Embed presentation
Downloaded 49 times


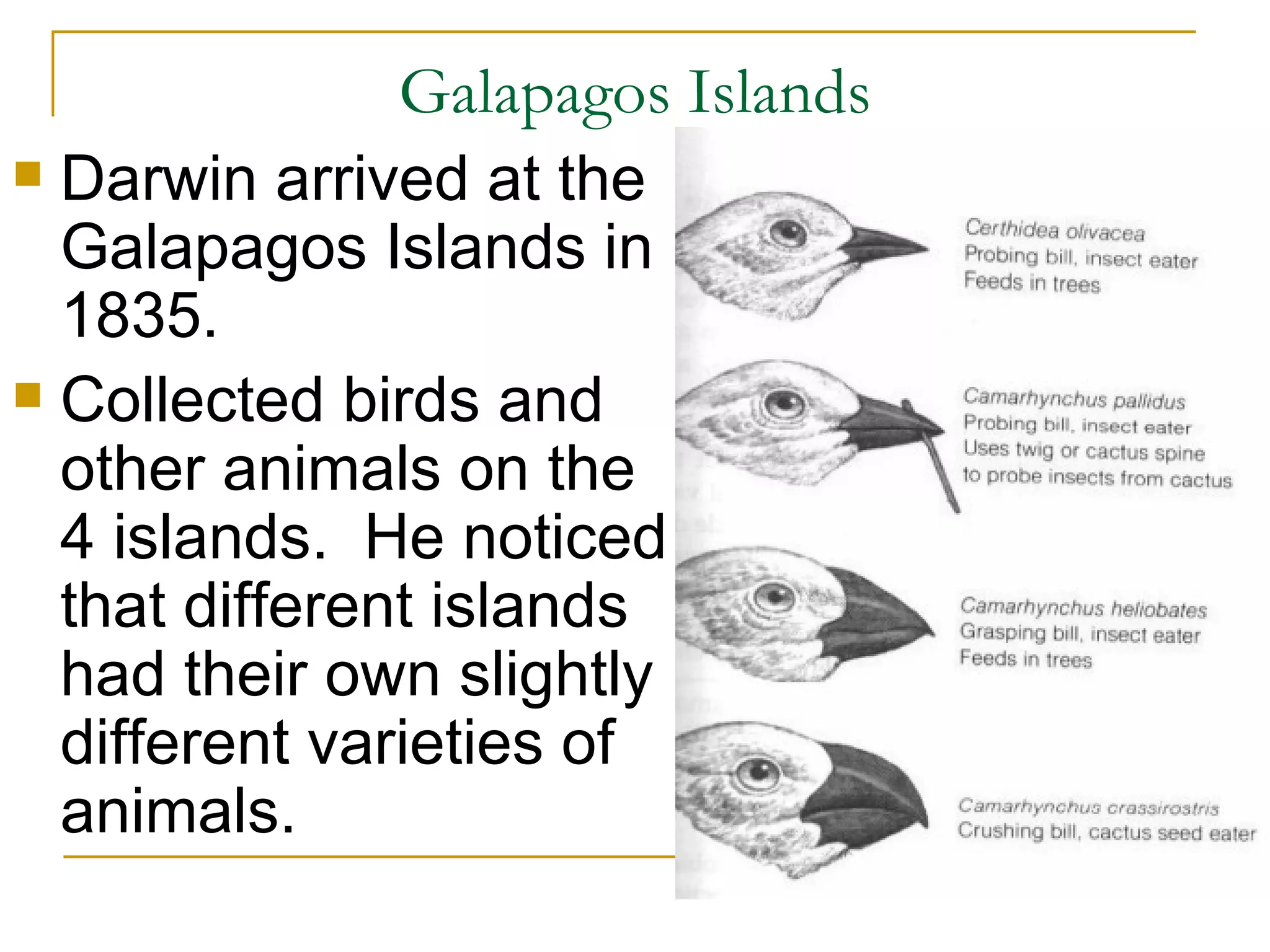


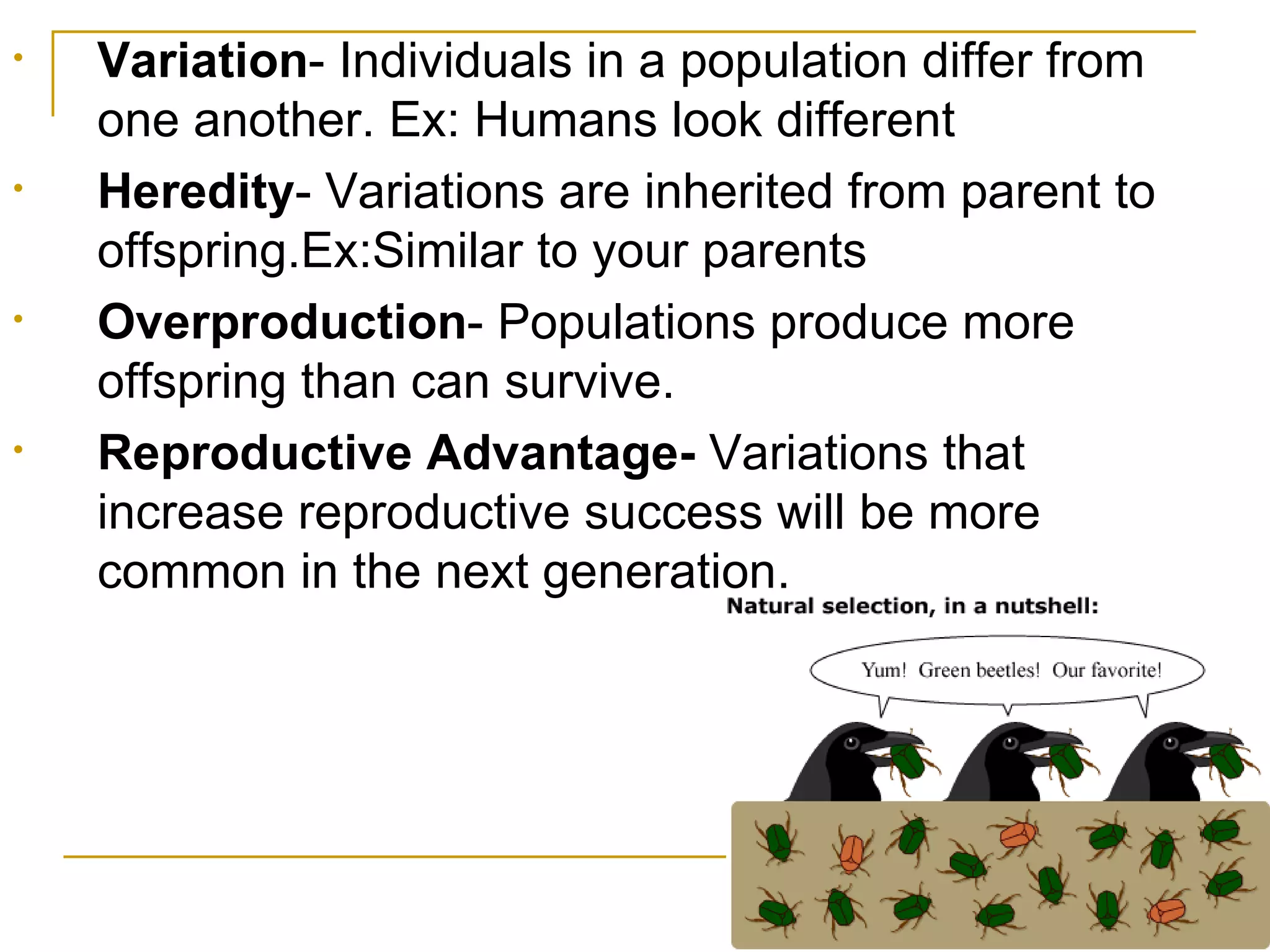

Charles Darwin developed the theory of evolution by natural selection based on his observations as a naturalist aboard the HMS Beagle in the 1830s. While visiting the Galapagos Islands, Darwin noticed that related but distinct animal species inhabited different islands. He later concluded that populations on the mainland evolved over generations as they adapted to their local environments, with better adapted traits being passed down. Darwin's theory proposed that natural selection drives evolution, as organisms better suited to their environment will survive and reproduce, passing on their favorable traits.






