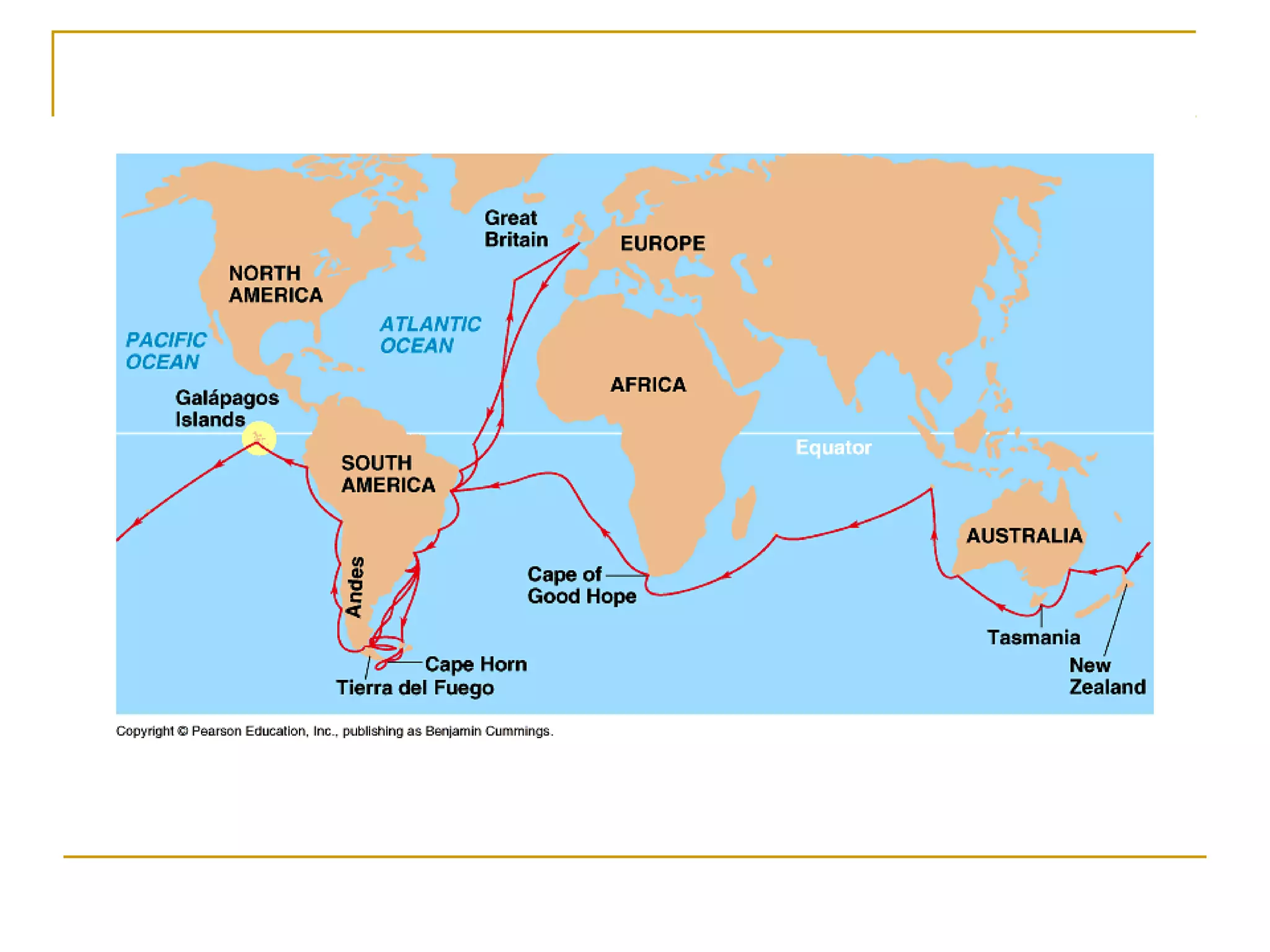
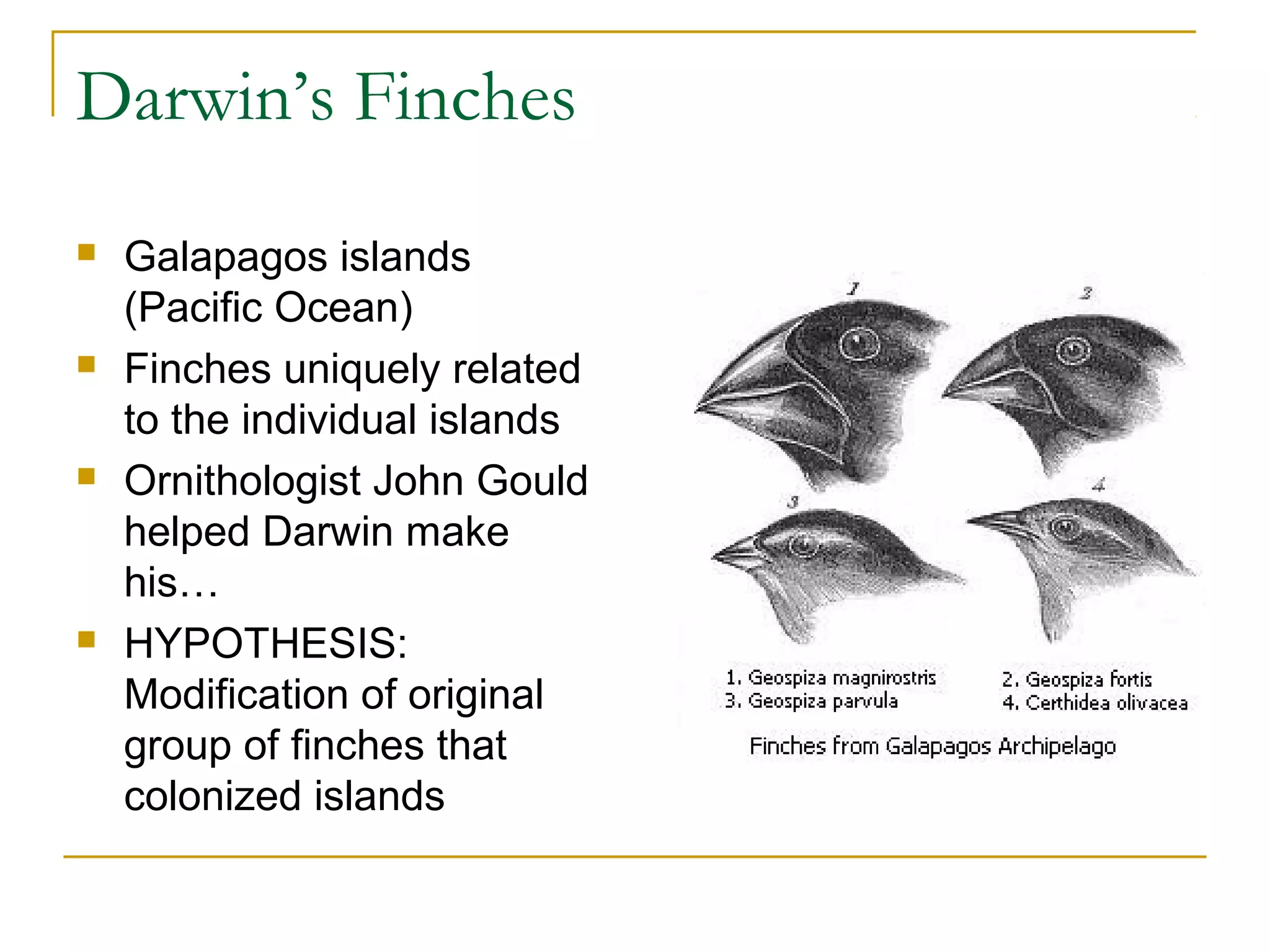
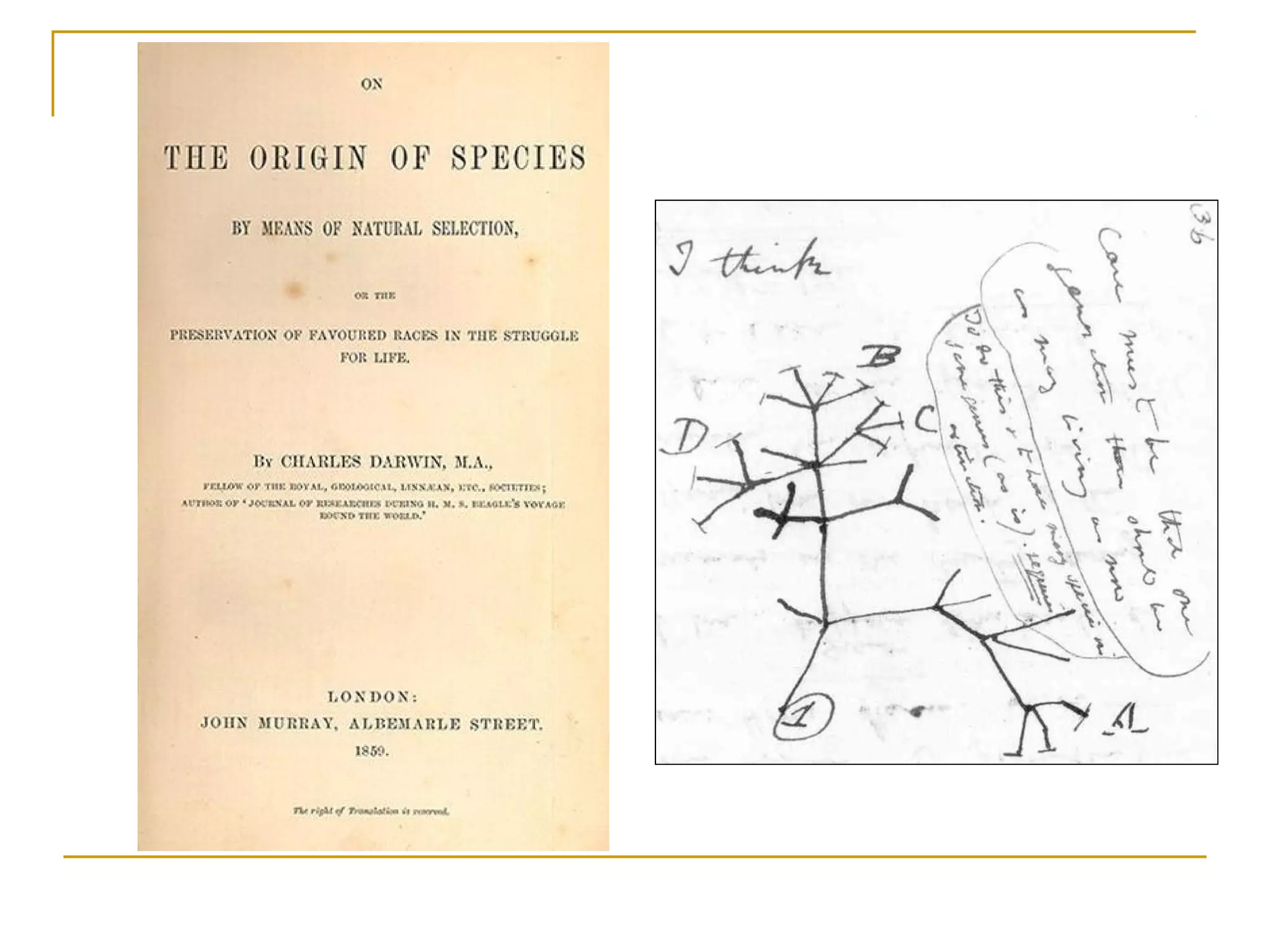
Charles Darwin developed the theory of evolution by natural selection based on observations from his voyage on the HMS Beagle. He noticed that finches on the Galapagos Islands had adaptations to the individual islands they inhabited. Darwin hypothesized that species slowly change over generations as beneficial genetic variations allow individuals to better survive and pass traits to offspring. His 1859 book On the Origin of Species explained how natural selection acts on genetic variation within populations to produce evolution, sparking scientific and religious controversy.