Embed presentation
Download to read offline

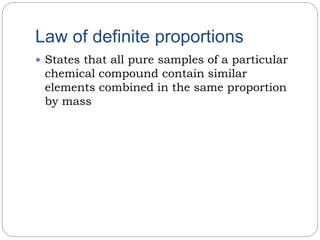
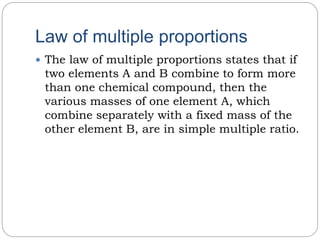
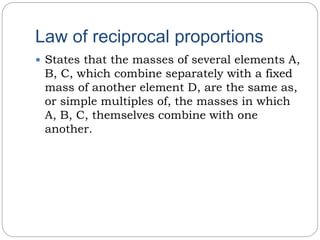


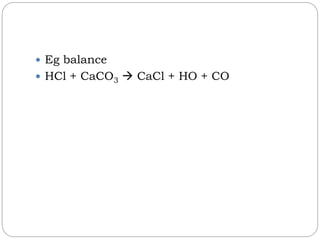


The document discusses several laws of chemical combinations and balancing chemical equations. It introduces the law of conservation of mass, law of definite proportions, law of multiple proportions, and law of reciprocal proportions. It also defines valency as the combining power of an element and discusses balancing chemical equations by ensuring the left and right sides match based on atom counts. An example calculation is provided to determine the mass of O2 needed to burn a given mass of sodium.









