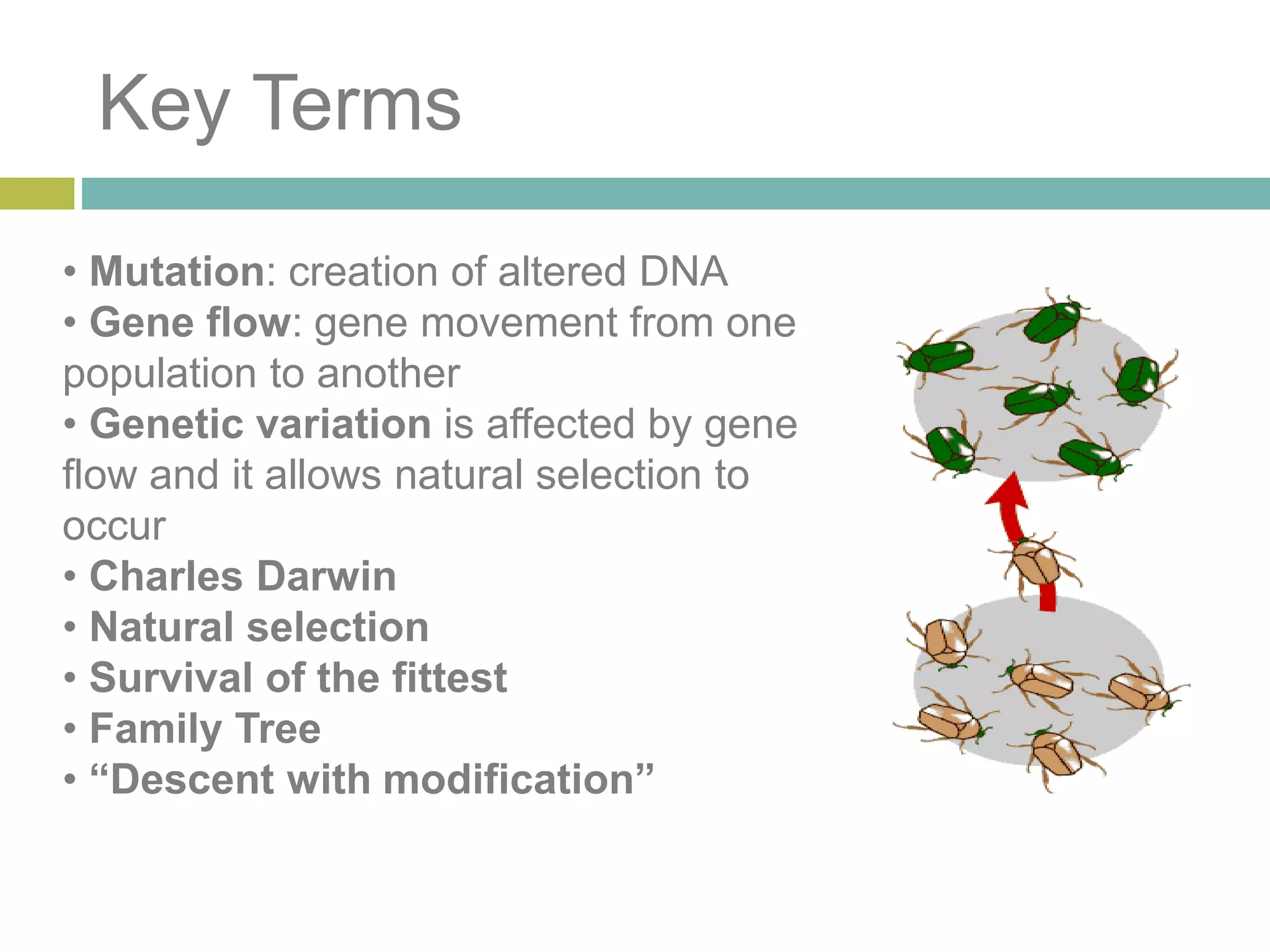
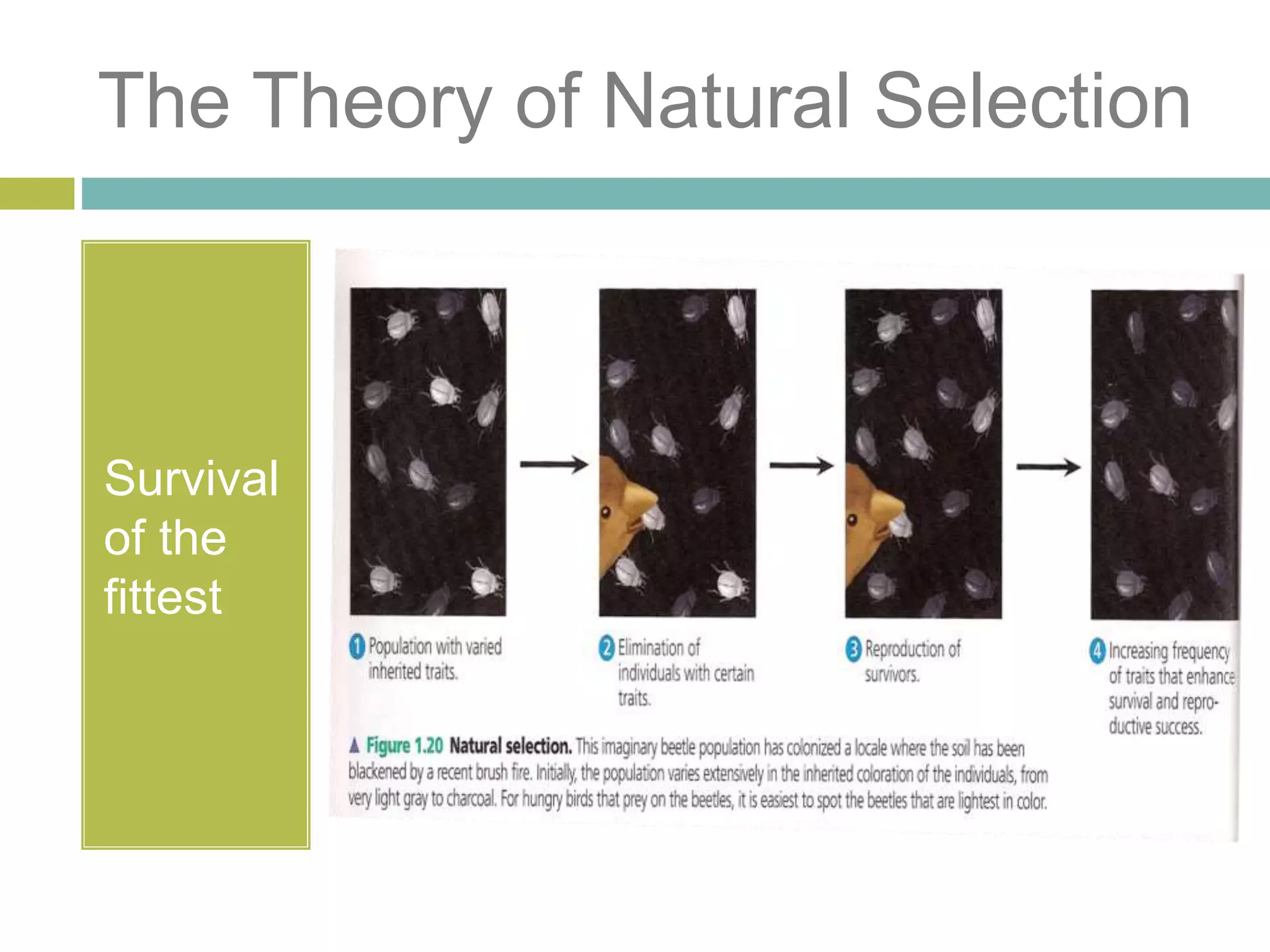
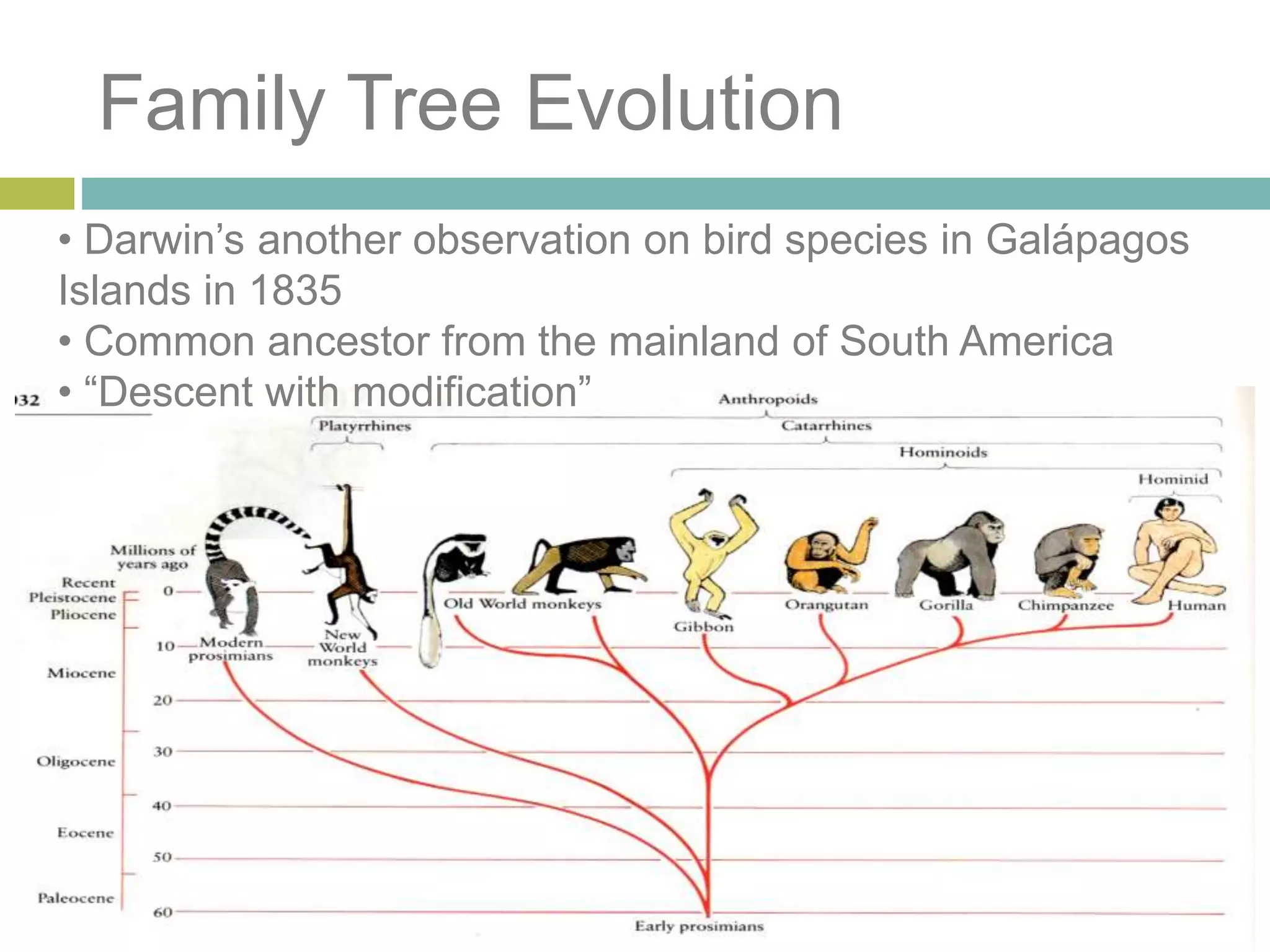
