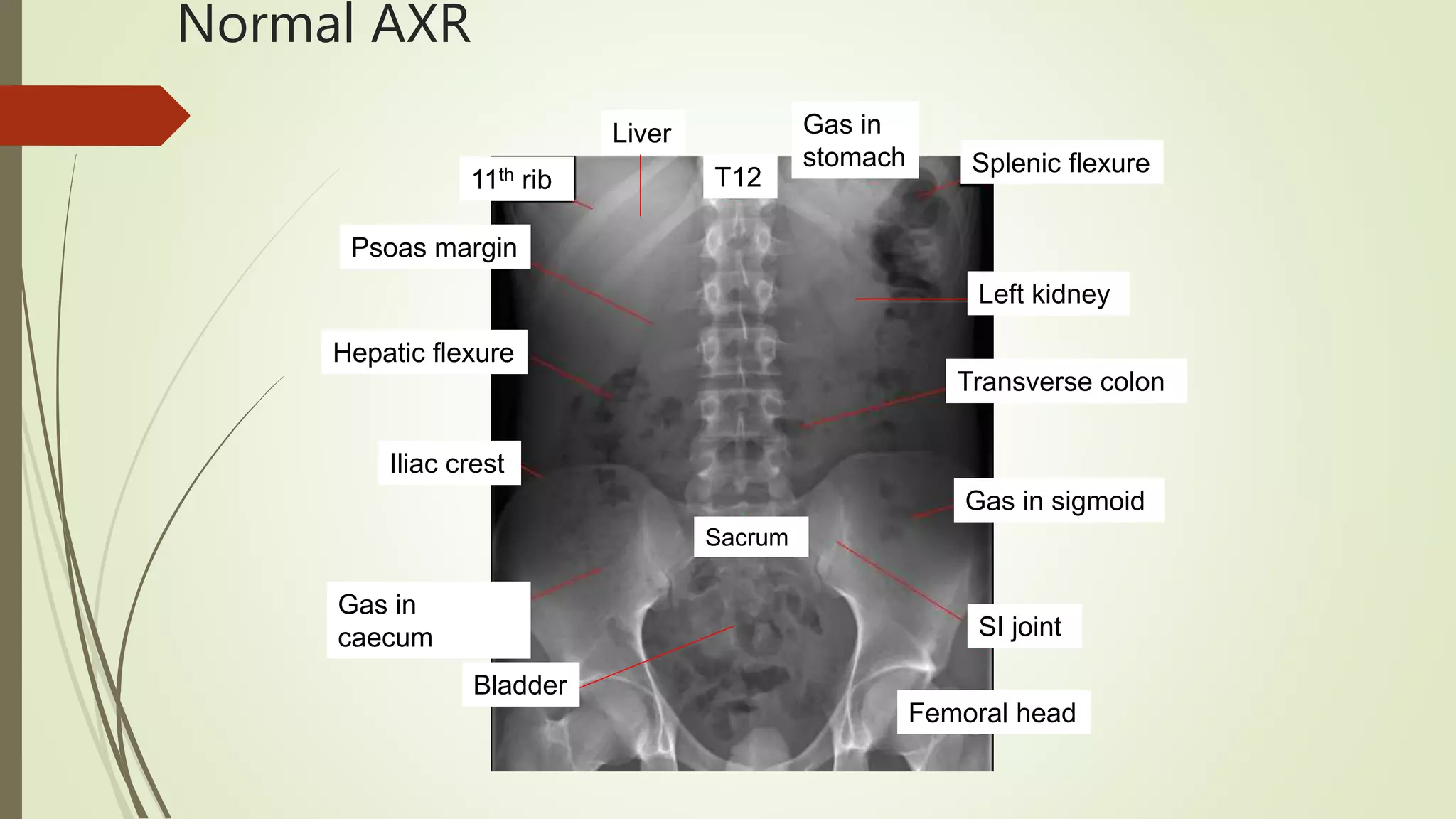
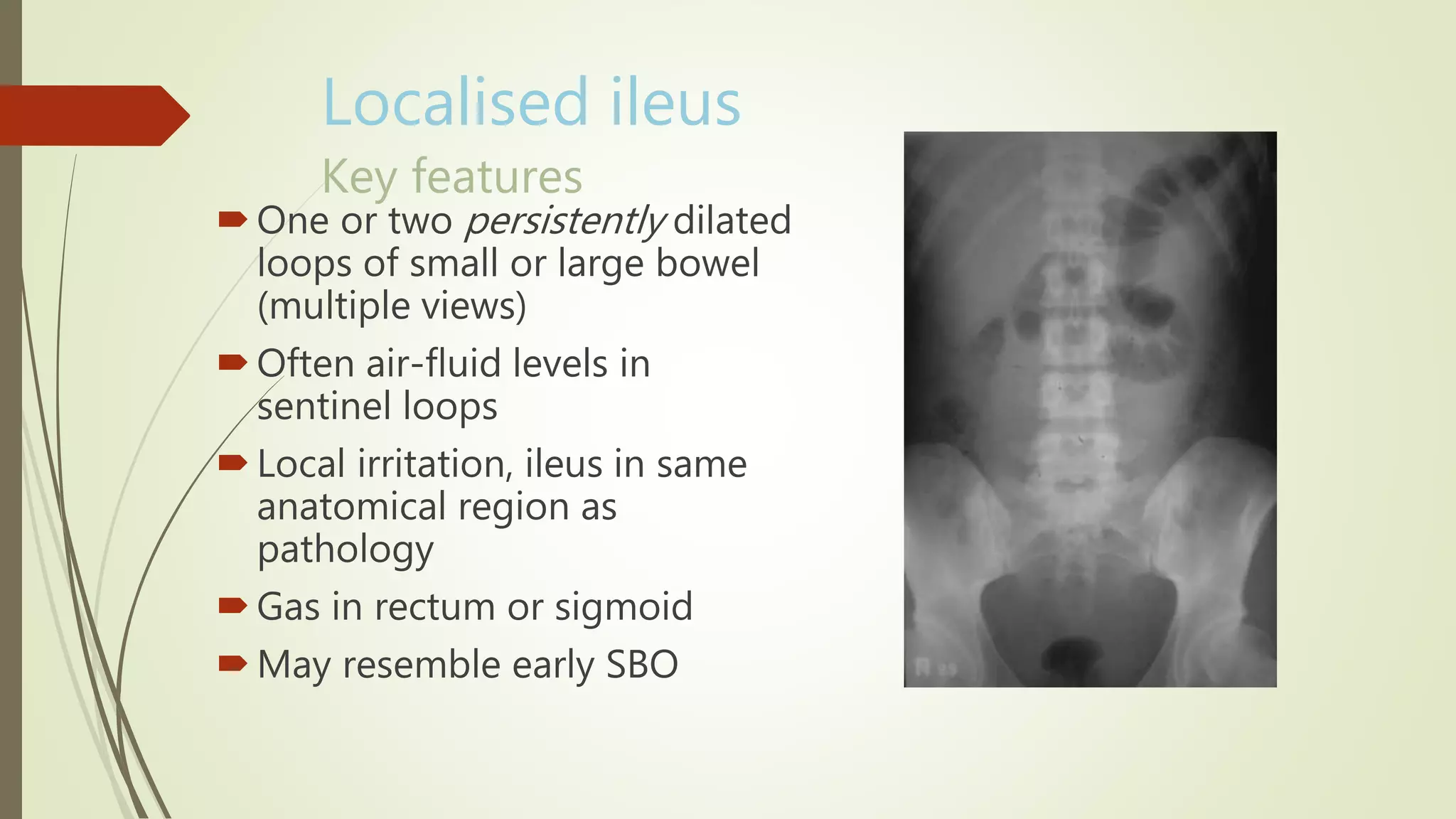
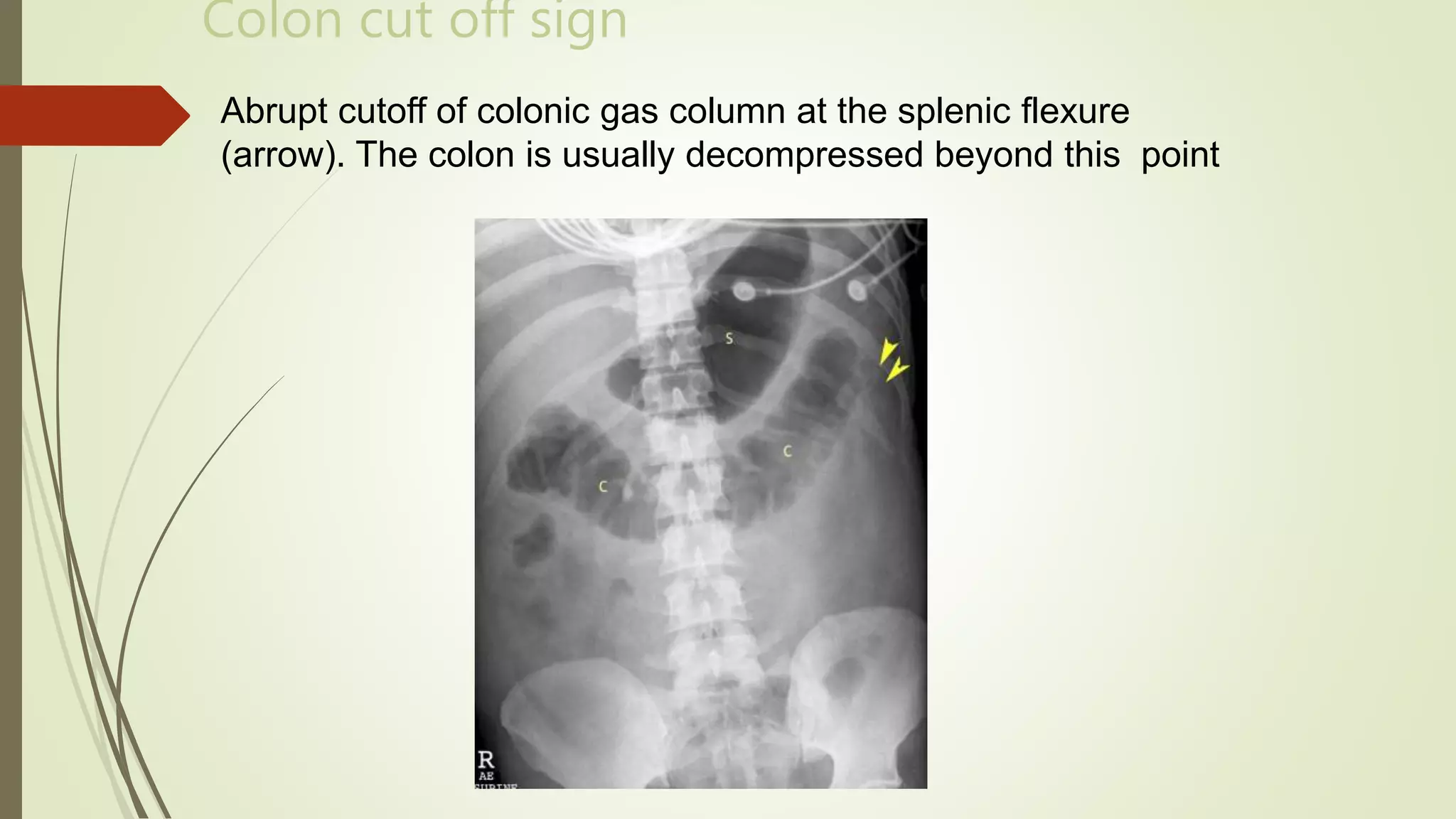
