Chapter2
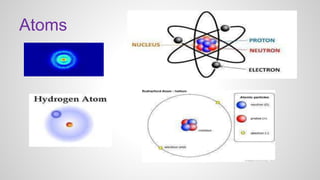
- 1. Atoms
- 2. Vocabulary ● Ion ● Valence Electrons ● Electron Orbitals ● Neutral Atom ● Chemical Bond ● Ionic Bond ● Covalent Bond ● Polar Covalent Bond ● Nonpolar Covalent Bond ● Polyatomic Ion ● Electronegativity ● Molecule ● Double Bond ● Triple Bond
- 6. All elements want to have a complete set of valence electrons; elements will react until they have a complete set. A complete set consists of eight electrons, this explains why Noble gases do not react. Helium is a Noble gas, even though its outer shell only has two electrons. Helium outer shell only accepts two electrons, therefore its set of valence electrons is complete; it will not react.
- 7. ***Pg 58 & 59
- 8. Ions Atoms may lose or gain electrons in order to have a complete outer shell. When an element loses an electron(-), it becomes positively charged. This is because it now has more protons (+) than electrons (-). Conversely, when an element gains an electron(-), it becomes negatively charged. This is because it now has more electrons (-) than protons (+) .
- 9. Valence Electrons & Ions The number of electrons lost, or gained, depends on the valence electrons of the element. (The outer shell) Sodium has one valence electron(outer shell), and the shell beneath has eight. If it loses the one valence electron, the shell underneath becomes the outer shell with eight electrons. The same concept applies to Magnesium. The difference is that Magnesium has two valence electrons.
- 10. Valence Electrons & Ions Nature is lazy… Chlorine Imagine you have to pay 1,000$ pesos to move each electron. Electron Store . . . . . . . . Calcium can: 1 move two away and leave the shell beneath with eight electrons, or (2) it can move six to itself. Option 1 - 2,000$ Option 2 - 6,000$ Option 1 - 7,000$ Chlorine can: (1) move seven away and leave the shell beneath with eight, or (2) it can move one to itself. Option 2 - 1,000$
- 11. Valence Electrons & Natural Ions Metals and transitional metals have a small number of valence electrons *Remember the group number tells you the number of valence electrons the element has. Metals lose electrons because they cannot “afford” to gain a large number of electrons. Calcium does not have enough protons to attract six electrons.
- 12. Valence Electrons & Natural Ions Nonmetals have a large number of valence electrons. Nonmetals tend to complete their outer shell by attracting electrons from other elements with their protons. *Remember the group number tells you the number of valence electrons the element has. Chlorine only needs one more electron to complete its outer shell.
- 13. Natural Ions Atoms may lose or gain electrons in order to have a complete outer shell. When an element loses an electron(-), it becomes positively charged. This is because it now has more protons (+) than electrons (-). Conversely, when an element gains an electron(-), it becomes negatively charged. This is because it now has more electrons (-) than protons (+) .
- 14. Valence Electrons & Natural Ions Atoms may lose or gain electrons in order to have a complete outer shell. In summary, the ion that an atom forms depends on its valence electrons *(Identifiable by the atoms group number). This will determine the type of bonds the atom will form.
- 16. ● Metal + Nonmetal ○ Na + Cl NaCl (Chemical Change? Pure Substance?) ■ Sodium (*Metal) losses an electron and become a cation Na+ ■ Calcium (Nonmetal) gains an election and becomes an anion Cl- ■ These changes allow both Na and Cl to have 8 electrons in their outermost shells Ionic Bonds
- 18. Draw Lewis Dot Structure CaF2 : BeF2 Natural Ions Be, F ? Draw the Lewis Dot Structure of the following Ionic Bonds:
- 19. Subscripts The subscripts following each element’s symbol represent how many atoms of that element are present in the molecule formed. In the molecule BeF2 , there is one Beryllium atom and two Fluorine atoms. You can determine the subscripts by exchanging them with the superscripts of the natural ions of the elements involved. Natural Ions Chemical Formula Be2+ F1- BeF2
- 20. Covalent Bonds When two neutral nonmetals share electrons they form a covalent bond. **NOT Ions In covalent bonds, atoms do not lose nor gain electrons; they share them in order to complete their valence electrons.
- 21. CH4 ClH NH3 Methane has four Hydrogen atoms, Hydrogen Chloride has one, and Ammonia has three. Why?? Elements rarely exist on their own; they normally have reacted with another element, sometimes with an identical atom. Only Noble Gases exist unbonded to another element. Why??
- 22. Subscripts The subscripts following each element’s symbol represent how many atoms of that element are present in the molecule formed. In the molecule H2O, there are two Hydrogen atoms and one Oxygen atom. You can determine the subscripts by exchanging them with the superscripts of the natural ions of the elements involved. Natural Ions Chemical Formula H1+ O-2 H2O
- 23. Polyatomic Ions A polyatomic ion is an ion formed with two or more atoms. When a covalent bond (Two or more Nonmetals) forms, and the resulting number of electrons and protons is not equal, an ion with two or more atoms is formed. (OH)- (CN)- (NH4)+
- 24. Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic Ion Hydroxide Cyanide Ammonium Protons (+) 6 (O) + 1 (H) = 7+ 4 (C ) + 1 (N) = 5+ 5(N) + 4 (H) = 9+ Electrons (-) 6(O) + 1 (H) + 1 (?) = 8- 4 (C ) + 5 (N) + 1 (?) = 10- 5(N) + 3 (H) = 8- Charge 1- 3- 1+ Once polyatomic ions have formed, they “act” as one atom and form ionic bonds with metals. **Ionic bonds with polyatomic ions work the same way as ionic bonds between metals and nonmetals.
- 26. Ionic Bonds with Polyatomic Ions K(NO3) Ca(OH)2 (NH4)2(CO3) I K+ Ca2+ (NH)+ 4O N (NO)- (OH)- (CO)2- S 33**Like “regular” ionic bonds, the number of atoms present and the combination in ionic bonds with polyatomic ions depends on the type of ion each atom and polyatomic molecule forms.
- 27. Ionic Bonds with Polyatomic Ions **Like “regular” ionic bonds, the number of atoms present and the combination in ionic bonds with polyatomic ions depends on the type of ion each atom and polyatomic molecule forms. In English…. Do these combinations equal 0?? 3+ 2- = 1+ 1+ 2- = 1- 4+ 1- = 3+ 1+ 1- = 0 2+ 1-x2 (2-) = 0 1+x 2(2+) 2- = 0 Atoms want to be happy. To be happy they need to be neutral, have no charge. They combine with other atoms until they are happy(have no charge). Atoms do not quit easily; they form complicated combinations as long as they can be happy.
- 28. Ionic Bonds with Polyatomic 1+ 1- = 0 2+ 1-x2 (2-) = 0 1+x 2(2+) 2- = 0 K+ (NO3)- = K(NO3) Ca2+ (OH)- = Ca(OH)2 (NH4)+ (CO3)2- = (NH4)2(CO3) Ions
- 29. Subscripts (Ionic Bonds with Polyatomic Ions) The subscripts following each element’s symbol represent how many atoms of that element are present in the molecule formed. In the molecule Ca(OH)2, there is one Calcium atom and two Hydroxide molecules. You can determine the subscripts by exchanging them with the superscripts of the ions of the atoms and molecules involved. Ions Chemical Formula Ca2+ (OH)-1 Ca(OH)2