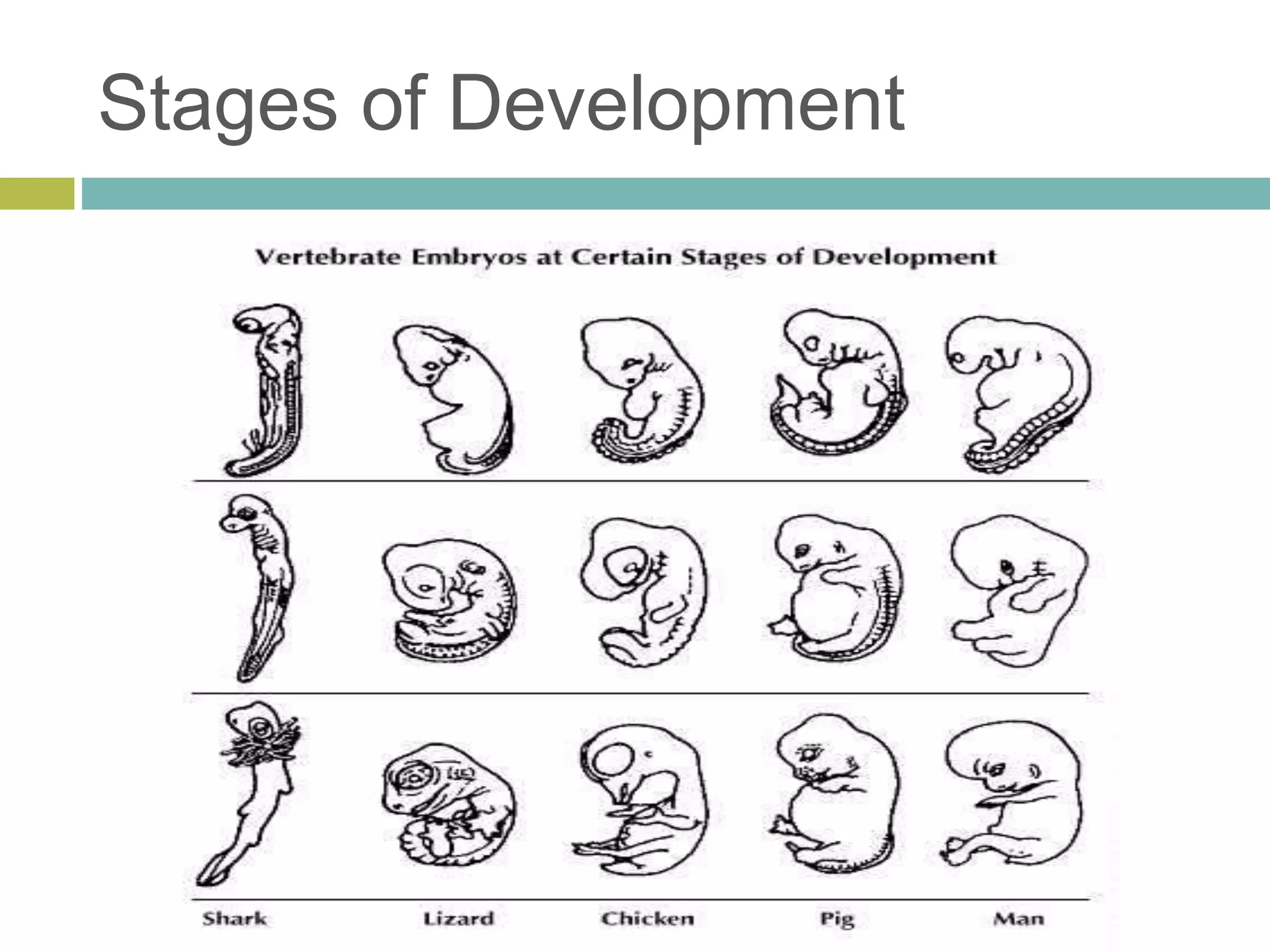
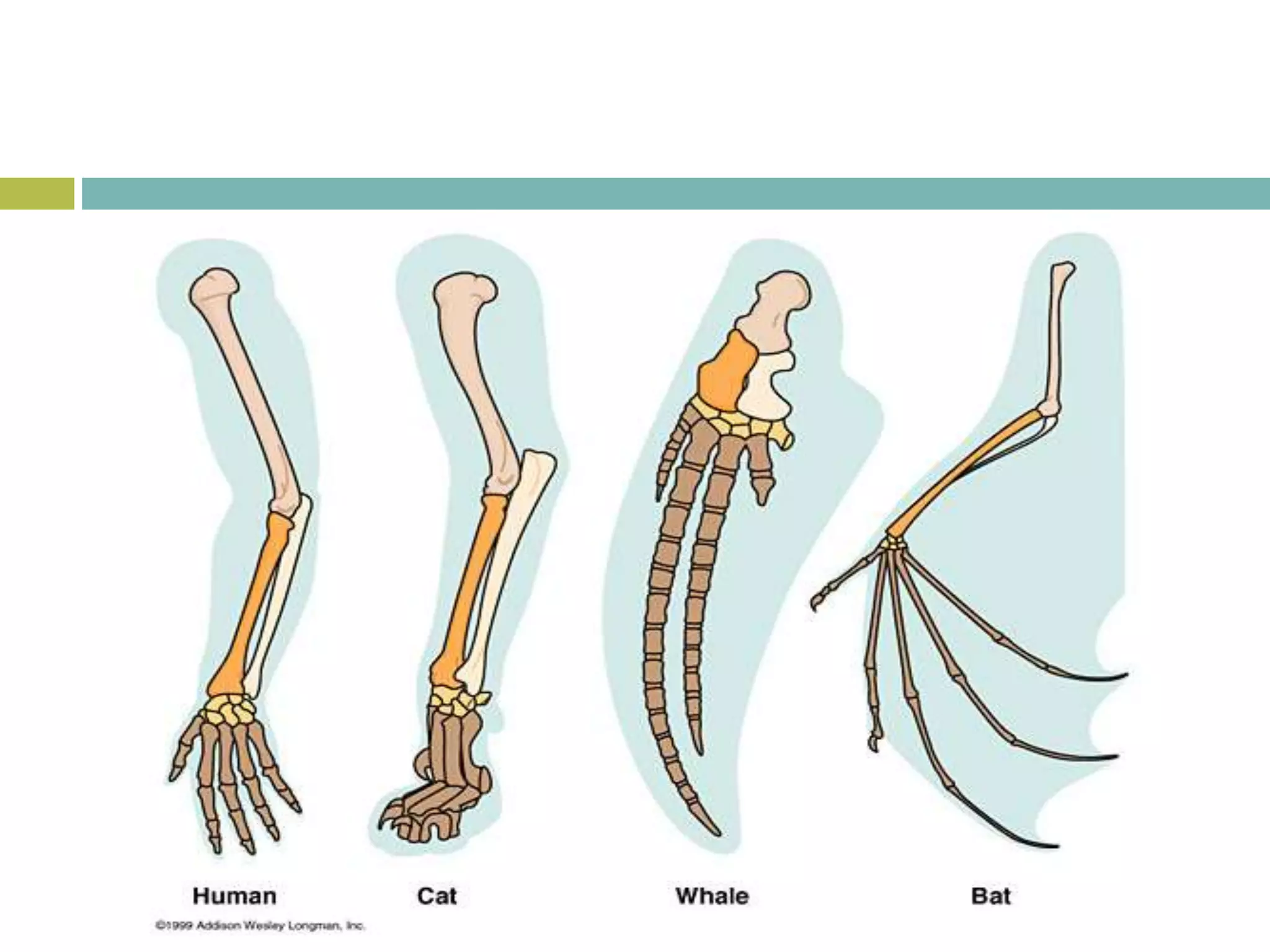
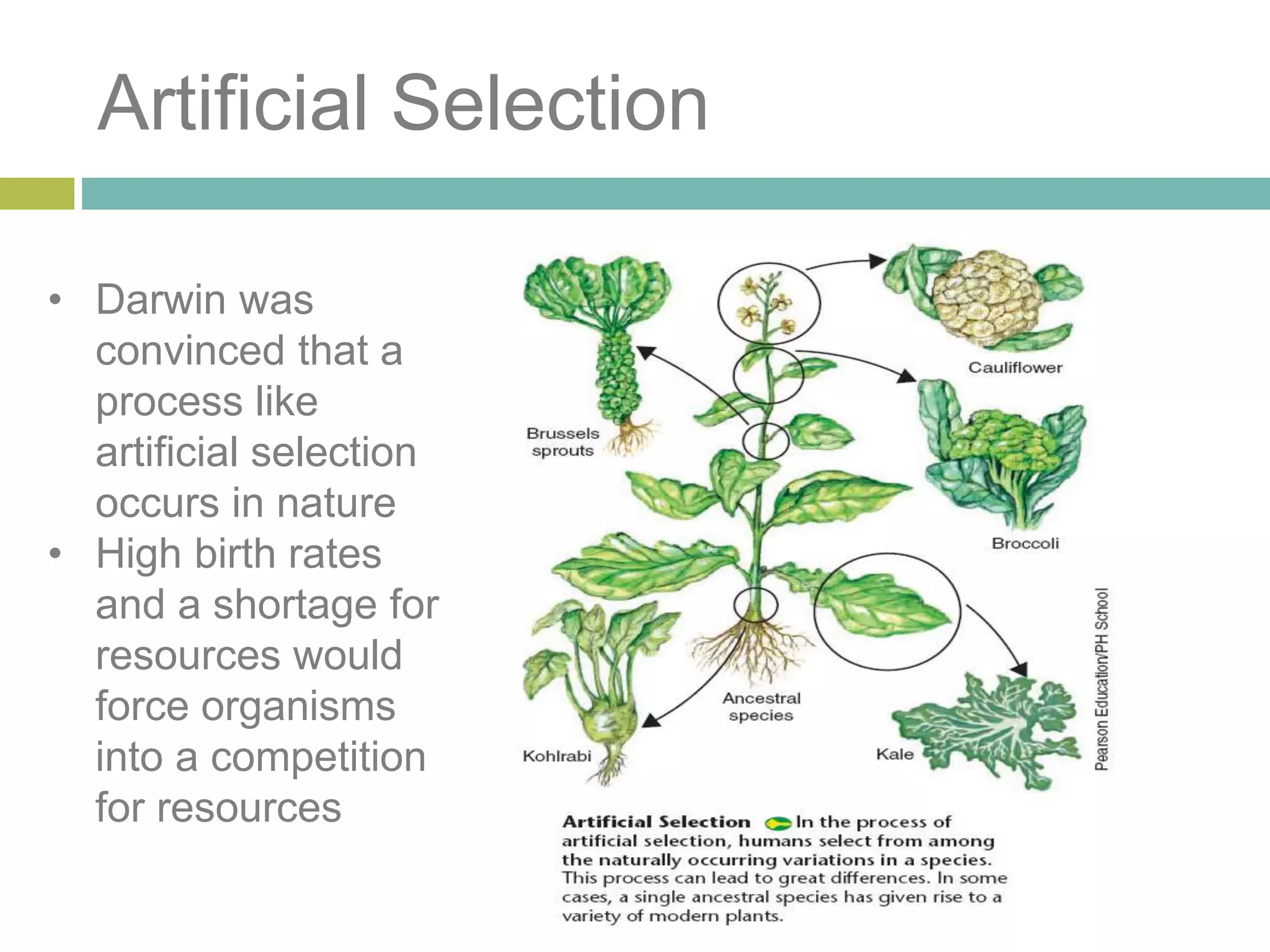