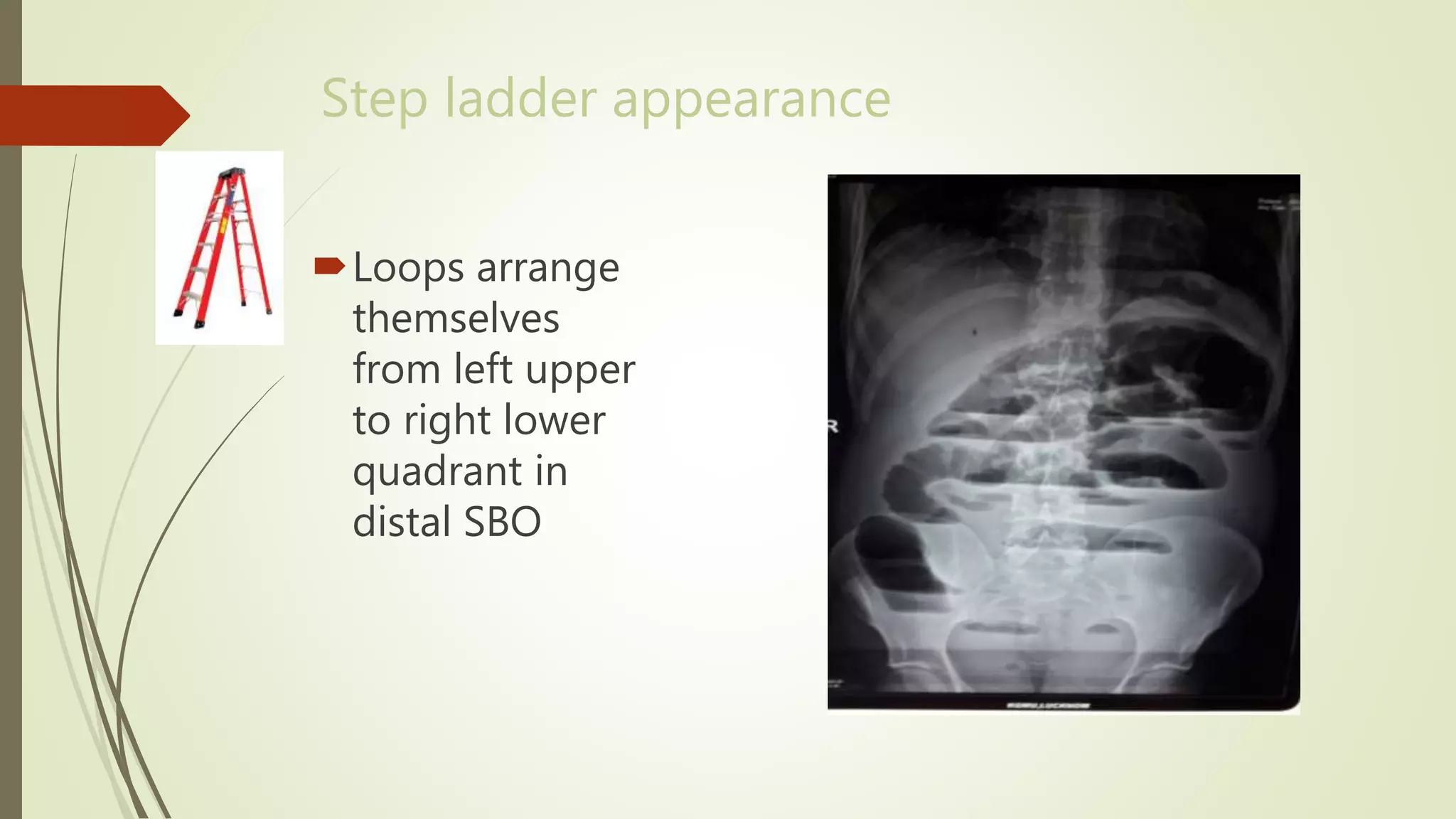
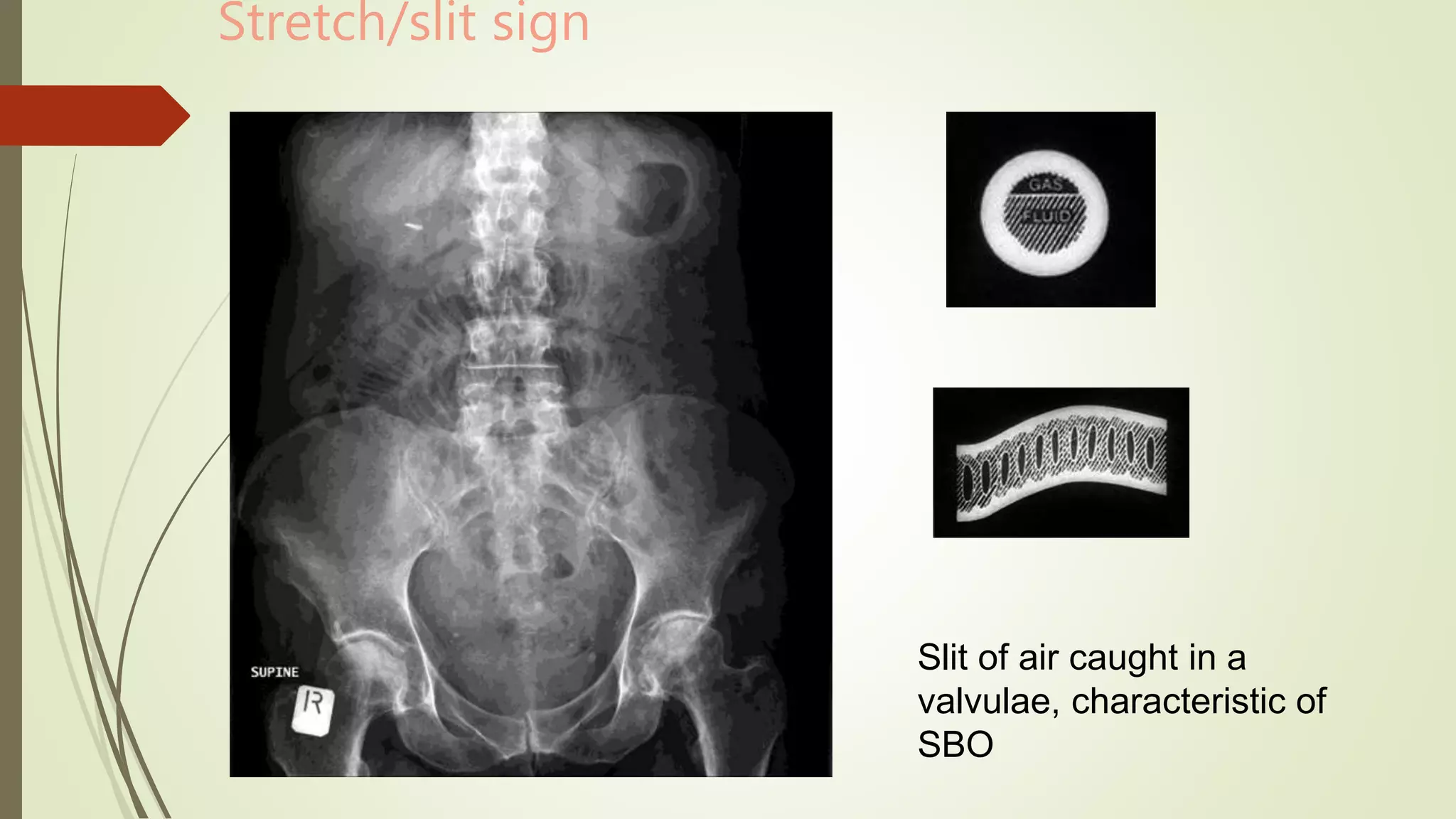
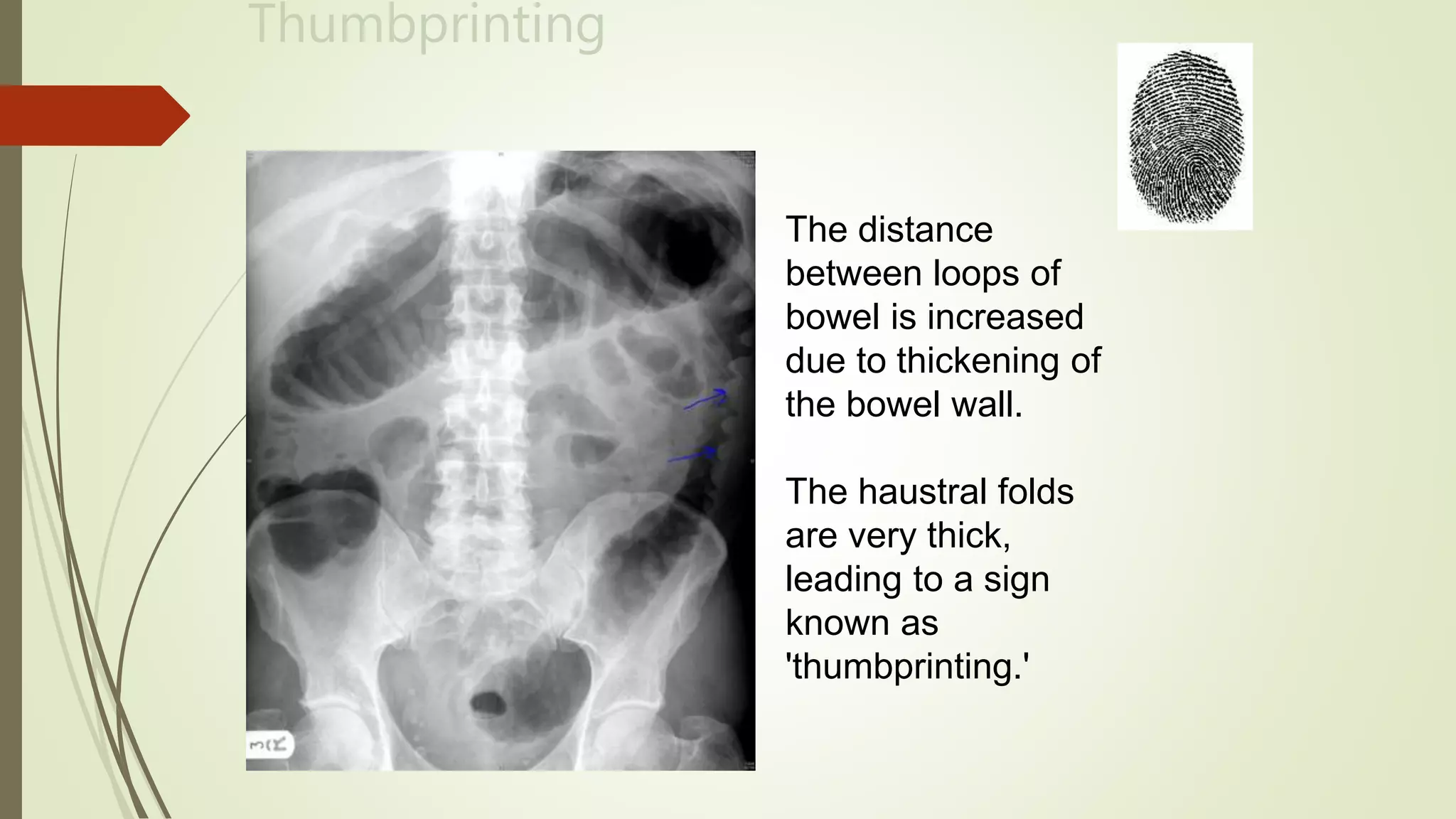
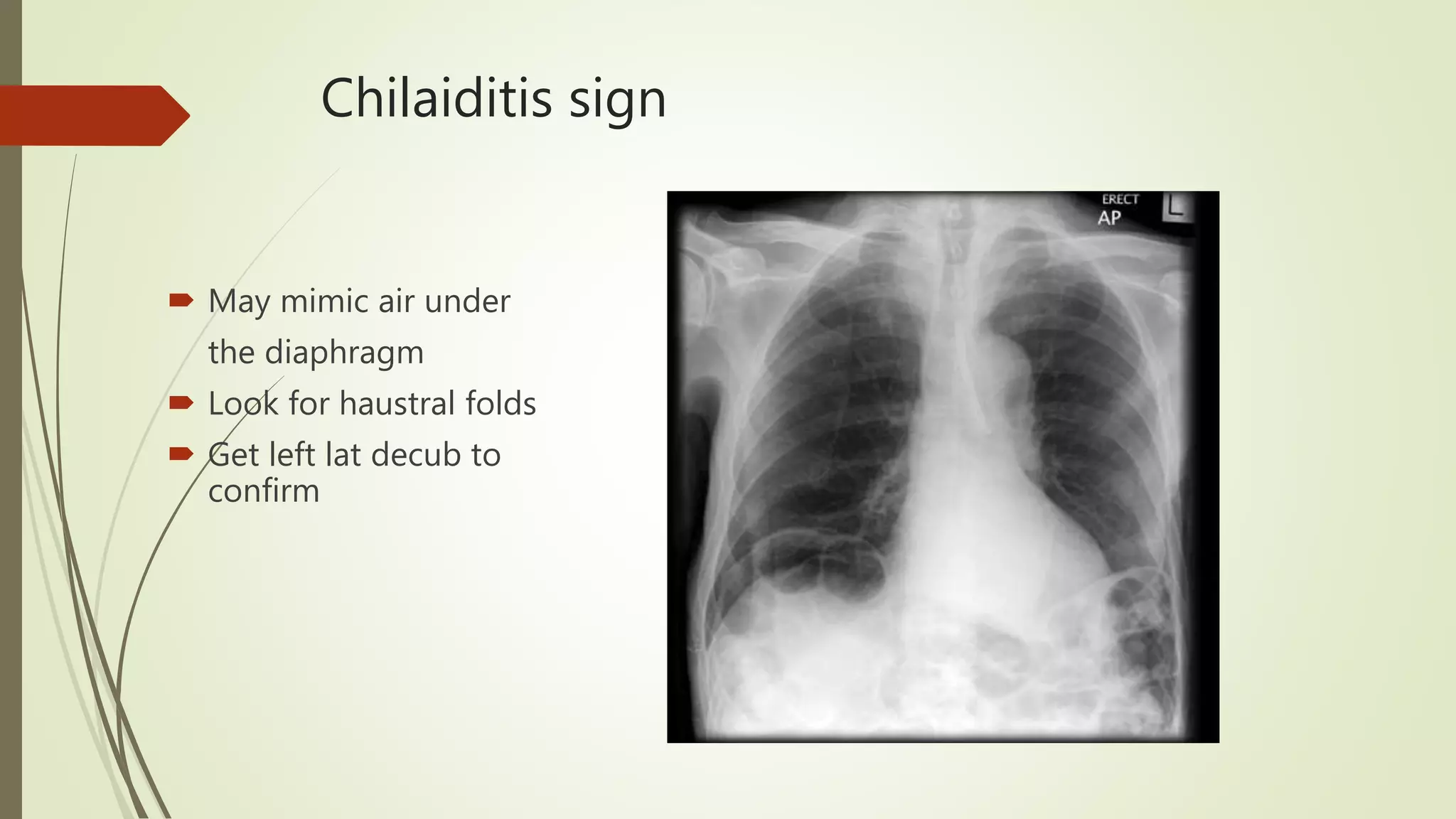
