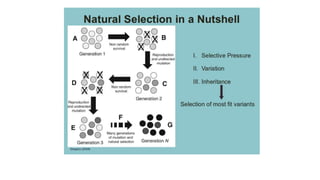
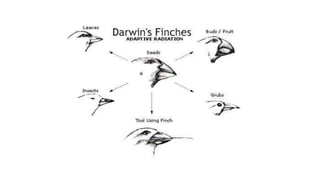
Charles Darwin developed the theory of evolution by natural selection after observing that species evolve over generations through natural processes. His theory proposed that species share common ancestors and that traits within a population become more or less common through natural selection as organisms with beneficial traits are more likely to survive and reproduce. The theory can explain how antibiotic resistance has developed in bacteria, as bacteria with genetic mutations that allow survival despite antibiotics will pass on those resistance traits.