Embed presentation
Downloaded 18 times
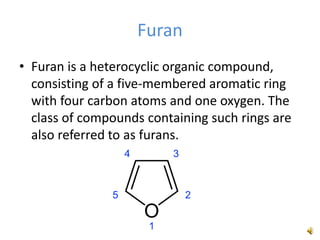


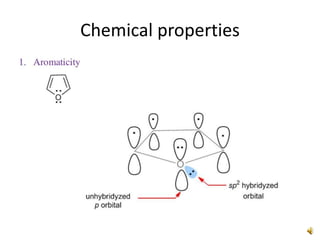
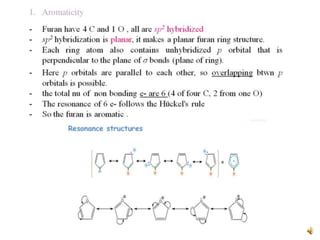

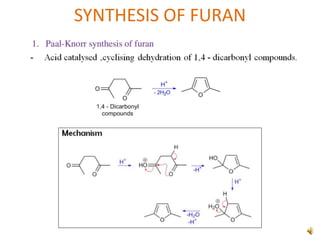
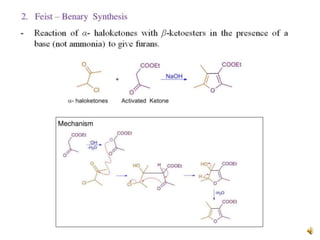

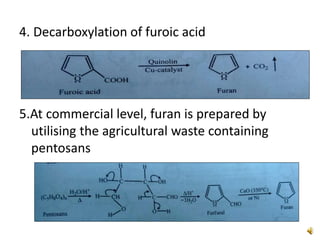
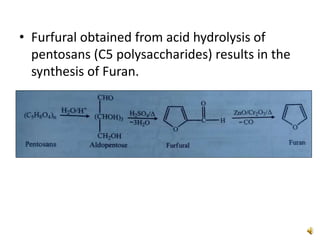
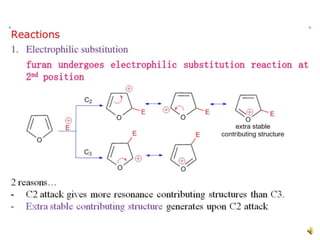
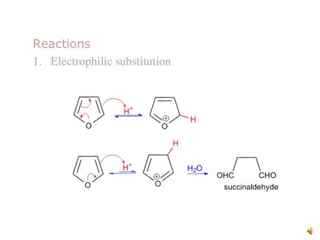
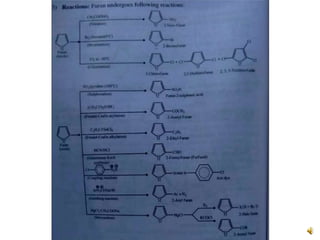
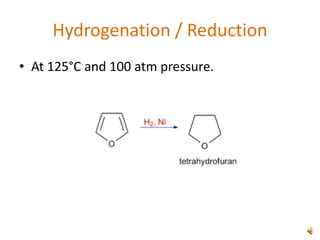
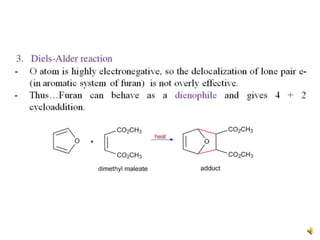
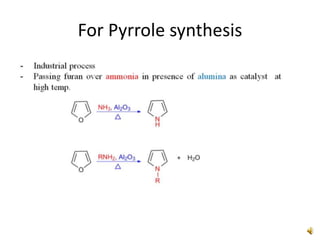
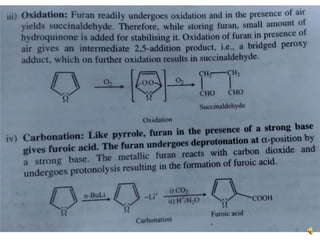

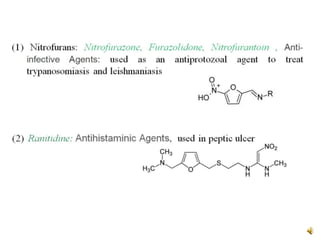
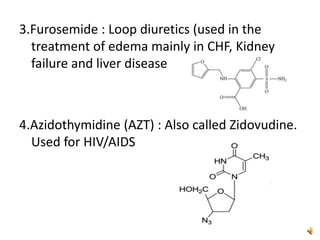
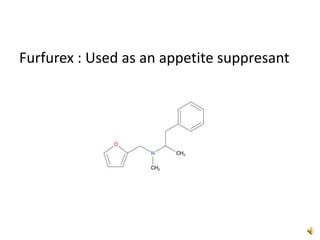

Furan is a colorless, flammable and volatile liquid with a five-membered aromatic ring containing four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. It melts at -85.6°C and boils at 31.3°C. Furan and its derivatives have a variety of medical uses, including as antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and diuretic agents. Commercially, furan is prepared by acid hydrolysis of pentosans from agricultural waste into furfural, which can then be reduced to furan.
