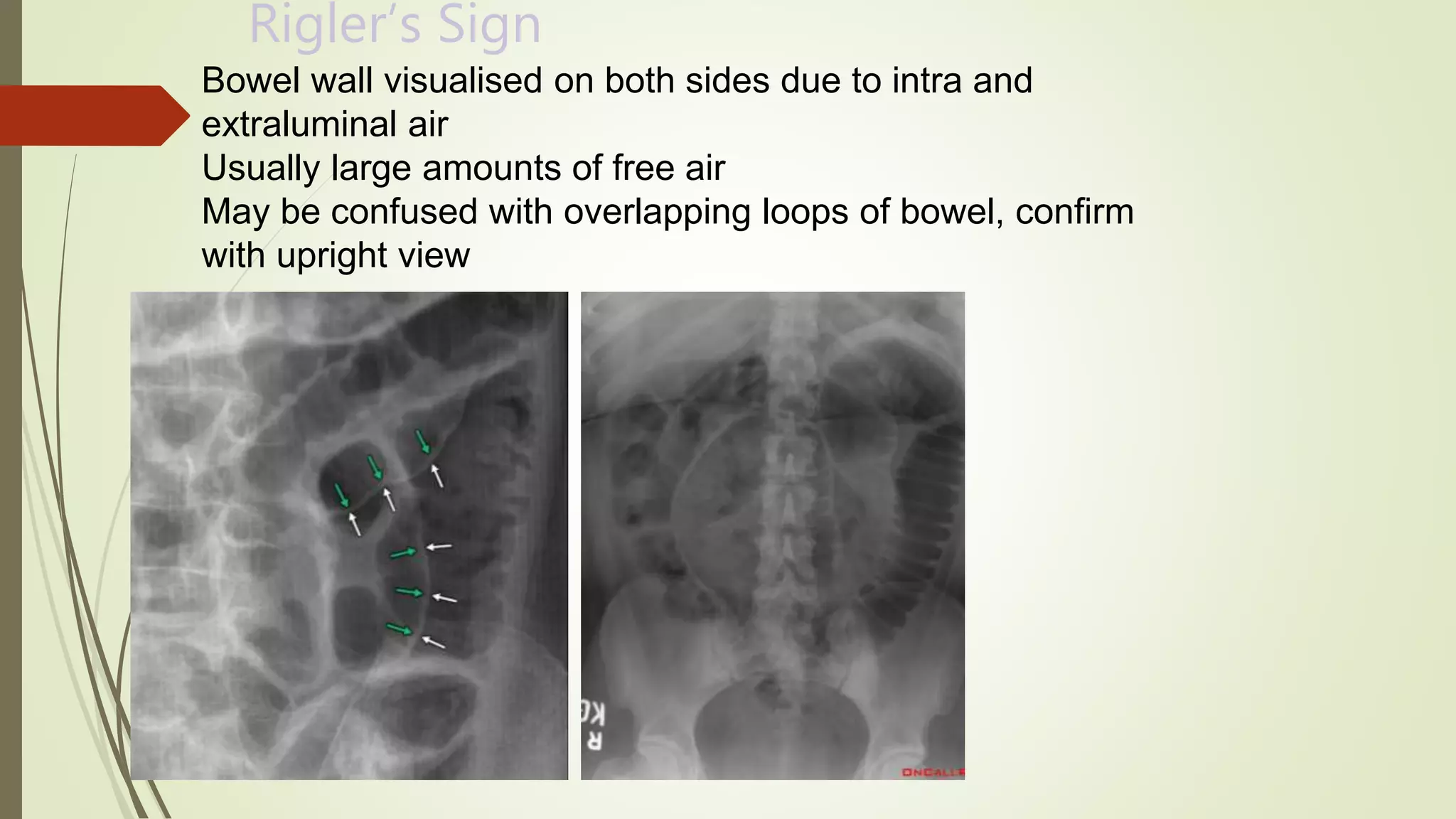
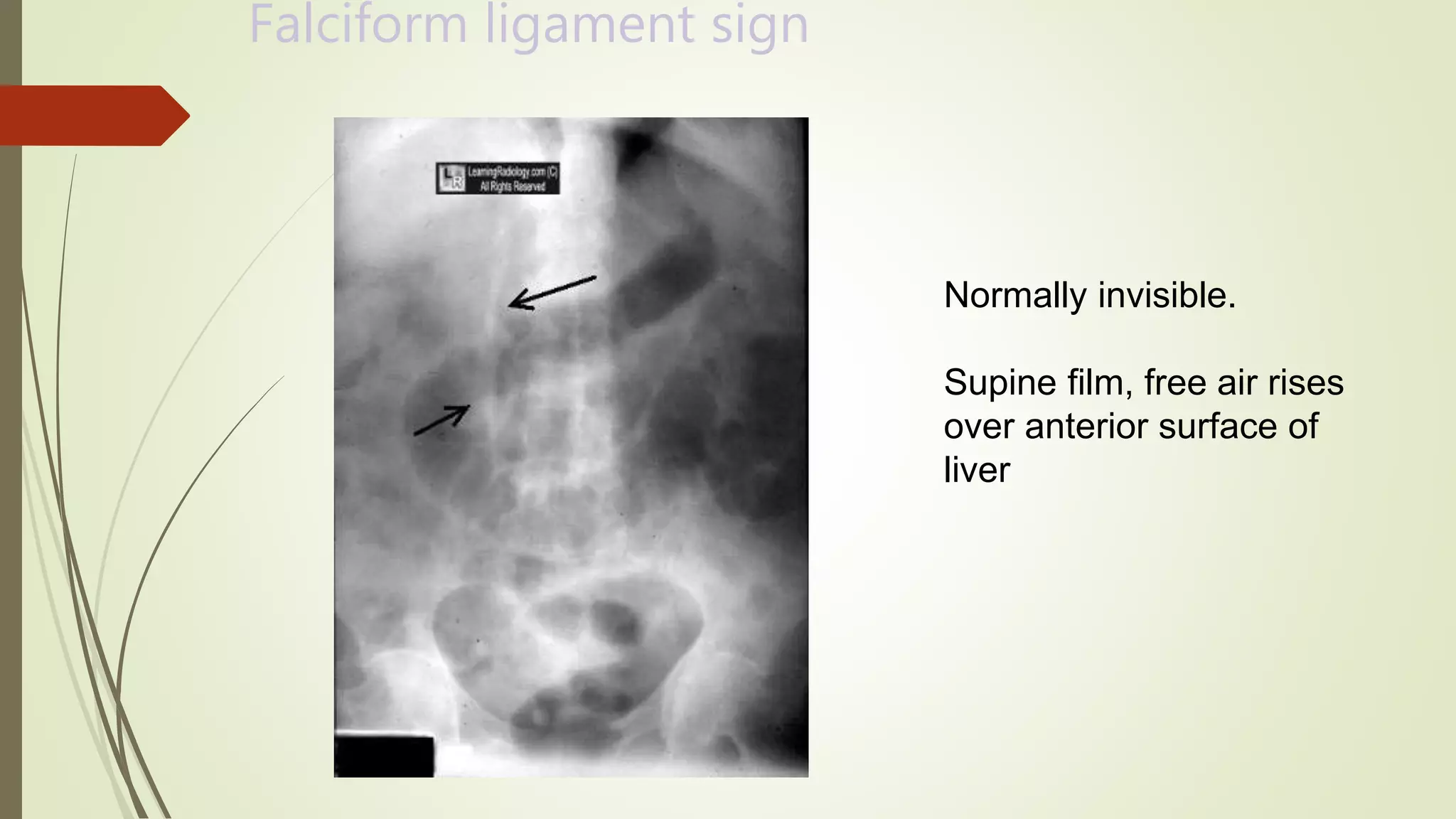
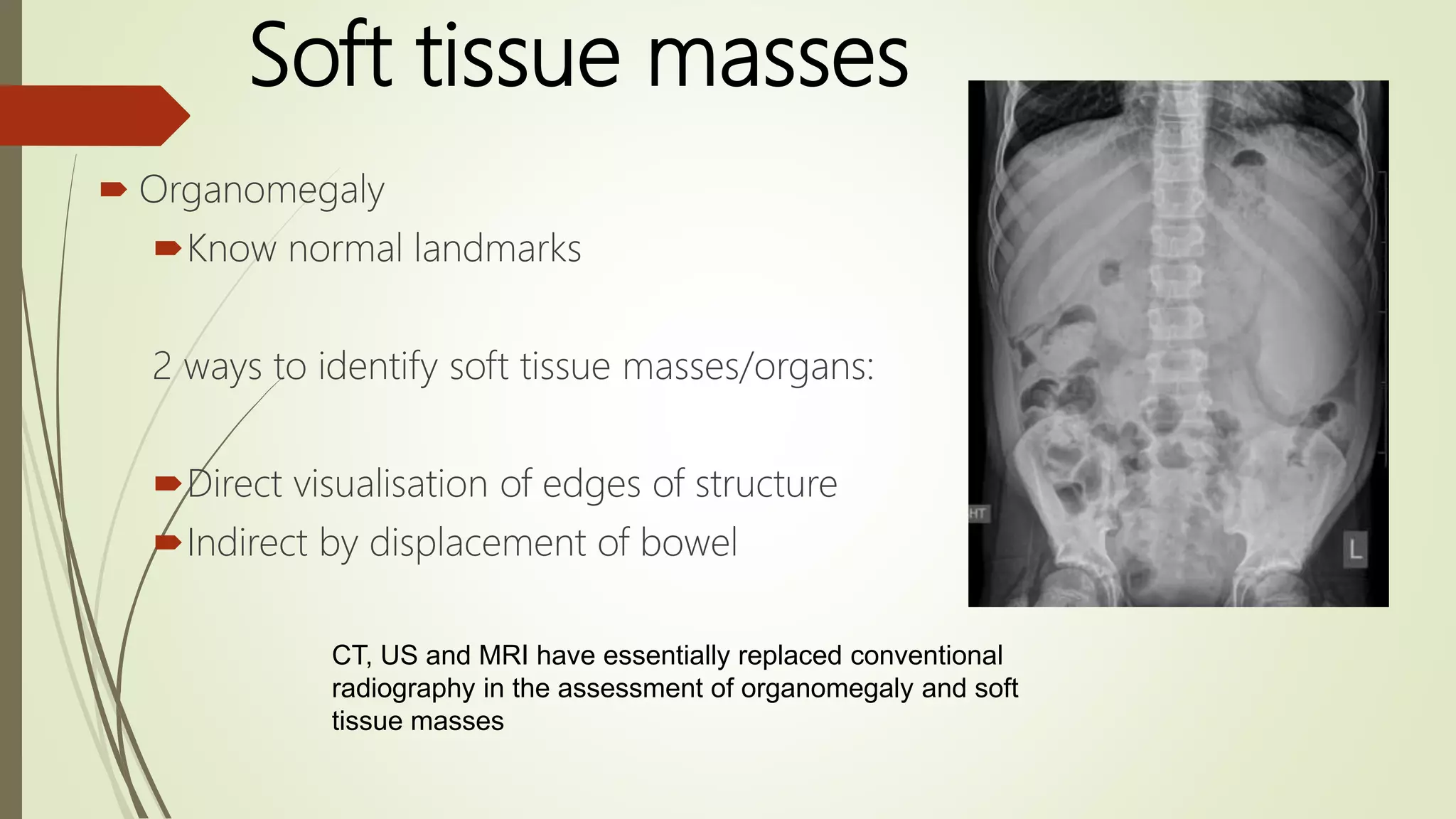
This document discusses the interpretation of abdominal x-rays. It provides information on common clinical indications for abdominal x-rays such as abdominal pain, distention, vomiting, and placement of lines or tubes. It also discusses the radiographic principles including the series of films taken and obtaining different views. Key things to look for on abdominal x-rays are described such as the bowel gas pattern, extraluminal air, soft tissue masses, and calcifications. Both normal findings and various abnormal findings are summarized, including signs of small bowel and large bowel obstruction, localized and generalized ileus, free air, and retroperitoneal air.