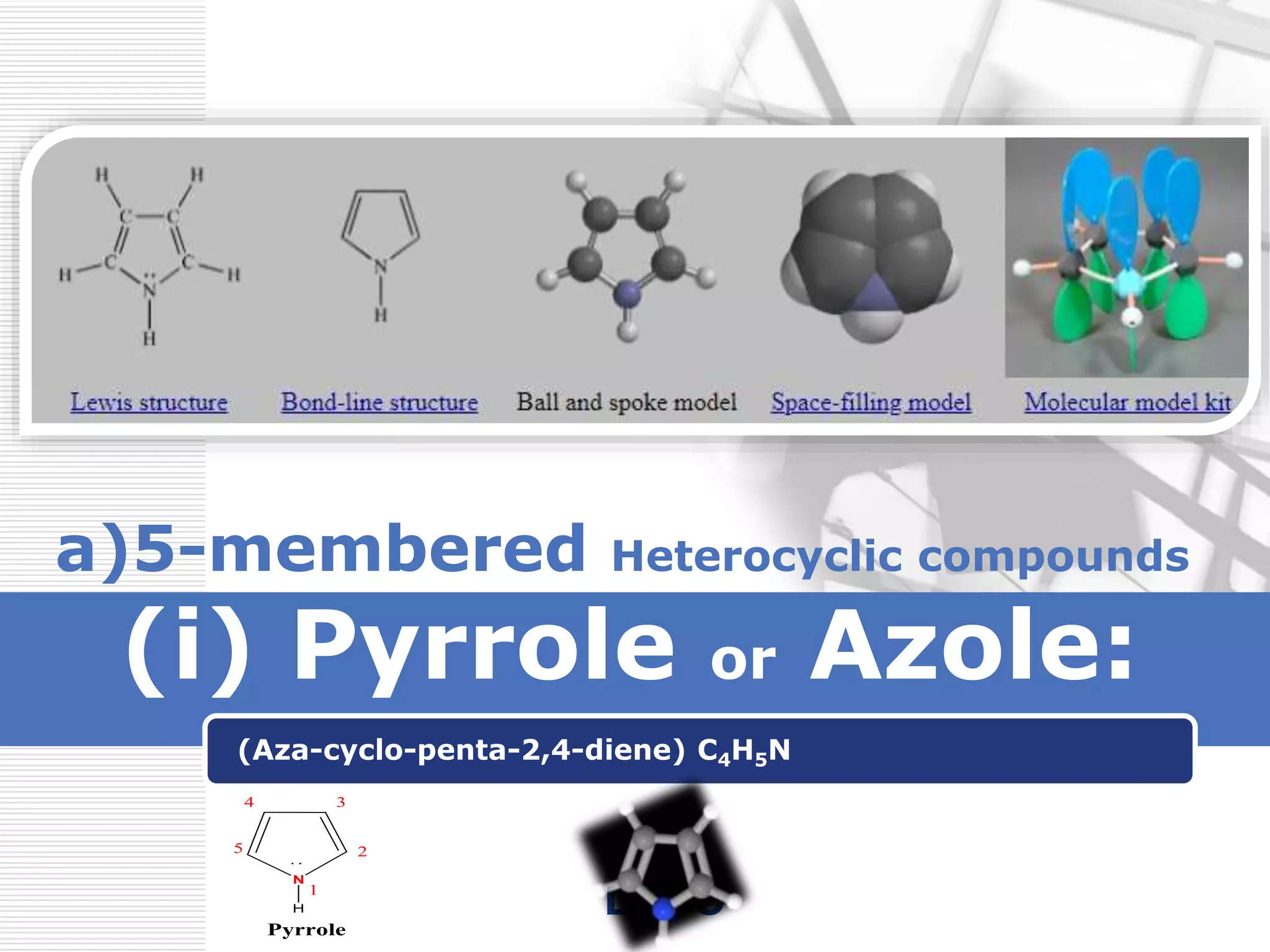
1. The document discusses the basic and acidic nature of the heterocyclic compound pyrrole.
2. Pyrrole acts as a weak base due to the lone pair on the nitrogen atom being involved in resonance within the aromatic pyrrole ring. This decreases the availability of the lone pair for donation.
3. Pyrrole also acts as a weak acid due to the N-H bond being weak as the nitrogen lone pair is delocalized through resonance. Proton removal forms a stabilized pyrryl anion through resonance delocalization of the negative charge.
















![Basic Nature (or Character) of Pyrrole:
When pyrrole is reacted with dil. HCl in absence of
oxygen (O2); to form crystalline salt, called as pyrrole
hydrochloride.
This reaction indicates pyrrole is a base.
C4H4NH + HCl [C4H4NH2] Cl
O2
N
H
O2
H Cl
N
H H
.. in absence of
Base Acid Pyrrole hydrochloride salt (Stable)
(Crystalline salt)
Or
+ in absence of
Acid
Pyrrole hydrochloride salt
Pyrrole
Base
....
Cl
Note:
Pyrrole hydrochloride is stable in absence of Oxygen, otherwise polymerization
rapidly occurs to produce a brown resin.
Any species that donates a pair of electrons to a Lewis acid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heterocycliccompoundspart-iiipyrrole-200910031153/75/Heterocyclic-compounds-part-III-Pyrrole-18-2048.jpg)











