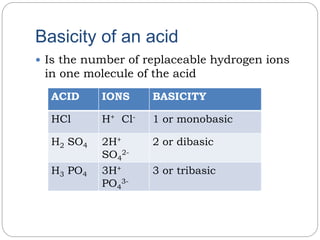
This document discusses acids and bases. It defines acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions in water and describes strong acids as completely ionizing and weak acids as partially ionizing. It discusses the basicity of acids based on the number of replaceable hydrogen ions. Acids have sour taste, turn litmus red, and are corrosive when concentrated. Acids react with metals and bases. Bases are substances that neutralize acids to form salts and water. The document also discusses alkalis, neutralization, properties of bases, pH scale, calculations involving concentrations and ions, and buffer solutions.