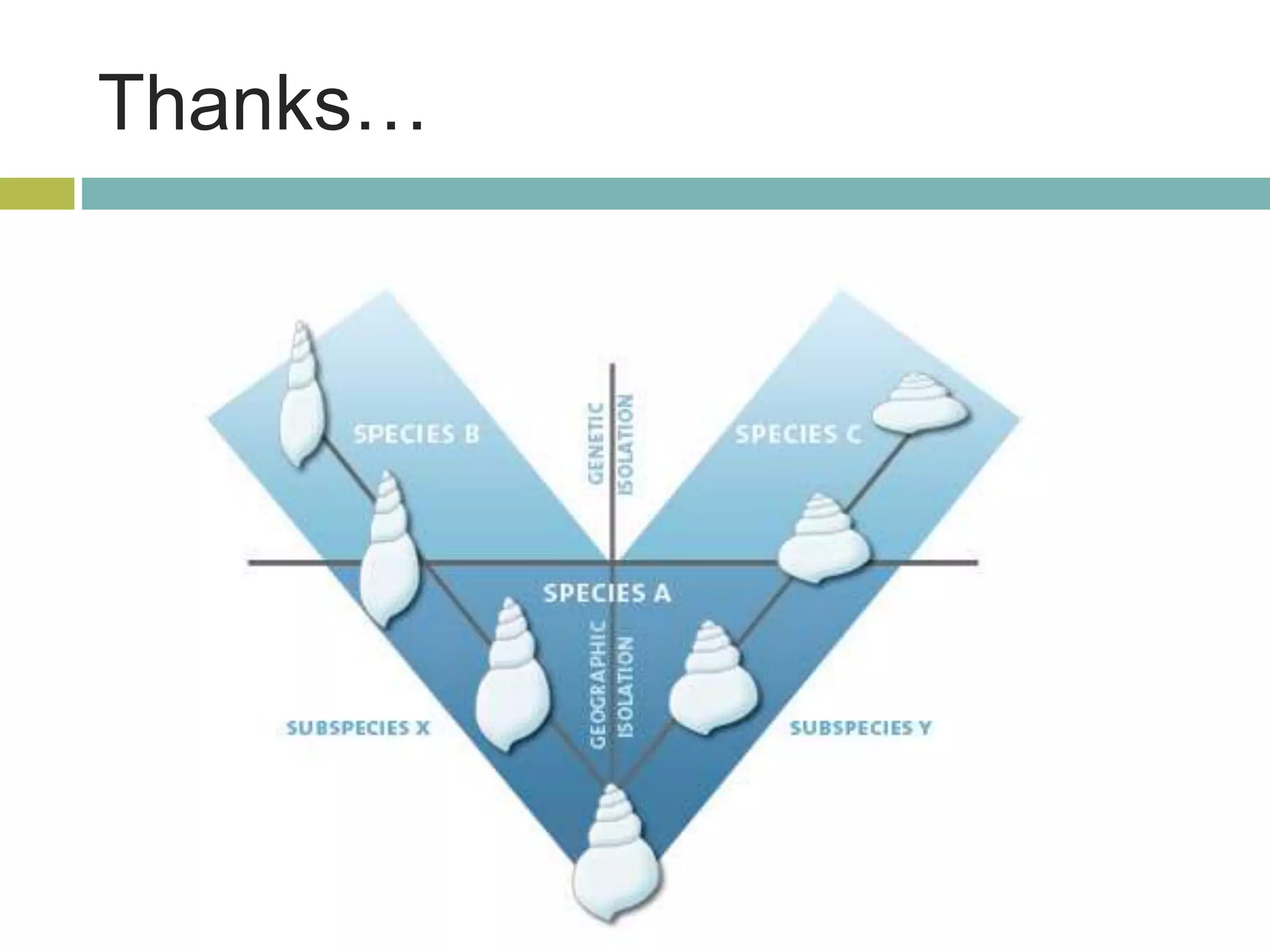
Charles Darwin developed the theory of evolution by natural selection. As a naturalist aboard the HMS Beagle, Darwin made observations and collected evidence that led him to propose that life evolves over generations through a process of natural selection, where organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and pass on their traits. Darwin believed that all species on Earth descended with modification from common ancestors over long periods of time. His theory challenged religious orthodoxy and provided a naturalistic explanation for the diversity and complexity of life.