Embed presentation
Download to read offline



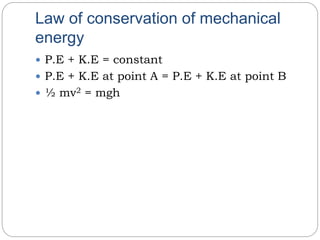
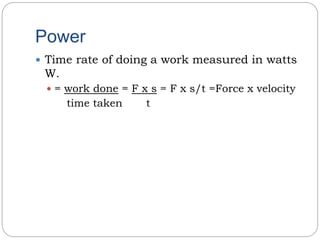
Work is done when a force moves an object through a distance in the direction of the force. Work (W) is equal to the product of the force (F) and distance (s) moved, or W=Fxs. Energy is the capacity to do work and is also measured in joules. The principle of conservation of energy states that in a closed system, the total amount of energy remains constant. Power is the time rate of doing work and is measured in watts. Power is equal to work done divided by the time taken, or W/t.





