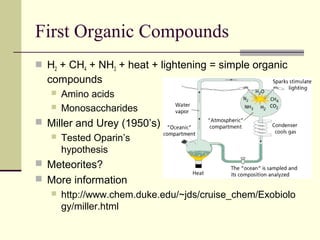
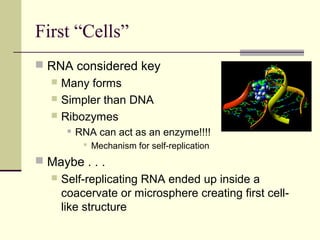
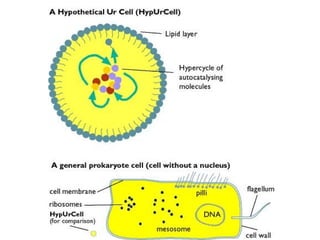
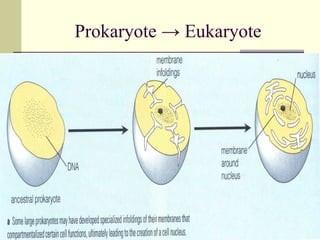
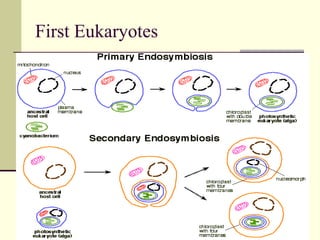
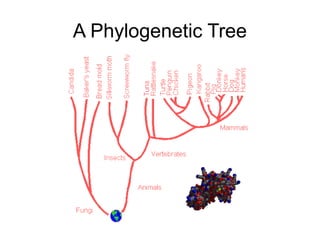
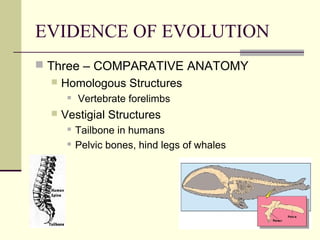
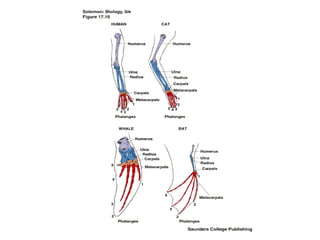
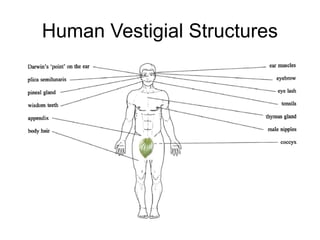
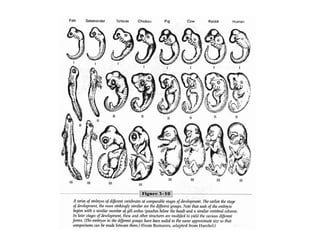
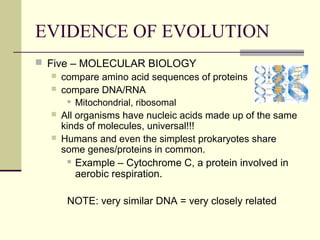
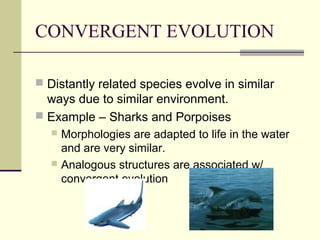
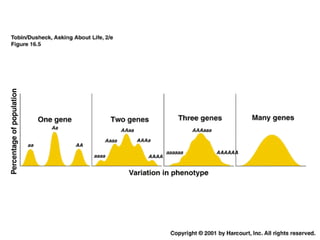
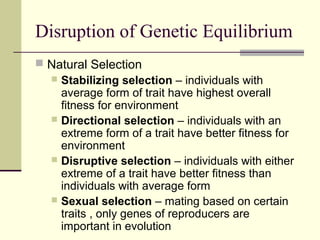
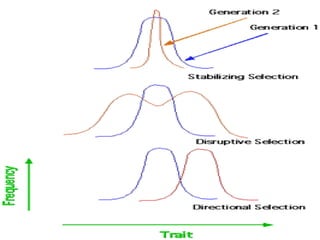
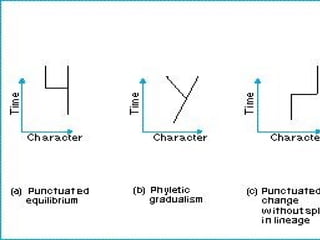
Evolution occurs through natural selection, where organisms better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and pass on their traits. The evidence for evolution includes fossils showing gradual changes over time, similarities in anatomy across species, and molecular comparisons showing closer genetic relatedness between more closely related organisms. Disruptions to genetic equilibrium such as mutations, genetic drift, and natural selection can drive evolutionary changes within populations over many generations.